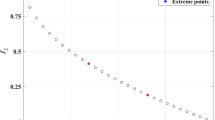
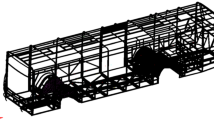
Abstract
To improve the computational cost and accuracy of approximate-based multi-objective optimization problems in engineering, an adaptive RBF neural network (ARBFNN) method integrating RBF neural network model, fuzzy subtractive clustering (FSC) sequence sampling method and non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II) is proposed. To solve the problem that the number of new sample points is difficult to determine, FSC sequence sampling is proposed to select the clustering center points as newly added sample points. First, the ARBFNN method is verified by the five test functions. The results show that the ARBFNN method is significantly better than static RBFNN model based on multi-objective optimization (SRBFNN) in terms of global convergence and efficiency performance, and the other two adaptive approximate optimization methods in terms of overall efficiency. Based on the above, the accuracy and efficiency of ARBFNN method are very high. Finally, the method is applied to an engineering example: the lightweight and crashworthiness design of floor rails. The cab model coupled with implicit parameterized floor rails model is built using the SFE-CONCEPT software to achieve collaborative optimization design of shape-size-material. The optimization results show that the ARBFNN method can guarantee the error of the approximate optimal solution and the finite element solution (expensive solution) within 2%, so the accuracy of highly nonlinear (finite element analysis of collision conditions) approximate optimization is improved. Hence, the proposed ARBFNN method is feasible and effective in solving complex and expensive engineering optimization problems.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandrov NM, Dennis JE, Lewis RM, Torczon V (1998) A trust-region framework for managing the use of approximation models in optimization. Struct Optim 15:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01197433
Avalle M, Chiandussi G, Belingardi G (2002) Design optimization by response surface methodology: application to crashworthiness design of vehicle structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 24:325–332
Box GEP, Wilson KB (1951) On the experimental attainment of optimum conditions. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 13:1–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1951.tb00067.x
Cai K, Wang D (2017) Optimizing the design of automotive S-rail using grey relational analysis coupled with grey entropy measurement to improve crashworthiness. Struct Multidiscip Optim 56:1539–1553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1728-y
Chakraborty S, Goswami S, Rabczuk T (2019) A surrogate assisted adaptive framework for robust topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 346:63–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2018.11.030
Chen GD, Han X, Liu GP, Jiang C, Zhao ZH (2012) An efficient multi-objective optimization method for black-box functions using sequential approximate technique. Appl Soft Comput 12:14–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2011.09.011
Chiandussi G, Avalle M (2002) Maximisation of the crushing performance of a tubular device by shape optimisation. Comput Struct 80:2425–2432
Chiu SL (1994) Fuzzy model identification based on cluster estimation. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 2:267–278. https://doi.org/10.3233/IFS-1994-2306
Costas M, Díaz J, Romera L, Hernández S (2014) A multi-objective surrogate-based optimization of the crashworthiness of a hybrid impact absorber. Int J Mech Sci 88:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2014.07.002
Duan LB, Xiao NC, Hu ZH, Li GY, Cheng AG (2017) An efficient lightweight design strategy for body-in-white based on implicit parameterization technique. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55:1927–1943. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1621-0
Duddeck F, Hunkeler S, Lozano P, Wehrle E, Zeng D (2016) Topology optimization for crashworthiness of thin-walled structures under axial impact using hybrid cellular automata. Struct Multidiscip Optim 54:415–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1445-y
Fang H, Rais-Rohani M, Liu Z, Horstemeyer MF (2005) A comparative study of metamodeling methods for multiobjective crashworthiness optimization. Comput Struct 83:2121–2136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2005.02.025
Fang JG, Sun GY, Qiu N, Kim NH, Li Q (2017) On design optimization for structural crashworthiness and its state of the art. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55:1091–1119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1579-y
Georgios K, Dimitrios S (2009) Multi-disciplinary design optimization exploiting the efficiency of ANSA-LSOPT-META coupling. 7th European LS-DYNA conference, Salzburg
Hou SJ, Li Q, Long SY, Yanga XJ, Li W (2008) Multiobjective optimization of multi-cell sections for the crashworthiness design. Int J Impact Eng 35:1355–1367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2007.09.003
Hu X, Chen X, Zhao Y, Yao W (2014) Optimization design of satellite separation systems based on multi-island genetic algorithm. Adv Space Res 53:870–876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2013.12.021
Huang T, Song X, Liu M (2016) The optimization of the loading path for T-shape tube hydroforming using adaptive radial basis function. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82:1843–1857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7534-z
Huang TL, Song XW, Liu M (2017) The multi-objective optimization of the loading paths for T-shape tube hydroforming using adaptive support vector regression. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 88:3447–3458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9055-9
