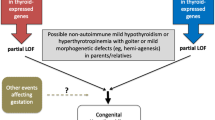
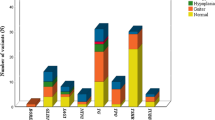
Abstract
Purpose
Congenital primary hypothyroidism (CH) is a state of inadequate thyroid hormone production detected at birth, caused either by absent, underdeveloped or ectopic thyroid gland (dysgenesis), or by defected thyroid hormone biosynthesis (dyshormonogenesis). A genetic component has been identified in many cases of CH. This review summarizes the clinical and biochemical features of the genetic causes of primary CH.
Methods
A literature review was conducted of gene defects causing congenital hypothyroidism.
Results
Mutations in five genes have predominantly been implicated in thyroid dysgenesis (TSHR, FOXE1, NKX2-1, PAX8, and NKX2-5), the primary cause of CH (85%), and mutations in seven genes in thyroid dyshormonogenesis (SLC5A5, TPO, DUOX2, DUOXA2, SLC6A4, Tg, and DEHAL1). These genes encode for proteins that regulate genes expressed during the differentiation of the thyroid, such as TPO and Tg genes, or genes that regulate iodide organification, thyroglobulin synthesis, iodide transport, and iodotyrosine deiodination. Besides thyroid dysgenesis and dyshormonogenesis, additional causes of congenital hypothyroidism, such as iodothyronine transporter defects and resistance to thyroid hormones, have also been associated with genetic mutations.
Conclusion
The identification of the underlying genetic defects of CH is important for genetic counseling of families with an affected member, for identifying additional clinical characteristics or the risk for thyroid neoplasia and for diagnostic and management purposes.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Toublanc J (1992) Comparison of epidemiological data on congenital hypothyroidism in Europe with those of other parts of the world. Horm Res (Basel) 38:230–235
Rastogi MV, LaFranchi SH (2010) Congenital hypothyroidism. Orphanet J Rare Dis 5:17
Lorey FW, Cunningham GC (1992) Birth prevalence of primary congenital hypothyroidism by sex and ethnicity. Hum Biol 64:531–538
Cao XY, Jiang XM, Dou ZH, Rakeman MA, Zhang ML, O’Donnell K, Ma T, Amette K, DeLong N, DeLong GR (1994) Timing of vulnerability of the brain to iodine deficiency in endemic cretinism. N Engl J Med 331:1739–1744
Rovet J, Ehrlich R (1995) Long-term effects of L-thyroxine treatment for congental hypothyroidism. J Pediatr 126:380–386
Grant DB, Smith I, Fuggle PW, Tokar S, Chapple J (1992) Congenital hypothyroidism detected by neonatal screening: relationship between biochemical severity and early clinical features. Arch Dis Child 67:87–90
Castanet M, Polak M, Bonaiti-Pellie C, Lyonnet S, Czernickow P, Leger J (2001) Nineteen years of national screening for congenital hypothyroidism: familial cases with thyroid dysgenesis suggest the involvement of genetic factors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:2009–2014
Nilsson M, Fagman H (2017) Development of the thyroid gland. Development. 144:2123–2140
Deladoey J, Vassart G, Van Vliet G (2007) Possible non-Mendelian mechanisms of thyroid dysgenesis. Endocr Dev 10:29–42
Park SM, Chatterjee VK (2005) Genetics of congenital hypothyroidism. J Med Genet 42:379–389
Field JB, Ealey PA, Marshall NJ, Cockcroft S (1987) Thyroid-stimulating hormone stimulates increases in inositol phosphates as well as cyclic AMP in the FRTL-5 rat thyroid cell line. Biochem J 247:519–524
Sunthornthepvarakul T, Gootschalk ME, Hayashi Y, Refetoff S (1995) Resistance to thyrotropin caused by mutations in the thyrotropin-receptor gene. N Engl J Med 332:155–160
