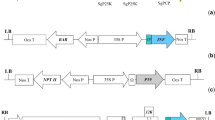
Abstract
Plant-virus–derived vectors are versatile tools with multiple applications in agricultural and medical biotechnology. In this study, we developed pepino mosaic virus (PepMV) (family Alphaflexiviridae; genus Potexvirus) into a vector for heterologous protein expression in plants. PepMV was initially cloned in a step-wise manner, fully sequenced and the full-length infectious clone was tested for infectivity in Nicotiana benthamiana. Initial infectious clones resulted in poor replication of PepMV and lack of systemic movement. Mutations in the viral sequence affected systemic infection. Two suspected mutations were altered to restore systemic infectivity. PepMV infection was apparent as early as 4 days post agroinfiltration (dpa) inoculation in N. benthamiana. A multiple cloning site was inserted into the PepMV genome for introduction and expression of foreign genes. Several modifications to the wild-type vector were made, such as a replacing the native subgenomic promoter (SGP) with a heterologous SGP, and introduction of translational enhancers and terminators, to improve heterologous expression of the foreign gene-of-interest. GFP was used as a reporter for monitoring virus infection and protein production. Strong GFP expression was observed as early as 4 dpa with a translational enhancer. The PepMV-based vector produces rapid expression of the foreign gene in comparison to two other potexvirus-based vectors. GFP production was monitored over time and optimal protein production was recorded between 5 and 7 dpa. GFP protein levels reached up to 4% and decreased to 0.5% total soluble protein at 7 and 14 dpa, respectively. Future studies will evaluate this virus-based vector for large-scale production of pharmaceutical compounds.
Key points
• A pepino mosaic virus isolate was developed into a plant-based expression vector.
• Expression levels of the heterologous protein were comparable or exceeded previously developed viral vectors.
• Protein levels in plants were highest between 5 and 7 days and decreased gradually.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data and materials presented in the article are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abrahamian P, Hammond RW, Hammond J (2020a) Plant virus–derived vectors: applications in agricultural and medical biotechnology. Annu Rev Virol 7:513–535. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-virology-010720-054958
Abrahamian P, Hammond J, Hammond RW (2020b) Complete genome sequence of an American Isolate of Pepino Mosaic Virus. Microbiol Resour Announc 9:e01124–e01119. https://doi.org/10.1128/MRA.01124-19
Allen GC, Spiker S, Thompson WF (2000) Use of matrix attachment regions (MARs) to minimize transgene silencing. Plant Mol Biol 43:361–376. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006424621037
Avesani L, Marconi G, Morandini F, Albertini E, Bruschetta M, Bortesi L, Pezzotti M, Porceddu A (2007) Stability of Potato virus X expression vectors is related to insert size: implications for replication models and risk assessment. Transgenic Res 16:587–597
Baulcombe DC, Chapman S, Santa Cruz S (1995) Jellyfish green fluorescent protein as a reporter for virus infections. Plant J 7:1045–1053. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1995.07061045.x
Blystad D-R, van der Vlugt R, Alfaro-Fernández A, del Carmen Cordoba M, Bese G (2015) Host range and symptomatology of Pepino mosaic virus strains occurring in Europe. Eur J Plant Pathol 141:43–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-015-0664-1
Bouton C, King RC, Chen H, Azhakanandam K, Bieri S, Hammond-Kosack KE, Kanyuka K (2018) Foxtail mosaic virus: a viral vector for protein expression in cereals. Plant Physiol 177:1352–1367. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.01679
Burén S, Ortega-Villasante C, Ötvös K, Samuelsson G, Bakó L, Villarejo A (2012) Use of the foot-and-mouth disease virus 2A peptide co-expression system to study intracellular protein trafficking in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 7:e51973. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0051973
Chapman S, Kavanagh T, Baulcombe D (1992) Potato virus X as a vector for gene expression in plants. Plant J 2:549–557. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1992.t01-24-00999.x
Chariou PL, Dogan AB, Welsh AG, Saidel GM, Baskaran H, Steinmetz NF (2019) Soil mobility of synthetic and virus-based model nanopesticides. Nat Nanotechnol 14:712–718. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0453-7
Chen TH, Hu CC, Liao JT, Lee YL, Huang YW, Lin NS, Lin YL, Hsu YH (2017) Production of Japanese encephalitis virus antigens in plants using bamboo mosaic virus-based vector. Front Microbiol 8:788. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00788
Cody WB, Scholthof HB (2019) Plant virus vectors 3.0: transitioning into synthetic genomics. Annu Rev Phytopathol 57:211–230. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-082718-100301
