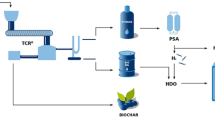
Abstract
Spent coffee grounds (SCGs) were utilized in the synthesis of a solid acid catalyst (SAC) through a carbonization–sulfonation process performed at low temperatures (350–500 °C for carbonization and 50–150 °C for sulfonation) and short processing times (1–10 h). The best SAC from the process was able to convert more than 90% of oleic acid to methyl oleate during esterification with methanol (10 mol OA/mol methanol, 80 °C, 7 h, 10%w/w catalyst loading). It was obtained by carbonizing SCG at 400 °C for 2 h and then sulfonating the biochar at 100 °C for 1 h. The reusability tests performed in 4 cycles at the same esterification conditions reveal loss of activity of about 70% of its original state, corresponding to a decrease in total acid and sulfonic acid densities from 4.22 and 3.36 mmol H+/g to 1.33 and 1.16 mmol H+/g, respectively. This process is a considerable improvement from that reported in previous works, having no activating agents in the carbonization process and with significantly shorter times for processing.
Graphic Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mićić, R., Tomić, M., Martinović, F., Kiss, F., Simikić, M., Aleksic, A.: Reduction of free fatty acids in waste oil for biodiesel production by glycerolysis: investigation and optimization of process parameters. Green Process. Synth. 8, 15–23 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2017-0118
Xie, W., Gao, C., Wang, H.: Biodiesel production from low-quality oils using heterogeneous cesium salts of vanadium-substituted polyoxometalate acid catalyst. Catalysts 10, 1–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10091060
Ambat, I., Srivastava, V., Sillanpää, M.: Recent advancement in biodiesel production methodologies using various feedstock: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 90, 356–369 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.03.069
Quitain, A.T., Sumigawa, Y., Mission, E.G., Sasaki, M., Assabumrungrat, S., Kida, T.: Graphene oxide and microwave synergism for efficient esterification of fatty acids. Energy Fuels 32, 3599–3607 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b00119
García Martín, J.F., Carrión Ruiz, J., Torres García, M., Feng, C.-H., Álvarez Mateos, P.: Esterification of free fatty acids with glycerol within the biodiesel production framework. Processes 7, 832 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7110832
Nongbe, M.C., Ekou, T., Ekou, L., Yao, K.B., Le Grognec, E., Felpin, F.X.: Biodiesel production from palm oil using sulfonated graphene catalyst. Renew. Energy 106, 135–141 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.01.024
Karmee, S.K.: Technical valorisation of spent coffee grounds and food waste using sulphuric acid immobilised on silica. Biofuels 11, 155–161 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/17597269.2017.1378989
Gao, Z., Tang, S., Cui, X., Tian, S., Zhang, M.: Efficient mesoporous carbon-based solid catalyst for the esterification of oleic acid. Fuel 140, 669–676 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.10.012
Yu, H., Niu, S., Lu, C., Li, J., Yang, Y.: Sulfonated coal-based solid acid catalyst synthesis and esterification intensification under ultrasound irradiation. Fuel 208, 101–110 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.06.122
Ngaosuwan, K., Goodwin, J.G., Prasertdham, P.: A green sulfonated carbon-based catalyst derived from coffee residue for esterification. Renew. Energy 86, 262–269 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.08.010
Wang, H., Wang, L., He, S., Xiao, F.-S.: Enhancement of catalytic properties by adjusting molecular diffusion in nanoporous catalysts. In: Advances in Catalysis, pp. 1–47. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2018)
Mansir, N., Taufiq-Yap, Y.H., Rashid, U., Lokman, I.M.: Investigation of heterogeneous solid acid catalyst performance on low grade feedstocks for biodiesel production: a review. Energy Convers. Manag. 141, 171–182 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.07.037
Xiu, Y., Chen, A., Liu, X., Chen, C., Chen, J., Guo, L., Zhang, R., Hou, Z.: Selective dehydration of sorbitol to 1,4-anhydro-d-sorbitol catalyzed by a polymer-supported acid catalyst. RSC Adv. 5, 28233–28241 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra01371b