De Roux N, Misrahi M, Brauner R, Houang M, Carel JC, Granier M, Le Bouc Y, Ghinea N, Boumeddienne A, Toublanc JE, Milgrom E (1996) Four families with loss of function mutations of the thyrotropin receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:4229–4235
Russo D, Betterle C, Arturi F, Chiefari E, Girelli ME, Filetti S (2000) A novel mutation in the thyrotropin (TSH) receptor gene causing loss of TSH binding but constitutive receptor activation in a family with resistance to TSH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:4238–4242
Nagashima T, Murakami M, Onigata K, Morimura T, Nagashima K, Mori M, Morikawa A (2001) Novel inactivating missense mutations in the thyrotropin receptor gene in Japanese children with resistance to thyrotropin. Thyroid 11:551–559
Tonacchera M, Agretti P, De Marco G, Perri A, Pinchera A, Vitti P, Chiovato L (2001) Thyroid resistance to TSH complicated by autoimmune thyroiditis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:4543–4546
Zannini M, Avantaggiato V, Biffali E, Arnone MI, Sato K, Pischetola M, Taylor BA, Phillips SJ, Simeone A, Di Lauro R (1997) TTF-2, a new forkhead protein, shows a temporal expression in the developing thyroid which is consistent with a role in controlling the onset of differentiation. EMBO J 16:3185–3197
Civitreale D, Lonigro R, Sinclair AJ, Di Lauro R (1989) A thyroid-specific nuclear protein essential for tissue-specific expression of the thyroglobulin promoter. EMBO J 8:2537–2542
Santisteban P, Acebron A, Polycarpou-Schwarz M, Di Lauro R (1992) Insulin and insulin- like growth factor I regulate a thyroid-specific nuclear protein that binds to the thyroglobulin promoter. Mol Endocrinol 6:1310–1317
Clifton-Bligh RJ, Wentworth JM, Heinz P, Crisp M, John R, Lazarus JH, Ludgate M, Chatterjee VKK (1998) Mutation of the gene encoding human TTF-2 associated with thyroid agenesis, cleft palate and choanal atresia. Nat Genet 19:399–401
Bamforth JS, Hughes IA, Lazarus JH, Weaver CM, Harper PS (1989) Congenital hypothyroidism, spiky hair, and cleft palate. J Med Genet 26:49–60
Francis-Lang H, Price M, Polycarpou-Schwartz M, Di Lauro R (1992) Cell-typespecific expression of the rat thyroperoxidase promoter indicates common mechanisms for thyroid-specific gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 12:576–588
Harvey RP (1996) NK-2 homeobox genes and heart development. Dev Biol 187:203–216
Lazzaro D, Price M, de Felice M, Di Lauro R (1991) The transcription factor TTF-1 is expressed at the onset of thyroid and lung morphogenesis and in restricted regions of the foetal brain. Development 113:1093–1104
Devriendt K, Vanhole C, Matthijs G, de Zegher F (1998) Deletion of the thyroid transcription factor-1 gene in an infant with neonatal thyroid dysfunction and respiratory failure. N Engl J Med 338:1317–1318
Doyle DA, Gonzalez I, Thomas B, Scavina M (2004) Autosomal dominant transmission of congenital hypothyroidism, neonatal respiratory distress, and ataxia caused by a mutation of NKX2–1. J Pediatr 145:190–193
Pohlenz J, Dumitrescu A, Zundel D, Martine U, Schonberger W, Koo E, Weiss RE, Cohen RN, Kimura S, Refetoff S (2002) Partial deficiency of thyroid transcription factor 1 produces predominantly neurological defects in humans and mice. J Clin Invest 109:469–473
di Magliano MP, Di Lauro R, Zannini M (2000) PAX8 has a key role in thyroid cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:13144–13149
Fraizer GC, Shimamura R, Zhang X, Saubders GF (1997) PAX8 regulates human WT1 transcription through a novel DNA binding site. J Biol Chem 272:30678–30687
