Abstract
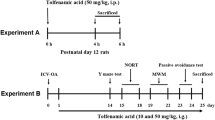
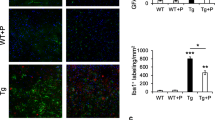
T-006, a small-molecule compound derived from tetramethylpyrazine (TMP), has potential for the treatment of neurological diseases. In order to investigate the effect of T-006 prophylactic treatment on an Alzheimer’s disease (AD) model and identify the target of T-006, we intragastrically administered T-006 (3 mg/kg) to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) transgenic mice (APP/PS1-2xTg and APP/PS1/Tau-3xTg) for 6 and 8 months, respectively. T-006 improved cognitive ability after long-term administration in two AD mouse models and targeted mitochondrial-related protein alpha-F1-ATP synthase (ATP5A). T-006 significantly reduced the expression of phosphorylated-tau, total tau, and APP while increasing the expression of synapse-associated proteins in 3xTg mice. In addition, T-006 modulated the JNK and mTOR-ULK1 pathways to reduce both p-tau and total tau levels. Our data suggested that T-006 mitigated cognitive decline primarily by reducing the p-tau and total tau levels in 3xTg mice, supporting further investigation into its development as a candidate drug for AD treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- APP:
-
Amyloid precursor protein
- NFTs:
-
Neurofibrillary tangles
- Aβ:
-
β-Amyloid
- 2xTg:
-
APP/PS1
- 3xTg:
-
APP/PS1/Tau
- PS1:
-
Presenilin 1
- ATP5A:
-
Alpha-F1-ATP synthase
- DARTS:
-
Drug affinity responsive target stability
- ATP synthase:
-
Complex V of electron transfer chain (ETC)
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- TMP:
-
Tetramethylpyrazine
- MWM:
-
Morris water maze
- NOR:
-
Novel object recognition
- SYP:
-
Synaptophysin
- PSD95:
-
Postsynaptic density protein 95
- i.g:
-
Intragastric administration
References
Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures (2020) Alzheimer’s & Dementia. Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association 16:391–460. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12068
Abrahams JP, Leslie AG, Lutter R, Walker JE (1994) Structure at 2.8 A resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria. Nature 370:621–628. https://doi.org/10.1038/370621a0
Ahmad A, Ali T, Park HY, Badshah H, Rehman SU, Kim MO (2017) Neuroprotective Effect of Fisetin Against Amyloid-Beta-Induced Cognitive/Synaptic Dysfunction Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegeneration in Adult Mice. Mol Neurobiol 54:2269–2285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9795-4
Alzheimer's A (2016) 2016 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association. 12:459–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2016.03.001
Augustinack JC, Schneider A, Mandelkow EM, Hyman BT (2002) Specific tau phosphorylation sites correlate with severity of neuronal cytopathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 103:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010100423
Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2007) Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:663–672. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2194
Banzhaf-Strathmann J et al (2014) MicroRNA-125b induces tau hyperphosphorylation and cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease. Embo j 33:1667–1680. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201387576
Boyer PD (1997) The ATP synthase—a splendid molecular machine. Annu Rev Biochem 66:717–749. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.66.1.717
Braithwaite SP et al (2010) Inhibition of c-Jun kinase provides neuroprotection in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 39:311–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2010.04.015
Brandeis R, Brandys Y, Yehuda S (1989) The use of the Morris Water Maze in the study of memory and learning. Int J Neurosci 48:29–69. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207458909002151
Caccamo A, Magri A, Medina DX, Wisely EV, Lopez-Aranda MF, Silva AJ, Oddo S (2013) mTOR regulates tau phosphorylation and degradation: implications for Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies. Aging Cell 12:370–380. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12057
Caceres A, Kosik KS (1990) Inhibition of neurite polarity by tau antisense oligonucleotides in primary cerebellar neurons. Nature 343:461–463. https://doi.org/10.1038/343461a0
Chen HY et al (2015) A Potent Multi-functional Derivative of Tetramethylpyrazine. J Mol Neurosci 56:977–987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0566-x
Cohen SJ, Stackman RW Jr (2015) Assessing rodent hippocampal involvement in the novel object recognition task A review. Behav Brain Res 285:105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.08.002
Corradi A, Zanardi A, Giacomini C, Onofri F, Valtorta F, Zoli M, Benfenati F (2008) Synapsin-I- and synapsin-II-null mice display an increased age-dependent cognitive impairment. J Cell Sci 121:3042–3051. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.035063
Deweerdt S (2011) Prevention: activity is the best medicine. Nature 475:S16–17 https://doi.org/10.1038/475S16a
Ebanks B, Ingram TL, Chakrabarti L (2020) ATP synthase and Alzheimer’s disease: putting a spin on the mitochondrial hypothesis. Aging 12:16647–16662. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103867
Fontana L, Partridge L, Longo VD (2010) Extending healthy life span—from yeast to humans. Science (New York, NY) 328:321–326. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1172539