Naeem, M.M., Al-Sakkari, E.G., Boffito, D.C., Gadalla, M.A., Ashour, F.H.: One-pot conversion of highly acidic waste cooking oil into biodiesel over a novel bio-based bi-functional catalyst. Fuel (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118914
Konwar, L.J., Boro, J., Deka, D.: Review on latest developments in biodiesel production using carbon-based catalysts. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 29, 546–564 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.09.003
Toda, M., Takagaki, A., Okamura, M., Kondo, J.N., Hayashi, S., Domen, K., Hara, M.: Biodiesel made with sugar catalyst. Nature 438, 177–178 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/438177a
Kastner, J.R., Miller, J., Geller, D.P., Locklin, J., Keith, L.H., Johnson, T.: Catalytic esterification of fatty acids using solid acid catalysts generated from biochar and activated carbon. Catal. Today 190, 122–132 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2012.02.006
Liu, T., Li, Z., Li, W., Shi, C., Wang, Y.: Preparation and characterization of biomass carbon-based solid acid catalyst for the esterification of oleic acid with methanol. Bioresour. Technol. 133, 618–621 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.163
Bureros, G.M.A., Tanjay, A.A., Cuizon, D.E.S., Go, A.W., Cabatingan, L.K., Agapay, R.C., Ju, Y.-H.: Cacao shell-derived solid acid catalyst for esterification of oleic acid with methanol. Renew. Energy 138, 489–501 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.01.082
Flores, K.P., Omega, J.L.O., Cabatingan, L.K., Go, A.W., Agapay, R.C., Ju, Y.H.: Simultaneously carbonized and sulfonated sugarcane bagasse as solid acid catalyst for the esterification of oleic acid with methanol. Renew. Energy 130, 510–523 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.06.093
International Coffee Organization, Coffee production by exporting countries and world coffee consumption. http://www.ico.org/trade_statistics.asp (2020). Accessed 20 June 2020
Murthy, P.S., Madhava Naidu, M.: Sustainable management of coffee industry by-products and value addition—a review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 66, 45–58 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2012.06.005
Kovalcik, A., Obruca, S., Marova, I.: Valorization of spent coffee grounds: a review. Food Bioprod. Process. 110, 104–119 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2018.05.002
Silva, M.A., Nebra, S.A., Machado Silva, M.J., Sanchez, C.G.: The use of biomass residues in the Brazilian soluble coffee industry. Biomass Bioenergy 14, 457–467 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0961-9534(97)10034-4
Vardon, D.R., Moser, B.R., Zheng, W., Witkin, K., Evangelista, R.L., Strathmann, T.J., Rajagopalan, K., Sharma, B.K.: Complete utilization of spent coffee grounds to produce biodiesel, bio-oil, and biochar. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 1, 1286–1294 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/sc400145w
Pujol, D., Liu, C., Gominho, J., Olivella, M.À., Fiol, N., Villaescusa, I., Pereira, H.: The chemical composition of exhausted coffee waste. Ind. Crops Prod. 50, 423–429 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.07.056
Loyao, A.S., Villasica, S.L.G., Dela Peña, P.L.L., Go, A.W.: Extraction of lipids from spent coffee grounds with non-polar renewable solvents as alternative. Ind. Crops Prod. 119, 152–161 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.04.017
Juarez, G.F.Y., Pabiloña, K.B.C., Manlangit, K.B.L., Go, A.W.: Direct dilute acid hydrolysis of spent coffee grounds: a new approach in sugar and lipid recovery. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 9, 235–246 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9813-9
Go, A.W., Conag, A.T., Bertumen, M.M.N.: Taguchi method to improve the production of sugar-rich hydrolysate from non-delipidated spent coffee grounds, and subsequent recovery of lipids and bioactive compounds. Biofuels 10, 193–205 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/17597269.2017.1309855
Obruca, S., Benesova, P., Petrik, S., Oborna, J., Prikryl, R., Marova, I.: Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates using hydrolysate of spent coffee grounds. Process Biochem. 49, 1409–1414 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.05.013
Kwon, E.E., Yi, H., Jeon, Y.J.: Sequential co-production of biodiesel and bioethanol with spent coffee grounds. Bioresour. Technol. 136, 475–480 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.052
