Abstract
Emerging evidence has shown that ursolic acid exerts antidepressant-like effects, however, its ability to elicit an antidepressant-like response in rodents subjected to stress model that mimics behavioral and neurochemical alterations found in depression remains to be determined. Thus, this study investigated the possible antidepressant-like effect of ursolic acid in mice subjected to chronic unpredictable stress (CUS) for 14 days, and whether this effect could be associated with the modulation of serum corticosterone levels and hippocampal Bcl-2/Bax mRNA expression. Our results indicated that CUS induced a depressive-like behavior, as demonstrated by an increase in the immobility time and latency to first grooming in the tail suspension test and splash test, respectively. Conversely, the repeated administration of ursolic acid (0.1 mg/kg, p.o.) or fluoxetine (10 mg/kg, p.o.) in the last 7 days of CUS completely prevented CUS-induced behavioral alterations, suggesting an antidepressant-like effect. Additionally, CUS significantly increased the mRNA expression of Bax (pro-apoptosis marker), but not Bcl-2 (anti-apoptosis marker) in the hippocampus. Moreover, reduced hippocampal mRNA expression of Bcl-2/Bax ratio was detected in CUS-exposed mice. Ursolic acid, but not fluoxetine, prevented CUS-induced increase in the expression of Bax, but both ursolic acid and fluoxetine prevented CUS-induced reduction on Bcl-2/Bax ratio. Furthermore, neither CUS nor treatments with ursolic acid or fluoxetine altered serum corticosterone levels. Our study unveils the ability of ursolic acid to prevent the depressive-like behavior induced by stress and the modulation of Bcl-2/Bax expression could be associated with this response.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Anacker C, Zunszain PA, Carvalho LA, Pariante CM (2011) The glucocorticoid receptor: Pivot of depression and of antidepressant treatment? Psychoneuroendocrinology 36:415–425
Chen Q, Luo S, Zhang Y, Chen Z (2011) Development of a liquid chromatography - Mass spectrometry method for the determination of ursolic acid in rat plasma and tissue: Application to the pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution study. Anal Bioanal Chem 399:2877–2884
Colla ARS, Oliveira Á, Pazini FL et al (2014) Serotonergic and noradrenergic systems are implicated in the antidepressant-like effect of ursolic acid in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 124:108–116
Cox BM, Alsawah F, McNeill PC et al (2011) Neurochemical, hormonal, and behavioral effects of chronic unpredictable stress in the rat. Behav Brain Res 220:106–111
Crisafulli C, Fabbri C, Porcelli S et al (2011) Pharmacogenetics of antidepressants. Front Pharmacol FEB:1–21
Engel D, Zomkowski ADE, Lieberknecht V et al (2013) Chronic administration of duloxetine and mirtazapine downregulates proapoptotic proteins and upregulates neurotrophin gene expression in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex of mice. J Psychiatr Res 47:802–808
Garcia LSB, Comim CM, Valvassori SS et al (2009) Ketamine treatment reverses behavioral and physiological alterations induced by chronic mild stress in rats. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:450–455
Gawali NB, Bulani VD, Gursahani MS et al (2017) Agmatine attenuates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced anxiety, depression-like behaviours and cognitive impairment by modulating nitrergic signalling pathway. Brain Res 1663:66–77
Goodyer IM, Herbert J, Tamplin A, Altham PME (2000) Recent life events, cortisol, dehydroepiandrosterone and the onset of major depression in high-risk adolescents. Br J Psychiatry 177:499–504
Gross A, Katz SG (2017) Non-apoptotic functions of BCL-2 family proteins. Cell Death Differ 24:1348–1358
Hong SY, Jeong WS, Jun M (2012) Protective effects of the key compounds isolated from Corni fructus against β-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in pc12 cells. Molecules 17:10831–10845
Jindal A, Mahesh R, Bhatt S (2013) Etazolate rescues behavioral deficits in chronic unpredictable mild stress model: Modulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity and brain-derived neurotrophic factor level. Neurochem Int 63:465–475
Richard EJ, Illuri R, Bethapudi B et al (2016) Anti-stress activity of Ocimum sanctum: Possible effects on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Phyther Res 30:805–814
Kaster MP, Machado NJ, Silva HB et al (2015) Caffeine acts through neuronal adenosine A2A receptors to prevent mood and memory dysfunction triggered by chronic stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:7833–7838