Garber K (2012) Genentech’s Alzheimer’s antibody trial to study disease prevention. Nat Biotechnol 30:731–732. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0812-731
Goldberg J et al (2018) The mitochondrial ATP synthase is a shared drug target for aging and dementia. Aging cell 17. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12715
Jack CR Jr et al (2013) Tracking pathophysiological processes in Alzheimer’s disease: an updated hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers. Lancet Neurol 12:207–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(12)70291-0
Jack CR Jr et al (2010) Hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers of the Alzheimer’s pathological cascade. Lancet Neurol 9:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(09)70299-6
Jimenez S et al (2011) Age-dependent accumulation of soluble amyloid beta (Abeta) oligomers reverses the neuroprotective effect of soluble amyloid precursor protein-alpha (sAPP(alpha)) by modulating phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt-GSK-3beta pathway in Alzheimer mouse model. J Biol Chem 286:18414–18425. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.209718
Jin Y et al (2019) Tetramethylpyrazine Reduces Epileptogenesis Progression in Electrical Kindling Models by Modulating Hippocampal Excitatory Neurotransmission. ACS Chem Neurosci 10:4854–4863. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00575
Kameyama T, Nabeshima T, Kozawa T (1986) Step-down-type passive avoidance- and escape-learning method suitability for experimental amnesia models. J Pharmacol Methods 16:39–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/0160-5402(86)90027-6
Karran E, De Strooper B (2016) The amyloid cascade hypothesis: are we poised for success or failure? J Neurochem 139(Suppl 2):237–252. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13632
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B, Guan KL (2011) AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol 13:132–141. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2152
Kühlbrandt W, Davies KM (2016) Rotary ATPases: A New Twist to an Ancient Machine. Trends Biochem Sci 41:106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2015.10.006
Lamark T, Svenning S, Johansen T (2017) Regulation of selective autophagy: the p62/SQSTM1 paradigm. Essays Biochem 61:609–624. https://doi.org/10.1042/ebc20170035
Lin MG, Hurley JH (2016) Structure and function of the ULK1 complex in autophagy. Curr Opin Cell Biol 39:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2016.02.010
Liu F, Li B, Tung EJ, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Gong CX (2007) Site-specific effects of tau phosphorylation on its microtubule assembly activity and self-aggregation. Eur J Neurosci 26:3429–3436. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05955.x
Lomenick B et al (2009) Target identification using drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS) Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106:21984–21989. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0910040106
Lu C et al (2014) Neuroprotective effects of tetramethylpyrazine against dopaminergic neuron injury in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease induced by MPTP. Int J Biol 10:350–357. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.8366
Mangialasche F, Solomon A, Winblad B, Mecocci P, Kivipelto M (2010) Alzheimer’s disease: clinical trials and drug development. Lancet Neurol 9:702–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(10)70119-8
Mao X et al (2015) Schisandrin C ameliorates learning and memory deficits by Abeta1–42 -induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in mice. Phytother Res : PTR 29:1373–1380. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5390
Martin L, Latypova X, Terro F (2011) Post-translational modifications of tau protein: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 58:458–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2010.12.023
Mucke L, Selkoe DJ (2012) Neurotoxicity of amyloid β-protein: synaptic and network dysfunction. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a006338. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a006338
Nixon RA, Yang DS (2011) Autophagy failure in Alzheimer's disease—locating the primary defect. Neurobiol Dis 43:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2011.01.021
O’Brien RJ, Wong PC (2011) Amyloid precursor protein processing and Alzheimer’s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 34:185–204. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-061010-113613
Ploia C et al (2011) JNK plays a key role in tau hyperphosphorylation in Alzheimer’s disease models. J Alzheimer’s Dis 26:315–329. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-2011-110320
Prior M, Dargusch R, Ehren JL, Chiruta C, Schubert D (2013) The neurotrophic compound J147 reverses cognitive impairment in aged Alzheimer's disease mice. Alzheimers Res Ther 5:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/alzrt179
Selkoe DJ (2012) Preventing Alzheimer's disease. Science (New York, NY) 337:1488–1492. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1228541
Selkoe DJ (2019) Alzheimer disease and aducanumab: adjusting our approach. Nat Rev Neurol 15:365–366. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-019-0205-1
Sun J, Zhang X, Wang C, Teng Z, Li Y (2017) Curcumin decreases hyperphosphorylation of tau by down-regulating caveolin-1/GSK-3beta in N2a/APP695swe cells and APP/PS1 double transgenic Alzheimer's disease mice. Am J Chin Med 45:1667–1682. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X17500902
