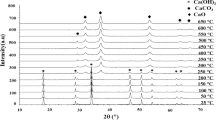
Abstract
Novel MgO-doped CaO sorbent pellets were prepared by gel-casting and wet impregnation. The effect of Na+ and MgO on the structure and CO2 adsorption performance of CaO sorbent pellets was elucidated. MgO-doped CaO sorbent pellets with the diameter range of 0.5–1.5 mm exhibited an excellent capacity for CO2 adsorption and adsorption rate due to the homogeneous dispersion of MgO in the sorbent pellets and its effects on the physical structure of sorbents. The results show that MgO can effectively inhibit the sintering of CaO and retain the adsorption capacity of sorbents during multiple adsorption-desorption cycles. The presence of mesopores and macropores resulted in appreciable change of volume from CaO (16.7 cm3·mol−1) to CaCO3 (36.9 cm3·mol−1) over repeated operation cycles. Ca2Mg1 sorbent pellets exhibited favorable CO2 capture capacity (9.49 mmol·g−1), average adsorption rate (0.32 mmol·g−1·min−1) and conversion rate of CaO (74.83%) after 30 cycles.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kheshgi H, de Coninck H, Kessels J. Carbon dioxide capture and storage: seven years after the IPCC special report. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 2012, 17(6): 563–567
Wang J, Huang L, Yang R, Zhang Z, Wu J, Gao Y, Wang Q, O’Hare D, Zhong Z. Recent advances in solid sorbents for CO2 capture and new development trends. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(11): 3478–3518
Yan Y, Wang K, Clough P T, Anthony E J. Developments in calcium/chemical looping and metal oxide redox cycles for high-temperature thermochemical energy storage: a review. Fuel Processing Technology, 2020, 199: 106280
Samanta A, Zhao A, Shimizu G K, Sarkar P, Gupta R, Sarkar P, Gupta R. Post-combustion CO2 capture using solid sorbents: a review. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(4): 1438–1463
Kenarsari S D, Yang D, Jiang G, Zhang S, Wang J, Russell A G, Fan M. Review of recent advances in carbon dioxide separation and capture. RSC Advances, 2013, 3(45): 22739–22773
Wang Q, Luo J, Zhong Z, Borgna A. CO2 capture by solid adsorbents and their applications: current status and new trends. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(1): 42–55
Mehrvarz E, Ghoreyshi A A, Jahanshahi M. Surface modification of broom sorghum-based activated carbon via functionalization with triethylenetetramine and urea for CO2 capture enhancement. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2017, 11(2): 252–265
Nie L, Bai L, Chen J, Jin J, Mi J. Grafting poly(ethyleneimine) on the pore surface of poly(glycidyl methacrylate-trimethylolpropane triacrylate) for preparation of the CO2 sorbent. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(12): 12610–12620
Liu W, Wu Y, Cai T, Chen X, Liu D. Use of nanoparticles Cu/TiO (OH)2 for CO2 removal with K2CO3/KHCO3 based solution: enhanced thermal conductivity and reaction kinetics enhancing the CO2 sorption/desorption performance of K2CO3/KHCO3. Greenhouse Gases. Science and Technology, 2019, 9(1): 10–18
Yu H, Wang X, Shu Z, Fujii M, Al Song C. 2O3 and CeO2-promoted MgO sorbents for CO2 capture at moderate temperatures. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018, 12(1): 83–93
Xiao Q, Tang X, Liu Y, Zhong Y, Zhu W. Comparison study on strategies to prepare nanocrystalline Li2ZrO3-based absorbents for CO2 capture at high temperatures. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2013, 7(3): 297–302
Choi S, Drese J H, Jones C W. Adsorbent materials for carbon dioxide capture from large anthropogenic point sources. Chem-SusChem, 2009, 2(9): 796–854
Kierzkowska A M, Pacciani R, Müller C R. CaO-based CO2 sorbents: from fundamentals to the development of new, highly effective materials. ChemSusChem, 2013, 6(7): 1130–1148
Li Y, Sun R, Liu H, Lu C. Cyclic CO2 capture behavior of limestone modified with pyroligneous acid (PA) during calcium looping cycles. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(17): 10222–10228
Miranda-Pizarro J, Perejón A, Valverde J M, Pérez-Maqueda L A, Sánchez-Jiménez P E. CO2 capture performance of Ca-Mg acetates at realistic calcium looping conditions. Fuel, 2017, 196(15): 497–507
Manovic V, Anthony E J, Grasa G, Abanades J C. CO2 looping cycle performance of a high-purity limestone after thermal activation/doping. Energy & Fuels, 2008, 22(5): 3258–3264
Wu S, Li Q, Kim J N, Yi K B. Properties of a nano CaO/Al2O3 CO2 sorbent. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008, 47(1): 180–184
Guo H, Wang S, Li C, Zhao Y, Sun Q, Ma X. Incorporation of Zr into calcium oxide for CO2 capture by a simple and facile sol-gel method. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(29): 7873–7879
Han R, Gao J, Wei S, Su Y, Qin Y. Development of highly effective CaO@Al2O3 with hierarchical architecture CO2 sorbents via a scalable limited-space chemical vapor deposition technique. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2018, 6(8): 3462–3470
Wang K, Gu F, Clough P T, Zhao P, Anthony E J. CO2 capture performance of gluconic acid modified limestone-dolomite mixtures under realistic conditions. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(8): 7550–7560
Wang S, Shen H, Fan S, Zhao Y, Ma X, Gong J. CaO-based meshed hollow spheres for CO2 capture. Chemical Engineering Science, 2015, 135(2): 532–539
Feng J, Guo H, Wang S, Zhao Y, Ma X. Fabrication of multi-shelled hollow Mg-modified CaCO3 microspheres and their improved CO2 adsorption performance. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 321(1): 401–411