van Engelen K, Mommersteeg MTM, Baars MJH, Lam J, Ilgun A, van Trotsenburg ASP, Smets AMJ, Christoffels VM, Mulder BJM, Postma AV (2012) The ambiguous role of NKX2-5 mutations in thyroid dysgenesis. PLoS One 7:e52685
Carvalho DP, Dupuy C (2013) Role of the NADPH oxidases DUOX and NOX4 in thyroid oxidative stress. Eur Thyroid J 2:160–167
Grasberger H (2010) Defects of thyroidal hydrogen peroxide generation in congenital hypothyroidism. Mol Cell Endocrinol 322(1–2):99–106
Desai MP (2012) Congenital hypothyroidism: screening dilemma. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 16:153–155
Lichti-Kaiser K, ZeRuth G, Jetten AM (2014) Transcription factor gli-similar 3 (Glis3): implications for the development of congenital hypothyroidism. J Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2:1024
de Filippis T, Gelmini G, Paraboschi E et al (2017) A frequent oligogenic involvement in congenital hypothyroidism. Hum Mol Genet 26:2507–2514
Dimitri P (2017) The role of GLIS3 in thyroid disease as part of a multisystem disorder. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 31:175–182
Patel SR, Richardson JL, Schulze H, Kahle E, Galjart N, Drabek K, Shivdasani RA, Hartwig JH, Italiano JE Jr (2015) Differential roles of microtubule assembly and sliding in proplatelet formation by megakaryocytes. Blood 106:4076–4085
Stoupa A, Adam F, Kariyawasam D et al (2018) TUBB1 mutations cause thyroid dysgenesis associated with abnormal platelet physiology. EMBO Mol Med 10:e9569
Carré A, Stoupa A, Kariyawasam D et al (2017) Mutations in BOREALIN cause thyroid dysgenesis. Hum Mol Genet 26:599–610
Peters C, van Trotsenburg ASP, Schoenmakers N (2018) DIAGNOSIS OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: congenital hypothyroidism: update and perspectives. Eur J Endocrinol 179:297–317
de Filippis T, Marelli F, Nebbia G et al (2016) JAG1 loss-of-function variations as a novel predisposing event in the pathogenesis of congenital thyroid defects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101:861–870
Opitz R, Hitz M-P, Vandernoot I et al (2015) Functional zebrafish studies based on human genotyping point to Netrin-1 as a link between aberrant cardiovascular development and thyroid dysgenesis. Endocrinology 156:377–388
Puppin C, Presta I, D'Elia AV et al (2004) Functional interaction among thyroid-specific transcription factors: Pax8 regulates the activity of hex promoter. Mol Cell Endocrinol 214:117–125
Puppin C, D'Elia AV, Pellizzari L et al (2003) Thyroid-specific transcription factors control hex promoter activity. Nucleic Acids Res 31:1845–1852
Barbera JPM, Clements M, Thomas P et al (2000) The homeobox gene hex is required in definitive endodermal tissues for normal forebrain, liver and thyroid formation. Development 127:2433–2445
Parlato R, Rosica A, Rodriguez-Mallon A et al (2004) An integrated regulatory network controlling survival and migration in thyroid organogenesis. Dev Biol 276:464–475
Ferretti E, Tosi E, Po A et al (2008) Notch signaling is involved in expression of Thyrocyte differentiation markers and is Down-regulated in thyroid tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:4080–4087
Carre A, Rachdi L, Tron E et al (2011) Hes1 is required for appropriate morphogenesis and differentiation during mouse thyroid gland development. PLoS One 6:e16752
Manley NR, Capecchi MR (1995) The role of Hoxa-3 in mouse thymus and thyroid development. Development 121:1989–2003
Xu P-X, Zheng W, Laclef C et al (2002) Eya1 is required for the morphogen- esis of mammalian thymus, parathyroid and thyroid. Development 129:3033–3044