Sun X et al (2014) A mitochondrial ATP synthase subunit interacts with TOR signaling to modulate protein homeostasis and lifespan in Drosophila. Cell reports 8:1781–1792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.08.022
Tang Z et al (2013) Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTor) mediates tau protein dyshomeostasis: implication for Alzheimer disease. Int J Biol Chem 288:15556–15570. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.435123
Tracy TE, Gan L (2018) Tau-mediated synaptic and neuronal dysfunction in neurodegenerative disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 51:134–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2018.04.027
Tsai TH, Liang C (2001) Pharmacokinetics of tetramethylpyrazine in rat blood and brain using microdialysis. Int J Pharm 216:61–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-5173(01)00572-5
van der Kant R, Goldstein LSB, Ossenkoppele R (2020) Amyloid-β-independent regulators of tau pathology in Alzheimer disease Nature reviews. Neuroscience 21:21–35. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-019-0240-3
Wang C, Zhang X, Teng Z, Zhang T, Li Y (2014) Downregulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in curcumin-induced autophagy in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice. Eur J Pharmacol 740:312–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.06.051
Wang Y, Mandelkow E (2016) Tau in physiology and pathology Nature reviews. Neuroscience 17:5–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2015.1
Wimo A et al (2017) The worldwide costs of dementia 2015 and comparisons with 2010. Alzheimers Dement 13:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2016.07.150
Wu W, Yu X, Luo XP, Yang SH, Zheng D (2013) Tetramethylpyrazine protects against scopolamine-induced memory impairments in rats by reversing the cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway. Behav Brain Res 253:212–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2013.07.052
Xu D et al (2016) Neuroprotection against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity and induction of neurite outgrowth by T-006, a novel multifunctional derivative of tetramethylpyrazine in neuronal cell models. Neurochem Int 99:194–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2016.07.006
Zare-Shahabadi A, Masliah E, Johnson GV, Rezaei N (2015) Autophagy in Alzheimer’s disease. Rev Neurosci 26:385–395. https://doi.org/10.1515/revneuro-2014-0076
Zhang ZH et al (2017) Selenomethionine mitigates cognitive decline by targeting both tau hyperphosphorylation and autophagic clearance in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J Neurosci : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 37:2449–2462. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3229-16.2017
Zhou H et al (2019a) Tetramethylpyrazine analogue T-006 promotes the clearance of alpha-synuclein by enhancing proteasome activity in Parkinson's disease models. Neurotherapeutics : the journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics 16:1225–1236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-019-00759-8
Zhou H et al (2019b) Tetramethylpyrazine analogue T-006 exerts neuroprotective effects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced Parkinson's disease in vitro and in vivo. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8169125
Zhou Q et al (2015) Inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation reverses Alzheimer disease phenotypes in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice. Ann Neurol 77:637–654. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24361
Zhou XW et al (2006) Assessments of the accumulation severities of amyloid beta-protein and hyperphosphorylated tau in the medial temporal cortex of control and Alzheimer’s brains. Neurobiol Dis 22:657–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2006.01.006
Acknowledgments
We thank Linda Wang for editing this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by grants from the Natural Science Fund of China (81803512, 81872842, 31861163001 and U1801287) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2018A030310562). We would also like to thank Ms. Linda Wang for editing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guiliang Zhang, Jiahui Wu, Zhiyang Su, Chunhui Huang, Jiehong Cheng, and Zeyu Zhu: development or design of methodology, data curation; Guiliang Zhang and Haiyun Chen: writing—original draft preparation; Xifei Yang, Baojian Guo, Liangmiao Wu, Zaijun Zhang, Gaoxiao Zhang, Haiyun Chen, Yewei Sun and Yuqiang Wang: investigation; Xifei Yang, Baojian Guo, Liangmiao Wu, Zaijun Zhang and Yuqiang Wang: investigation and supervision; Haiyun Chen, Yewei Sun, Zaijun Zhang and Yuqiang Wang: supervision, writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
All animal experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines of the Laboratory Animal Care and Use Ethics Committee of the Shenzhen Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Wu, J., Huang, C. et al. The Tetramethylpyrazine Analogue T-006 Alleviates Cognitive Deficits by Inhibition of Tau Expression and Phosphorylation in Transgenic Mice Modeling Alzheimer’s Disease. J Mol Neurosci 71, 1456–1466 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01762-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01762-x