Kaster MP, Moretti M, Cunha MP, Rodrigues ALS (2016) Novel approaches for the management of depressive disorders. Eur J Pharmacol 771:236–240
Khan I, Karim N, Ahmad W et al (2016) GABA-A receptor modulation and anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, and antidepressant activities of constituents from Artemisia indica Linn. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016:1215393
Kosten TA, Galloway MP, Duman RS et al (2008) Repeated unpredictable stress and antidepressants differentially regulate expression of the Bcl-2 family of apoptotic genes in rat cortical, hippocampal, and limbic brain structures. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:1545–1558
Latt HM, Matsushita H, Morino M et al (2018) Oxytocin inhibits corticosterone-induced apoptosis in primary hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience 379:383–389
Lee AL, Ogle WO, Sapolsky RM (2002) Stress and depression: Possible links to neuron death in the hippocampus. Bipolar Disord 4:117–128
Li N, Liu RJ, Dwyer JM et al (2011) Glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists rapidly reverse behavioral and synaptic deficits caused by chronic stress exposure. Biol Psychiatry 69:754–761
Lieberknecht V, Engel D, Rodrigues ALS, Gabilan NH (2020) Neuroprotective effects of mirtazapine and imipramine and their effect in pro- and anti-apoptotic gene expression in human neuroblastoma cells. Pharmacol Rep 72:563–570
Liu B, Zhang H, Xu C et al (2011) Neuroprotective effects of icariin on corticosterone-induced apoptosis in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res 1375:59–67
Liu WX, Wang J, Xie ZM et al (2016) Regulation of glutamate transporter 1 via BDNF-TrkB signaling plays a role in the anti-apoptotic and antidepressant effects of ketamine in chronic unpredictable stress model of depression. Psychopharmacology 233:405–415
Liu Y-M, Shen J-D, Xu L-P et al (2017) Ferulic acid inhibits neuro-inflammation in mice exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. Int Immunopharmacol 45:128–134
Lu XY, Kim CS, Fraser A, Zhang W (2006) Leptin: A potential novel antidepressant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:1593–1598
Lucassen PJ, Müller MB, Holsboer F et al (2001) Hippocampal apoptosis in major depression is a minor event and absent from subareas at risk for glucocorticoid overexposure. Am J Pathol 158:453–468
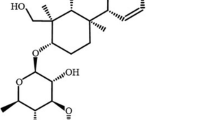
Machado DG, Neis VB, Balen GO et al (2012) Antidepressant-like effect of ursolic acid isolated from Rosmarinus officinalis L. in mice: Evidence for the involvement of the dopaminergic system. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 103:204–211
Manosso LM, Moretti M, Colla AR et al (2016) Involvement of glutamatergic neurotransmission in the antidepressant-like effect of zinc in the chronic unpredictable stress model of depression. J Neural Transm 123:339–352
McKlveen JM, Myers B, Flak JN et al (2013) Role of prefrontal cortex glucocorticoid receptors in stress and emotion. Biol Psychiatry 74:672–679
Mizoguchi K, Ishige A, Aburada M, Tabira T (2003) Chronic stress attenuates glucocorticoid negative feedback: Involvement of the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Neuroscience 119:887–897
Moretti M, Colla A, De Oliveira Balen G et al (2012) Ascorbic acid treatment, similarly to fluoxetine, reverses depressive-like behavior and brain oxidative damage induced by chronic unpredictable stress. J Psychiatr Res 46:331–340
Neis VB, Bettio LEB, Moretti M et al (2016) Acute agmatine administration, similar to ketamine, reverses depressive-like behavior induced by chronic unpredictable stress in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 150–151:108–114
Noschang CG, Pettenuzzo LF, von Pozzer Toigo E et al (2009) Sex-specific differences on caffeine consumption and chronic stress-induced anxiety-like behavior and DNA breaks in the hippocampus. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 94:63–69
Otte C, Gold SM, Penninx BW et al (2016) Major depressive disorder. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2:1–21
Pariante CM, Lightman SL (2008) The HPA axis in major depression: classical theories and new developments. Trends Neurosci 31:464–468
Planchez B, Surget A, Belzung C (2019) Animal models of major depression: drawbacks and challenges. J Neural Transm 126:1383–1408
Rai SN, Zahra W, Singh S, Sen et al (2019) Anti-inflammatory activity of ursolic acid in MPTP-induced parkinsonian mouse model. Neurotox Res 36:452–462
Ramos-Hryb AB, Pazini FL, Kaster MP, Rodrigues ALS (2017a) Therapeutic potential of ursolic acid to manage neurodegenerative and psychiatric diseases. CNS Drugs 31:1029–1041