Huband S, Hingston P, Barone L, While L (2006) A review of multiobjective test problems and a scalable test problem toolkit. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 10:477–506. https://doi.org/10.1109/tevc.2005.861417
Kerry K, Hawick KA (1998) Kriging interpolation on high-performance computers. Int Conf High Perform Comput Netw 1401:429–438. https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0037170
Lancaster P, Salkauskas K (1981) Surfaces generated by moving least squares methods. Math Comput 37:141–158
Li YH, Qiang S, Zhuang XY, Kaynak O (2004) Robust and adaptive backstepping control for nonlinear systems using RBF neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 15:693–701. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnn.2004.826215
Powell MJ (1992) The theory of radial basis function approximation in 1990. Adv Numer Anal 2:105–210
Shan SQ, Wang GG (2005) An efficient pareto set identification approach for multiobjective optimization on black-box functions. J Mech Des 127:866–874. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1904639
Sun GY, Song XG, Baek S, Li Q (2014) Robust optimization of foam-filled thin-walled structure based on sequential Kriging metamodel. Struct Multidiscip Optim 49:897–913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-013-1017-3
ULSAB-AVC Consortium (2001) Technical Transfer Dispatch# 6. ULSAC-AVC Body Structure Materials
Vapnik V, Golowich SE, Smola AJ (1997) Support vector method for function approximation, regression estimation and signal processing. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 9:281–287
Wang DF, Xie C (2020) An efficient hybrid sequential approximate optimization method for problems with computationally expensive objective and constraints. Eng Comput 12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01093-w
Wang ZP, Ma J, Zhang L (2017) State-of-health estimation for lithium-ion batteries based on the multi-island genetic algorithm and the Gaussian process Regression. IEEE Access 5:21286–21295. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2017.2759094
Xie C, Wang DF (2020) Multi-objective cross-sectional shape and size optimization of S-rail using hybrid multi-criteria decision-making method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 62:3477–3492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-020-02651-y
Xie S, Li H, Yang W, Wang N (2017) Crashworthiness optimisation of a composite energy-absorbing structure for railway vehicles. Struct Multidiscip Optim 57:1793–1807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1829-7
Xiong F, Wang D, Ma Z, Chen S, Lv T, Lu F (2017a) Structure-material integrated multi-objective lightweight design of the front end structure of automobile body. Struct Multidiscip Optim 57:829–847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1778-1
Xiong F, Wang D, Zhang S, Cai K, Wang S, Lu F (2017b) Lightweight optimization of the side structure of automobile body using combined grey relational and principal component analysis. Struct Multidiscip Optim 57:441–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1749-6
Xiong F, Wang D, Chen S, Gao Q, Tian S (2018) Multi-objective lightweight and crashworthiness optimization for the side structure of an automobile body. Struct Multidiscip Optim 58:1823–1843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-1986-3
Ye PC, Pan G (2015) A novel sequential approximate optimization approach using data mining for engineering design optimization. Optim Method Softw 30:1255–1275. https://doi.org/10.1080/10556788.2015.1043604
Yin HF, Fang HB, Wen GL, Wang Q, Xiao YY (2016) An adaptive RBF-based multi-objective optimization method for crashworthiness design of functionally graded multi-cell tube. Struct Multidiscip Optim 53:129–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1313-1
Zhang JH, Xiao M, Gao L, Chu S (2019) A combined projection-outline-based active learning Kriging and adaptive importance sampling method for hybrid reliability analysis with small failure probabilities. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 344:13–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2018.10.003
Zhang J, Ma Y, Ouyang L, Wang J (2020) A multi-points infill sampling criterion and parallel surrogate-based optimization algorithm based on Kriging model. Xitong Gongcheng Lilun yu Shijian/Syst Eng Theory Pract 40:251–261. https://doi.org/10.12011/1000-6788-2018-0757-11
Zhao L, Yang YP, Zeng Y (2009) Eliciting compact T-S fuzzy models using subtractive clustering and coevolutionary particle swarm optimization. Neurocomputing 72:2569–2575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2008.11.001
Zimmer H, Prabhuwaingankar M, Duddeck F (2009) Topology-and geometry-based structure optimization using implicit parametric models and LS-OPT. 7th European LS-DYNA Conference. Salzburg, Austria
Zitzler E, Deb K, Thiele L (2000) Comparison of multiobjective evolutionary algorithms: empirical results. Evol Comput 8:173–195. https://doi.org/10.1162/106365600568202
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 51975244] and Graduate Innovation Fund of Jilin University [grant number 101832020CX131].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Palaniappan Ramu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Xie, C. & Wang, S. An adaptive RBF neural network–based multi-objective optimization method for lightweight and crashworthiness design of cab floor rails using fuzzy subtractive clustering algorithm. Struct Multidisc Optim 63, 915–928 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-020-02797-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-020-02797-9