Kopp P (2013) Thyroid hormone synthesis. In: Braverman LE, Cooper D (eds) Werner and Ingbar’s the thyroid. A fundamental and clinical text, ed, vol 10. Lippincottt Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 48–74
de Vijlder JJM, Vulsma T (1996) Hereditary metabolic disorders causing hypothyroidism. In: Braverman LE, Utiger RD (eds) Werner and Ingbar’s the thyroid, 7th edn. Lippincott-Raven p, Philadelphia, pp 749–755
Mangkalbruks A, Correa Billerbeck A-E, Wajchenberg B, Knobel M, Cox NJ, DeGroot LJ, Medeiros-Neto G (1991) Genetic linkage studies of thyroid peroxidase (TPO) gene in families with TPO deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 72:471–476
Fujiwara H, Tatsumi K, Miki K, Harada T, Miyai K, Takai SI, Amino N (1997) Congenital hypothyroidism caused by a mutation in the Na+/I2 symporter. Nat Genet 16:124–125
Kosugi S, Sato Y, Matsuda A, Ohyama Y, Fujieda K, Inomata H, Kameya T, Isozak O, Jhiang SM (1998) High prevalence of T354P sodium/iodide symporter gene mutation in Japanese patients with iodide transport defect who have heterogeneous clinical pictures. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:4123–4129
Reardon W, O’Mahoney CF, Trembath R, Jan H, Phelps PD (2000) Enlarged vestibular aqueduct: a radiological marker of Pendred syndrome, and mutation of the PDS gene. Q J Med 93:99–104
Reardon W, Trembath RC (1996) Pendred syndrome. J Med Genet 33:1037–1040
Batsakis JG, Nishiyama RH (1962) Deafness with sporadic goitre. Arch Otolaryngol 76:401–406
Everett LA, Glaser B, Beck JC, Idol JR, Buchs A, Heyman M, Adawi F, Hazani E, Nassir E, Baxevanis AD, Sheffield VC, Green ED (1997) Pendred syndrome is caused by mutations in a putative sulphate transporter gene (PDS). Nat Genet 17:411–422
Royaux IE, Suzuki K, Mori A, Katoh R, Everett LA, Kohn LD, Green ED (2000) Pendrin, the protein encoded by the Pendred syndrome gene (PDS), is an apical porter of iodide in the thyroid and is regulated by thyroglobulin in FRTL-5 cells. Endocrinology 14:839–845
Everett LA, Belyantseva IA, Noben-Trauth K, Cantos R, Chen A, Thakkar SI, Hoogstraten-Miller SL, Kachar B, Wu DK, Green ED (2001) Targeted disruption of mouse Pds provides insight about the inner-ear defects encountered in Pendred syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 10:153–161
Scott DA, Wang R, Kreman TM, Andrews M, McDonald JM, Bishop JR, Smith RJH, Karniski LP, Sheffield VC (2000) Functional differences of the PDS gene products are associated with phenotypic variation in patients with Pendred syndrome and non-syndromic hearing loss (DFNB4). Hum Mol Genet 9:1709–1715
Pfarr N, Borck G, Turk A, Napiontek U, Keilmann A, Muller-Forell W, Kopp P, Pohlenz J (2006) Goitrous congenital hypothyroidism and hearing impairment associated with mutations in the TPO and SLC26A4/PDS genes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:2678–2881
Ishii J, Suzuki A, Kimura T, Tateyama M, Tanaka T, Yazawa T et al (2019) Congenital goitrous hypothyroidism is caused by dysfunction of the iodide transporter SLC26A7. Commun Biol 2:270
Virion A, Michot JL, Deme D, Kaniewski J, Pommier J (1984) NADPH-dependent H2O2 generation and peroxidase activity in thyroid particular fraction. Mol Cell Endocrinol 36(1–2):95–105
Caillou B, Dupuy C, Lacroix L, Nocera M, Talbot M, Ohayon R, Deme D, Bidart JM, Schlumberger M, Virion A (2001) Expression of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (ThoX, LNOX, Duox) genes and proteins in human thyroid tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:3351–3358
Moreno JC, Bikker H, Kempers MJ, van Trotsenburg AS, Baas F, de Vijlder JJ, Vulsma T, Ris-Stalpers C (2002) Inactivating mutations in the gene for thyroid oxidase 2 (THOX2) and congenital hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med 347:95–102