Cay, H., Duman, G., Yanik, J.: Two-step gasification of biochar for hydrogen-rich gas production: effect of the biochar type and catalyst. Energy Fuels 33, 7398–7405 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.9b01354
Statistics Division - Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Crop Production and Trade Data, FAOSTAT. http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (2019). Accessed 13 June 2020
Goertzen, S.L., Thériault, K.D., Oickle, A.M., Tarasuk, A.C., Andreas, H.A.: Standardization of the Boehm titration. Part I. CO2 expulsion and endpoint determination. Carbon N. Y. 48, 1252–1261 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2009.11.050
Scandinavian Pulp Paper and Board Testing Committee, SCAN-CM 65:02: Pulp total acidic group content - conductometric titration method, SCAN-Test Methods 1–4 (2002)
Go, A.W., Tran Nguyen, P.L., Huynh, L.H., Liu, Y.T., Sutanto, S., Ju, Y.H.: Catalyst free esterification of fatty acids with methanol under subcritical condition. Energy 70, 393–400 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.04.013
Mendaros, C.M., Go, A.W., Nietes, W.J.T., Gollem, B.E.J.O., Cabatingan, L.K.: Direct sulfonation of cacao shell to synthesize a solid acid catalyst for the esterification of oleic acid with methanol. Renew. Energy 152, 320–330 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.01.066
Huang, M., Luo, J., Fang, Z., Li, H.: Biodiesel production catalyzed by highly acidic carbonaceous catalysts synthesized via carbonizing lignin in sub- and super-critical ethanol. Appl. Catal. B 190, 103–114 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.02.069
Zhou, Y., Niu, S., Li, J.: Activity of the carbon-based heterogeneous acid catalyst derived from bamboo in esterification of oleic acid with ethanol. Energy Convers. Manag. 114, 188–196 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.02.027
Okamura, M., Takagaki, A., Toda, M., Kondo, J.N., Domen, K., Tatsumi, T., Hara, M., Hayashi, S.: Acid-catalyzed reactions on flexible polycyclic aromatic carbon in amorphous carbon. Chem. Mater. 18, 3039–3045 (2006)
Estes, C.S., Gerard, A.Y., Godward, J.D., Hayes, S.B., Liles, S.H., Shelton, J.L., Stewart, T.S., Webster, R.I., Webster, H.F.: Preparation of highly functionalized carbon nanoparticles using a one-step acid dehydration of glycerol. Carbon N. Y. 142, 547–557 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.10.074
Chellappan, S., Nair, V., Sajith, V., Aparna, K.: Synthesis, optimization and characterization of biochar based catalyst from sawdust for simultaneous esterification and transesterification. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2018.02.034
Zeng, D., Zhang, Q., Chen, S., Liu, S., Wang, G.: Synthesis porous carbon-based solid acid from rice husk for esterification of fatty acids. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 219, 54–58 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.07.028
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Taiwan Building Technology Center (Grant/Project Number—108P011) from the Featured Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education in Taiwan, as well as the National Taiwan University of Science and Technology for the teaching and research start-up grant (Grant/Project Number—109O210007/109O410307) provided for 2019–2021 to organize the research group involved and partially supported the acquisition of the materials used in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Formal analysis, visualization, writing–original draft, writing–review and editing [RCA]; methodology, investigation, formal analysis, data curation [H-CL]; supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, writing–review and editing [Y-HJ]; conceptualization, formal analysis, writing—review and editing, project administration and funding acquisition [AWG]; writing–review and editing [AEA]; writing–review and editing [PLT-N]; writing–review and editing [CTT]; writing–review and editing [KLQ].
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agapay, R.C., Liu, HC., Ju, YH. et al. Synthesis and Initial Evaluation of Solid Acid Catalyst Derived from Spent Coffee Grounds for the Esterification of Oleic Acid and Methanol. Waste Biomass Valor 12, 4387–4397 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01325-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01325-6