Abstract
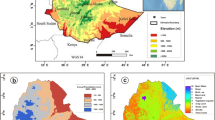
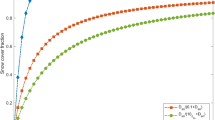
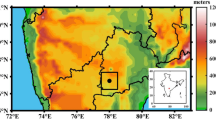
Obtaining surface albedo of high accuracy and analyzing spatial and temporal characteristics are essential for detecting change mechanism and influencing factors of surface albedo in deserts. Surface albedo from the Operational Land Imager (OLI) was assimilated into black-sky short-wave albedo (BSA) with an ensemble Kalman filter (EnKF) algorithm, to retrieve the surface albedo of high accuracy in Badain Jaran Desert. The results show that the average relative error decreases from 14.813% to 8.530% when surface albedo based on OLI is assimilated into BSA with the EnKF, and assimilated value can accurately describe the spatial and temporal distribution of surface albedo. The surface albedo has an obvious seasonal difference and presents a U-shape curve in a year, with the highest albedo in winter and lowest in summer. Owing to snow cover in some high-altitude areas, surface albedo is the highest and the spatial difference reaches maximum (variation coefficient=0.14) in winter. The Structure Similarity in surface albedo increases from the hinterland of desert (0.40–0.70) to the outer areas (0.70–0.90), as dune number decreases and distance between dunes increases. Compared with mobile and semi-mobile dunes, the minimum surface albedo of semi-fixed and fixed dunes postpones one month due to lag effect of the vegetation response to precipitation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd Elaziz M, Bhattacharyya S, Lu SF (2019) Swarm selection method for multilevel thresholding image segmentation. Expert systems with Applications 138:138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.07.035
Bloch MR (2017) Dust-induced albedo changes of polar ice sheets and glacierization. J Glaciol 5:241–244
Burakowski EA, Ollinger SV, Lepine L, Schaaf CB, Wang Z, Dibb JE, Hollinger DY, Kim JH, Erb A, Martin M (2015) Spatial scaling of reflectance and surface albedo over a mixed-use, temperate forest landscape during snow-covered periods. Remote Sens Environ 158:465–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2014.11.023
Cao X, Chen X, Bao A (2011) Response of vegetation to temperature and precipitation in Xinjiang during the period of 1998-2009. J Arid Land 3:94–103. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1227.2011.00094
Charney J, Quirk WJ, Chow SH, Kornfield J (1977) A Comparative Study of the Effects of Albedo Change on Drought in Semi–Arid Regions. J Atmospheric Sci 34:1366–1385. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1977)034<1366:ACSOTE>2.0.CO;2
Chen AJ, Liu YJ, Bian LG, Zhu XX, Wang W (2012) Analysis of the differences between the two kinds of MODIS albedos over China. Acta Meteorol Sin 70(5):1119–1127
Cherchali S, Amram O, Flouzat G (2000) Retrieval of temporal profiles of reflectances from simulated and real NOAA-AVHRR data over heterogeneous landscapes Int J Remote Sens 21:753–775
Cierniewski J, Ceglarek J, Karnieli A, Krolewicz S, Kazmierowski C, Zagajewski B (2017) Predicting the diurnal blue-sky albedo of soils using their laboratory reflectance spectra and roughness indices. J Quanti SpectroscRadiat Transf 200:25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2017.05.033
Csiszar I, Gutman G (1999) Mapping global land surface albedo from NOAA AVHRR. J Geophys Res Atmosph 104:6215–6228
Curry JA, Schramm JL, Ebert EE (1995) Sea Ice-Albedo Climate Feedback Mechanism. J Clim 8:240–247
de Wit AJW, van Diepen CA (2007) Crop model data assimilation with the ensemble Kalman filter for improving regional crop yield forecasts. Agric Forest Meteorol 146:38–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2007.05.004
Dickinson RE (1983) Land Surface Processes and Climate—Surface Albedos and Energy. Bal Adv Geophys 25:305–353
El Kenawy AM, Hereher ME, Robaa SM (2019) An Assessment of the Accuracy of MODIS Land Surface Temperature over Egypt Using Ground-Based Measurements. Remote Sens 11:1–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202369
Gao F, He T, Masek JG, Shuai YM, Schaaf CB, Wang ZS (2014) Angular effects and correction for medium resolution sensors to support crop monitoring. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 7:4480–4489. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2343592