Cruz SS, Chapman S, Roberts AG, Roberts IM, Prior DA, Oparka KJ (1996) Assembly and movement of a plant virus carrying a green fluorescent protein overcoat. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A 93:6286–6290. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.13.6286
Davino S, Accotto GP, Masenga V, Torta L, Davino M (2009) Basil (Ocimum basilicum), a new host of Pepino mosaic virus. Plant Pathol 54:407
de Felippes FF, McHale M, Doran RL, Roden S, Eamens AL, Finnegan EJ, Waterhouse PM (2020) The key role of terminators on the expression and post-transcriptional gene silencing of transgenes. Plant J 104:96–112. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14907
Diamos AG, Mason HS (2018) Chimeric 3’flanking regions strongly enhance gene expression in plants. Plant Biotechnol J 16:1971–1982. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12931
Diamos AG, Rosenthal SH, Mason HS (2016) 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions strongly enhance performance of geminiviral replicons in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. Front Plant Sci 7:200. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00200
Dickmeis C, Fischer R, Commandeur U (2014) Potato virus X-based expression vectors are stabilized for long-term production of proteins and larger inserts. Biotechnol J 9:1369–1379. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201400347
Dolgova AS, Dolgov SV (2019) Matrix attachment regions as a tool to influence plant transgene expression. 3 Biotech 9:176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1709-5
Goodin MM, Dietzgen RG, Schichnes D, Ruzin S, Jackson AO (2002) pGD vectors: versatile tools for the expression of green and red fluorescent protein fusions in agroinfiltrated plant leaves. Plant J 31:375–383. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01360.x
Guilford PJ, Beck DL, Forster RL (1991) Influence of the poly (A) tail and putative polyadenylation signal on the infectivity of white clover mosaic potexvirus. Virology 182:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/0042-6822(91)90648-u
Hanssen IM, Thomma BP (2010) Pepino mosaic virus: a successful pathogen that rapidly evolved from emerging to endemic in tomato crops. Mol Plant Pathol 11:179–189. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2009.00600.x
Hasiów-Jaroszewska B, Borodynko N, Jackowiak P, Figlerowicz M, Pospieszny H (2011) Single mutation converts mild pathotype of the Pepino mosaic virus into necrotic one. Virus Res 159:57–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2011.04.008
Hefferon K (2017) Plant virus expression vectors: a powerhouse for global health. Biomedicines 5:44. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines5030044
Hu B, Pillai-Nair N, Hemenway C (2007) Long-distance RNA–RNA interactions between terminal elements and the same subset of internal elements on the potato virus X genome mediate minus-and plus-strand RNA synthesis. RNA 13:267–280. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.243607
Ibrahim A, Odon V, Kormelink R (2019) Plant viruses in plant molecular pharming: toward the use of enveloped viruses. Front Plant Sci 10:803. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00803
Jiang M-C, Hu C-C, Lin N-S, Hsu Y-H (2019) Production of human IFNγ protein in Nicotiana benthamiana plant through an enhanced expression system based on Bamboo mosaic virus. Viruses 11:509. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060509
Jorda C, Lazaro Perez A, Martinez-Culebras P, Lacasa A (2001) First report of Pepino mosaic virus on natural hosts. Plant Dis 85:1292. https://doi.org/10.1094/pdis.2001.85.12.1292d
Kanoria S, Burma PK (2012) A 28 nt long synthetic 5′ UTR (synJ) as an enhancer of transgene expression in dicotyledonous plants. BMC Biotechnol 12:85. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-12-85
Kim KH, Hemenway CL (1999) Long-distance RNA-RNA interactions and conserved sequence elements affect potato virus X plus-strand RNA accumulation. RNA 5:636–645
Koenig R, Lesemann DE, Loss S, Engelmann J, Commandeur U, Deml G, Schiemann J, Aust H, Burgermeister W (2006) Zygocactus virus X-based expression vectors and formation of rod-shaped virus-like particles in plants by the expressed coat proteins of Beet necrotic yellow vein virus and Soil-borne cereal mosaic virus. J Gen Virol 87:439–443. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.81477-0
Kreuze JF, Vaira AM, Menzel W, Candresse T, Zavriev SK, Hammond J, Hyun Ryu K, Report Consortium IC (2020) ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Alphaflexiviridae. J Gen Virol 101:699–700. https://doi.org/10.1099/jgv.0.001436
Kuo SY, Lin YC, Lai YC, Liao JT, Hsu YH, Huang HC, Hu CC (2018) Production of fluorescent antibody-labeling proteins in plants using a viral vector and the application in the detection of Acidovorax citrulli and Bamboo mosaic virus. PLoS One 13:e0192455. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0192455