Grasberger H, Refetoff S (2006) Identification of the maturation factor for dual oxidase: evolution of an eukaryotic operon equivalent. J Biol Chem 281:18269–18272
Berge-Lefranc JL, Cartonzon G, Mattei MG, Passage E, Malezet-Desmoulins C, Lissitzky S (1985) Localisation of the thyroglobulin gene by in situ hybridization to human chromosomes. Hum Genet 69:28–31
Hishinuma A, Takamatsu J, Ohyama Y, Yokozawa T, Kanno Y, Kuma K, Yoshida S, Matsuura N, Ieiro T (1999) Two novel cysteine substitutions (C1263R and C1995S) of thyroglobulin cause a defect in intracellular transport of thyroglobulin in patients with congenital goiter and the variant type of adenomatous goiter. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:1438–1444
Moreno JC (2003) Identification of novel genes involved in congenital hypothyroidism using serial analysis of gene expression. Horm Res 60:96–102
Moreno JC, Klootwijk W, van Toor H, Pinto G, D'Alessandro M, Leger A, Goudie D, Polak M, Gruters A, Visser TJ (2008) Mutations in the iodotyrosine deiodinase gene and hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med 358:1811–1818
Nicoletti A, Bal M, De Marco G, Baldazzi L, Agretti P, Menabo S, Ballarini E, Cicognani A, Tonacchera M, Cassio A (2009) Thyrotropin-stimulating hormone receptor gene analysis in pediatric patients with non-autoimmune subclinical hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:4187–4194
Cassio A, Nicoletti A, Rizzelo A, Zazzetta E, Bal M, Baldazzi L (2013) Current loss-of-function mutations in the thyrotropin receptor gene: when to investigate, clinical effects, and treatment. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 5:29–39
Weinstein LS, Yu S, Warner DR, Liu J (2001) Endocrine manifestations of stimulatory G protein alpha-subunit mutations and the role of genomic imprinting. Endocr Rev 22(5):675–705
Park E, Jung J, Araki O, Tsunekawa K, Park SY, Kim J, Murakami M, Jeong SY, Lee S (2018) Concurrent TSHR mutations and DIO2 T92A polymorphism result in abnormal thyroid hormone metabolism. Sci Rep 8:10090
Van Herle AJ, Vassart G, Dumont JE (1979) Control of thyroglobulin synthesis and secretion. (first of two parts). N Engl J Med 301:239–249
Friesema EC, Ganguly S, Abdalla A, Manning Fox JE, Halestrap AP, Visser TJ (2003) Identification of monocarboxylate transporter 8 as a specific thyroid hormone transporter. J Biol Chem 278:40128–40135
Dumitrescu AM, Liao XH, Best TB, Brockmann K, Refetoff S (2004) A novel syndrome combining thyroid and neurological abnormalities is associated with mutations in a monocarboxylate transporter gene. Am J Hum Genet 74:168–175 Erratum in: Am J Hum Genet 2004;74:598
Schwartz CE, May MM, Carpenter NJ, Rogers RC, Martin J, Bialer MG, Ward J, Sanabria J, Marsa S, Lewis JA, Echeverri R, Lubs HA, Voeller K, Simensen RJ, Stevenson RE (2005) Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome and the monocarboxylate transporter 8 (MCT8) gene. Am J Hum Genet 77(1):41–53
Gao B, Huber RD, Wenzel A, Vavricka SR, Ismair MG, Remé C, Meier PJ (2005) Localization of organic anion transporting polypeptides in the rat and human ciliary body epithelium. Exp Eye Res 80(1):61–72
Rodriguez PA, Ibarrola N, Ifiguez MA, Mufioz A, Bernal J (1993) J Clin Invest 91:812–818
Sap J, Munoz A, Damm K, Goldberg Y, Ghysdael J, Leutz A, Beug H, Vennstrom B (1986) The c-erb-a protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature 324:635–640