He T, Liang S, Wang D, Cao Y, Gao F, Yu Y, Feng M (2018) Evaluating land surface albedo estimation from Landsat MSS, TM, ETM +, and OLI data based on the unified direct estimation approach. Remote Sens Environ 204:181–196
Huang JX, Sedano F, Huang YB, Ma HY, Li XL, Liang SL, Tian LY, Zhang XD, Fan JL, Wu WB (2016) Assimilating a synthetic Kalman filter leaf area index series into the WOFOST model to improve regional winter wheat yield estimation. Agric For Meteorol 216:188–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2015.10.013
Kandel R, Viollier M, Raberanto P, Duvel JP, Collins W (1998) The ScaRaB Earth Radiation Budget Dataset. Bull Ame Meteorol Soc 79:765–783
Karnieli A, Qin ZH, Wu B, Panov N, Yan F (2014) Spatio-temporal dynamics of land-use and land-cover in the mu us Sandy land, China. Using Change Vector Anal Techn Remote Sens 6:9316–9339. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6109316
Kosmas C (2014) Evaluation and Selection of Indicators for Land Degradation and Desertification. Monitor: Methodol Appr Environ Manag 54:951–970
Labarre S, Jacquemouda S, Ferraria C, Ferraria A, Derrienb A, Grandina R, Jalludinc M, Lemaîtred F, Métoise M, Pierrot-Deseillignyf M, Rupnikf E, Tanguy B (2019) Retrieving soil surface roughness with the Hapke photometric model: confrontation with the ground truth. Remote Sens Environ 225:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.02.014
Li Q, Sun R, Liu Q, Yu T, Liu QR, Zhu AR (2019) The spatial-temporal variation of land surface Albedo in Hengshui during 2001–2015 by blending landsat and GLASS data. Int J Earth Environ Sci 4:167–177. https://doi.org/10.15344/2456-351X/2019/167
Liang S (2001) Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo I algorithms. Remote Sens Environ 76:213–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(00)00205-4
Liang S, Shuey CJ, Russ AL, Fang HL, Chen MZ, Walthall CL, Daughtry CST, Jr RH (2003) Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo: II. Valid Remote Sens Enviro 84:25–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00068-8
Limbacher JA, Kahn RA (2014) MISR research-aerosol-algorithm refinements for dark water retrievals. Atmosph Meas Techn 7:3989–4007
Liu C, Zhao W, Liu B, Meng Y (2019) Distribution characteristics and dynamic changes of vegetation in Badain Jaran desert: based on UAV and MODIS data. J Desert Res 39:92–102. https://doi.org/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2018.00096
Liu FS, Chen Y, Lu HY, Shao HB (2017) Albedo indicating land degradation around the Badain Jaran Desert for better land resources utilization. Sci Total Environ 578:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.171
Liu H, Wang B, Fu C (2008) Relationships between surface albedo, Soil Thermal Parameters and Soil Moisture in the Semi-arid Area of Tongyu. N China Adv Atmosph Sci 25:757–764
Meng J, Du X, Wu B (2013) Generation of high spatial and temporal resolution NDVI and its application in crop biomass estimation. Int J Digit Earth 6:203–218. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2011.623189
Roman MO, Gatebe CK, Shuai Y, Wang Z, Gao F, Masek JG, He T, Liang S, Schaaf CB (2013) Use of in situ and airborne multiangle data to assess MODIS- and Landsat-based estimates of directional reflectance and Albedo IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 51: 1393–1404 https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2013.2243457
Sha ZY, Zhong JL, Bai YF, Tan XC, Li J (2016) Spatio-temporal patterns of satellite-derived grassland vegetation phenology from 1998 to 2012 in Inner Mongolia, China. J Arid Land 8(3):462–477
Shang L, Zhang Y, Lu S, Wang S (2015) Energy exchange of an alpine grassland on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci Bull 60:435–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0685-8
Shuai YM, Masek JG, Gao F, Schaaf CB (2011) An algorithm for the retrieval of 30-m snow-free albedo from Landsat surface reflectance and MODIS BRDF. Remote Sens Environ 115:2204–2216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.04.019
Su JL, Wang JH, Li JP, Shang KZ, Kang YZ, Jia XW, Wu ZX (2016) Preliminary analysis of precipitation characteristics in the Badain Jaran and Tengger deserts. J Arid Meteorol 34:216–268. https://doi.org/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2016)-02-0261