Ramos-Hryb AB, Cunha MP, Pazini FL et al (2017b) Ursolic acid affords antidepressant-like effects in mice through the activation of PKA, PKC, CAMK-II and MEK1/2. Pharmacol Rep 69:1240–1246
Ramos-Hryb AB, Platt N, Freitas AE et al (2019) Protective effects of ursolic acid against cytotoxicity induced by corticosterone: role of protein kinases. Neurochem Res 44:2843–2855
Rodrigues ALS, Rocha JBT, Mello CF, Souza DO (1996) Effect of perinatal lead exposure on rat behaviour in open-field and two-way avoidance tasks. Pharmacol Toxicol 79:150–156
Sheline YI, Wang PW, Gado MH et al (1996) Hippocampal atrophy in recurrent major depression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:3908–3913
Shen J, Qu C, Xu L et al (2019) Resveratrol exerts a protective effect in chronic unpredictable mild stress–induced depressive-like behavior: involvement of the AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway in hippocampus. Psychopharmacology 236:591–602
Shih YH, Chein YC, Wang JY, Fu YS (2004) Ursolic acid protects hippocampal neurons against kainate-induced excitotoxicity in rats. Neurosci Lett 362:136–140
Singla RK, Scotti L, Dubey AK (2017) In Silico studies revealed multiple neurological targets for the antidepressant molecule ursolic acid. Curr Neuropharmacol 15:1100–1106
Siteneski A, Cunha MP, Lieberknecht V et al (2018) Central irisin administration affords antidepressant-like effect and modulates neuroplasticity-related genes in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 84:294–303
Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B, Simon P (1985) The tail suspension test: A new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology 85:367–370
Tsai SJ, Yin MC (2008) Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory protection of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid in PC12 cells. J Food Sci 73:174–178
Wang XH, Zhou SY, Qian ZZ et al (2013) Evaluation of toxicity and single-dose pharmacokinetics of intravenous ursolic acid liposomes in healthy adult volunteers and patients with advanced solid tumors. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 9:117–125
Watson S, Mackin P (2006) HPA axis function in mood disorders. Psychiatry 5:166–170
Willner P (2005) Chronic mild stress (CMS) revisited: Consistency and behavioural- neurobiological concordance in the effects of CMS. Neuropsychobiology 52:90–110
World Health Organization (2017) Depression and other common mental disorders: global health estimates. World Health Organization, Geneva, pp 1–24
Yoon JH, Youn K, Ho CT et al (2014) P-coumaric acid and ursolic acid from corni fructus attenuated β-amyloid25 – 35-induced toxicity through regulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway in PC12 cells. J Agric Food Chem 62:4911–4916
Zhang Y, Liu L, Liu Y-Z et al (2015) NLRP3 inflammasome mediates chronic mild stress-induced depression in mice via neuroinflammation. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 18:1–8
Zhang YQ, Wang XB, Xue RR et al (2019) Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like effect via regulating NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway in rats. Neuroreport 30:893–900
Zhu Z, Qian Z, Yan Z et al (2013) A phase I pharmacokinetic study of ursolic acid nanoliposomes in healthy volunteers and patients with advanced solid tumors. Int J Nanomedicine 8:129–136
Acknowledgements
The authors thank funding agencies CNPq and CAPES by the financial support, and the Laboratório Multiusuário de Estudos em Biologia (LAMEB) by technical support.
Funding
This study was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, #310113/2017-2 and #150082/2018-5), and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Ensino Superior (CAPES). ALSR is a CNPq Research Fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ana Lúcia S. Rodrigues and André R.S. Colla designed the study and wrote the protocol. André R.S. Colla, Francis L. Pazini, Vicente Lieberknecht, and Anderson Camargo performed the behavioral and biochemical tests and undertook the statistical analysis. All authors wrote the first draft of the manuscript, as well as approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All procedures were carried out in accordance with the National Institute of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and the protocols were approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colla, A.R.S., Pazini, F.L., Lieberknecht, V. et al. Ursolic acid abrogates depressive-like behavior and hippocampal pro-apoptotic imbalance induced by chronic unpredictable stress. Metab Brain Dis 36, 437–446 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00658-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00658-4