Naeem M A, Armutlulu A, Imtiaz Q, Donat F, Schäublin R, Kierzkowska A, Müller C R. Optimization of the structural characteristics of CaO and its effective stabilization yield high-capacity CO2 sorbents. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1–11
MacDowell N, Florin N, Buchard A, Hallett J, Galindo A, Jackson G, Adjiman C S, Williams C K, Shah N, Fennell P. An overview of CO2 capture technologies. Energy & Environmental Science, 2010, 3(11): 1645–1669
Diego M E, Arias B, Abanades J C. Investigation of the dynamic evolution of the CO2 carrying capacity of solids with time in La Pereda 1.7 MWth calcium looping pilot plant. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2020, 92: 102856
Mattisson T, Lyngfelt A. A sulphur capture model for circulating fluidized-bed boilers. Chemical Engineering Science, 1998, 53(6): 1163–1173
Lu D Y, Hughes R W, Anthony E J. Ca-based sorbent looping combustion for CO2 capture in pilot-scale dual fluidized beds. Fuel Processing Technology, 2008, 89(12): 1386–1395
Su C, Duan L, Anthony E J. CO2 capture and attrition performance of competitive eco-friendly calcium-based pellets in fluidized bed. Greenhouse Gases. Science and Technology, 2018, 8(6): 1124–1133
Abanades J C, Anthony E J, Lu D Y, Salvador C, Alvarez D. Capture of CO2 from combustion gases in a fluidized bed of CaO. AIChE Journal. American Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2004, 50(7): 1614–1622
Wang X, Li Y, Shi J, Zhao J, Wang Z, Liu H, Zhou X. Simultaneous SO2/NO removal performance of carbide slag pellets by bagasse templating in a bubbling fluidized bed reactor. Fuel Processing Technology, 2018, 180: 75–86
Hu Y, Qu M, Li H, Yang Y, Yang J, Qu W, Liu W. Porous extruded-spheronized Li4SiO4 pellets for cyclic CO2 capture. Fuel, 2019, 236(15): 1043–1049
Wang P, Sun J, Guo Y, Zhao C, Li W, Wang G, Lu P. Structurally improved, urea-templated, K2CO3-based sorbent pellets for CO2 capture. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 374(15): 20–28
Zhang Z, Pi S, He D, Qin C, Ran J. Investigation of pore-formers to modify extrusion-spheronized CaO-based pellets for CO2 capture. Processes (Basel, Switzerland), 2019, 7(2): 62
Li H, Qu M, Yang Y, Hu Y, Liu W. One-step synthesis of spherical CaO pellets via novel graphite-casting method for cyclic CO2 capture. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 374(15): 619–625
Hu Y, Liu W, Peng Y, Yang Y, Sun J, Chen H, Xu M. One-step synthesis of highly efficient CaO-based CO2 sorbent pellets via gelcasting technique. Fuel Processing Technology, 2017, 160(1): 70–77
Luo C, Zheng Y, Xu Y, Ding N, Shen Q, Zheng C. Wet mixing combustion synthesis of CaO-based sorbents for high temperature cyclic CO2 capture. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 267(1): 111–116
Armutlulu A, Naeem M A, Liu H, Kim S M, Kierzkowska A, Fedorov A, Müller C R. Multishelled CaO microspheres stabilized by atomic layer deposition of Al2O3 for enhanced CO2 capture performance. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(41): 1702896
Guo H, Kou X, Zhao Y, Wang S, Ma X. Role of microstructure, electron transfer, and coordination state in the CO2 capture of calcium-based sorbent by doping (Zr-Mn). Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 336(15): 376–385
Hu Y, Lu H, Liu W, Yang Y, Li H. Incorporation of CaO into inert supports for enhanced CO2 capture: A review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 396(15): 125253
Li Z, Ouyang J, Luo G, Yao H. High-efficiency CaO-based sorbent modified by aluminate cement and organic fiber through wet mixing method. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(48): 22040–22047
Zhao P, Sun J, Li Y, Wang K, Yin Z, Zhou Z, Su Z. Synthesis of efficient CaO sorbents for CO2 capture using a simple organometallic calcium-based carbon template route. Energy & Fuels, 2016, 30(9): 7543–7550
Liao J, Jin B, Zhao Y, Liang Z. Highly efficient and durable metal-organic framework material derived Ca-based solid sorbents for CO2 capture. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 372(15): 1028–1037
Lee B B, Ravindra P, Chan E S. Size and shape of calcium alginate beads produced by extrusion dripping. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2013, 36(10): 1627–1642
Papageorgiou S K, Katsaros F K, Kouvelos E P, Nolan J W, Le Deit H, Kanellopoulos N K. Heavy metal sorption by calcium alginate beads from Laminaria digitata. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 137(3): 1765–1772
Manovic V, Anthony E J. Thermal activation of CaO-based sorbent and self-reactivation during CO2 capture looping cycles. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(11): 4170–4174
Gupta H, Fan L. Carbonation-calcination cycle using high reactivity calcium oxide for carbon dioxide separation from flue gas. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2002, 41(16): 4035–4042
Wu S, Lan P. A kinetic model of nano-CaO reactions with CO2 in a sorption complex catalyst. AIChE Journal. American Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2012, 58(5): 1570–1577
Acknowledgements
Financial support by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFB0603300), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (Grant No. NCET-13-0411) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Jiang, T., Zhang, H. et al. Efficient MgO-doped CaO sorbent pellets for high temperature CO2 capture. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 15, 698–708 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-020-1981-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-020-1981-2