Tian X, Liu Q, Song Z, Dou B, Li X (2018) Aerosol optical depth retrieval from Landsat 8 OLI images over urban areas supported by MODIS BRDF/Albedo data. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 15:976–980. https://doi.org/10.1109/lgrs.2018.2827200
Waggoner DG, Sokolik IN (2010) Seasonal dynamics and regional features of MODIS-derived land surface characteristics in dust source regions of East Asia. Remote Sens Environ 114:2126–2136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2010.04.017
Wang M, Dong ZB, Luo WY, Lu JF, Li JY (2015) Spatial variability of vegetation characteristics, soil properties and their relationships in and around China’s Badain Jaran Desert. Environ Earth Sci 74:6847–6858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4685-z
Wang ZS, Schaaf CB, Sun QS, Kim J, Erb AM, Gao F, Roman MO, Yang Y, Petroy S, Taylor JR, Masek JG, Morisette JT, Zhang XY, Papuga SA (2017) Monitoring land surface albedo and vegetation dynamics using high spatial and temporal resolution synthetic time series from Landsat and the MODIS BRDF/NBAR/albedo product. Int J Appl Earth Observ Geoinform 59:104–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2017.03.008
Wu ZH, Lei SG, Bian ZF, Huang J, Zhang Y (2019) Study of the desertification index based on the albedo-MSAVI feature space for semi-arid steppe region. Environ Earth Sci 78:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8111-9
Xie Y, Wang PX, Bai XJ, Khan J, Zhang SY, Li L, Wang L (2017) Assimilation of the leaf area index and vegetation temperature condition index for winter wheat yield estimation using Landsat imagery and the CERES-Wheat model. Agricult Forest Meteorol 246:194–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.06.015
Yang B, Bräuning A, Zhang Z, Dong Z, Esper J (2007) Dust storm frequency and its relation to climate changes in northern China during the past 1000 years. Atmosph Environ 41:9288–9299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.09.025
Yang X, Rost KT, Lehmkuhl F, Zhu Z, Dodson J (2004) The evolution of dry lands in northern China and in the Republic of Mongolia since the Last Glacial Maximum. Quaternary Int 118:69–85
Yu T, Sun R, Xiao Z, Zhang Q, Wang J, Zhang Q, Wang JM, Liu G (2018) Generation of High Resolution Vegetation Productivity from a Downscaling Method. Remote Sens 10:1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111748
Zhang J, Dong W, Fu C, Wu L (2003a) The influence of vegetation cover on summer precipitation in China: A statistical analysis of NDVI and climate data. Adv Atmosph Sci 20:1002–1006
Zhang M, Lin W, Bretherton CS, Hack JJ, Rasch PJ (2003b) A modified formulation of fractional stratiform condensation rate in the NCAR Community Atmosphere Model (CAM2). J Geophys Res 108:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002523
Zheng XQ, Yang F, Li CF, Pan HL, Ji CR, Ali M, Huo W, Yang XH, Zhou CL (2019) The turbulence intensity of surface layer and land surface processes over Guaizi Lake shifting Sandy land on the northern margin of Badain Jaran Desert. J Desert Res 39:103–112
Zhou W, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13:600–612
Zhou Y, Wang D, Liang S, Yu Y, He T (2016) Assessment of the Suomi NPP VIIRS Land Surface Albedo Data Using Station Measurements and High-Resolution Albedo Maps. Remote Sens 8:137–153. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020137
Zhu J, Wang N, Chen H, Dong C, Ha Z (2010) Study on the Boundary and the Area of Badain Jaran Desert Based on Remote Sensing Imagery. Progress Geograp 29:1087–1094
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [41505008] and Natural Science Foundation for Young Scientists of Shanxi Province, China [201801D221043].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Peng He analysed the data and wrote the article, Lishuai Xu made substantial contributions to the conception and designed of the work, Fan Yang agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved, Ruitian Bi revised it critically for important intellectual content, and Zhilei Zhen performed the experiment and collected the data.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, P., Xu, L., Bi, R. et al. Spatial and temporal characteristics of surface albedo in Badain Jaran Desert, China. Earth Sci Inform 14, 429–440 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-020-00565-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-020-00565-3