Singh BK, Yen PM (2017) A clinician’s guide to understanding resistance to thyroid hormone due to receptor mutations in the TRα and TRβ isoforms. Clin Diabetes Endocrinol 3:8
Ortiga-Carvalho TM, Sidhaye AR, Wondisford FE (2014) Thyroid hormone receptors and resistance to thyroid hormone disorders. Nat Rev Endocrinol 10:582–591
Refetoff S, Weiss RE, Usala SJ (1993) The syndromes of resistance to thyroid hormone. Endocr Rev 14:348–399
Alzahrani AS, Baitei EY, Zou M, Shi Y (2006) Clinical case seminar: metastatic follicular thyroid carcinoma arising from congenital goiter as a result of a novel splice donor site mutation in the thyroglobulin gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:740–746
Camargo R, Limbert E, Gillam M, Henriques MM, Fernandes C, Catarino AL, Soares J, Alves VA, Kopp P, Medeiros-Neto G (2001) Aggressive metastatic follicular thyroid carcinoma with anaplastic transformation arising from a long-standing goiter in a patient with Pendred's syndrome. Thyroid 11:981–988
Yoon JH, Hong AR, Kim HK, Kang HC (2020) Anaplastic thyroid cancer arising from dyshormonogenetic goiter: c.3070T>C and novel c.7070T>C mutation in the thyroglobulin gene. Thyroid ahead of print https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2020.0248
Hishinuma A, Fukata S, Kakudo K, Murata Y, Ieiri T (2005) High incidence of thyroid cancer in long-standing goiters with thyroglobulin mutations. Thyroid 15:1079–1084
Raef H, Al-Rijjal R, Al-Shehri S, Zou M, Al-Mana H, Baitei EY, Parhar RS, Al-Mohanna FA, Shi Y (2010) Biallelic p.R2223H mutation in the thyroglobulin gene causes thyroglobulin retention and severe hypothyroidism with subsequent development of thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:1000–1006
Boelaert K (2009) The association between serum TSH concentration and thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 16:1065–1072
Chertok Shacham E, Ishay A, Irit E, Pohlenz J, Tenenbaum-Rakover Y (2012) Minimally invasive follicular thyroid carcinoma developed in dyshormonogenetic multinodular goiter due to thyroid peroxidase gene mutation. Thyroid 22(5):542–546
Corrias A, Mussa A (2013) Thyroid nodules in pediatrics: which ones can be left alone, which ones must be investigated, when and how. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 5:57–69
Kaykhaei MA, Heidari Z, Mehrazin A (2014) Large thyroid cyst in a patient with congenital hypothyroidism. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab 58:9
Persani L (2012) Clinical review: central hypothyroidism: pathogenic, diagnostic, and therapeutic challenges. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(9):3068–3078
Alatzoglou KS, Dattani MT (2009) Genetic forms of hypopituitarism and their manifestation in the neonatal period. Early Hum Dev 85(11):705–712
García M, Fernández A, Moreno JC (2014) Central hypothyroidism in children. In Paediatric Thyroidology. Endocr Dev 26:79–107 Ed G Szinnai Basel, Karger
Kelberman D, Rizzoti K, Lovell-Badge R, Robinson IC, Dattani MT (2009) Genetic regulation of pituitary gland development in human and mouse. Endocr Rev 30(7):790–829
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Eirini Kostopoulou: conceptualization, literature review, original draft preparation, and writing. Konstantinos Miliordos: literature investigation and writing. Bessie Spiliotis: review, editing, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostopoulou, E., Miliordos, K. & Spiliotis, B. Genetics of primary congenital hypothyroidism—a review. Hormones 20, 225–236 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-020-00267-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-020-00267-x