Lim HS, Vaira AM, Domier LL, Lee SC, Kim HG, Hammond J (2010) Efficiency of VIGS and gene expression in a novel bipartite potexvirus vector delivery system as a function of strength of TGB1 silencing suppression. Virology 402:149–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2010.03.022
Ling KS, Wintermantel WM, Bledsoe M (2008) Genetic composition of Pepino mosaic virus population in North American greenhouse tomatoes. Plant Dis 92:1683–1688. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-92-12-1683
Ling KS, Li R, Bledsoe M (2013) Pepino mosaic virus genotype shift in North America and development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid genotype identification. Virol J 10:117. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-10-117
Liu Z, Kearney CM (2010) An efficient Foxtail mosaic virus vector system with reduced environmental risk. BMC Biotechnol 10:88. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-10-88
Mardanova ES, Blokhina EA, Tsybalova LM, Peyret H, Lomonossoff GP, Ravin NV (2017) Efficient transient expression of recombinant proteins in plants by the novel pEff vector based on the genome of potato virus X. Front Plant Sci 8:247. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00247
Maroon-Lango CJ, Guaragna MA, Jordan RL, Hammond J, Bandla M, Marquardt SK (2005) Two unique US isolates of Pepino mosaic virus from a limited source of pooled tomato tissue are distinct from a third (European-like) US isolate. Arch Virol 150:1187–1201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-005-0495-z
Mei Y, Beernink BM, Ellison EE, Konečná E, Neelakandan AK, Voytas DF, Whitham SA (2019) Protein expression and gene editing in monocots using foxtail mosaic virus vectors. Plant Direct 3:e00181. https://doi.org/10.1002/pld3.181
Minato N, Komatsu K, Okano Y, Maejima K, Ozeki J, Senshu H, Takahashi S, Yamaji Y, Namba S (2014) Efficient foreign gene expression in planta using a plantago asiatica mosaic virus-based vector achieved by the strong RNA-silencing suppressor activity of TGBp1. Arch Virol 159:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-013-1860-y
Minicka J, Elena SF, Borodynko-Filas N, Rubiś B, Hasiów-Jaroszewska B (2017) Strain-dependent mutational effects for Pepino mosaic virus in a natural host. BMC Evol Biol 17:67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-017-0920-4
Oparka KJ, Roberts AG, Santa Cruz S, Boevink P (1997) Using GFP to study virus invasion and spread in plant tissues. Nature 388:401–402. https://doi.org/10.1038/41145
Osman TA, Olsthoorn RC, Livieratos IC (2014) Role of the Pepino mosaic virus 3′-untranslated region elements in negative-strand RNA synthesis in vitro. Virus Res 190:110–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2014.06.018
Papayiannis LC, Kokkinos CD, Alfaro-Fernández A (2012) Detection, characterization and host range studies of Pepino mosaic virus in Cyprus. Eur J Plant Pathol 132:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-011-9854-7
Park MR, Kwon SJ, Choi HS, Hemenway CL, Kim KH (2008) Mutations that alter a repeated ACCA element located at the 5′ end of the Potato virus X genome affect RNA accumulation. Virology 378:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2008.05.004
Peyret H, Lomonossoff GP (2015) When plant virology met Agrobacterium: the rise of the deconstructed clones. Plant Biotechnol J 13:1121–1135. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12412
Pogue GP, Lindbo JA, Garger SJ, Fitzmaurice WP (2002) Making an ally from an enemy: plant virology and the new agriculture. Annu Rev Phytopathol 40:45–74. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.40.021102.150133
Regnard GL, Halley-Stott RP, Tanzer FL, Hitzeroth II, Rybicki EP (2010) High level protein expression in plants through the use of a novel autonomously replicating geminivirus shuttle vector. Plant Biotechnol J 8:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2009.00462.x
Röder J, Dickmeis C, Commandeur U (2019) Small, smaller, nano: new applications for Potato virus X in nanotechnology. Front Plant Sci 10:158. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00158
Ruiz-Ramón F, Sempere RN, Méndez-López E, Sánchez-Pina MA, Aranda MA (2019) Second generation of pepino mosaic virus vectors: improved stability in tomato and a wide range of reporter genes. Plant Methods 15:58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-019-0446-4
Sempere RN, Gómez P, Truniger V, Aranda MA (2011) Development of expression vectors based on pepino mosaic virus. Plant Methods 7:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-4811-7-6
Sempere RN, Gómez-Aix C, Ruiz-Ramón F, Gómez P, Hasiów-Jaroszewska B, Sánchez-Pina MA, Aranda MA (2016) Pepino mosaic virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase pol domain is a hypersensitive response-like elicitor shared by necrotic and mild isolates. Phytopathology 106:395–406. https://doi.org/10.1094/phyto-10-15-0277-r
Shivprasad S, Pogue GP, Lewandowski DJ, Hidalgo J, Donson J, Grill LK, Dawson WO (1999) Heterologous sequences greatly affect foreign gene expression in tobacco mosaic virus-based vectors. Virology 255:312–323. https://doi.org/10.1006/viro.1998.9579
Tian Y, Zhou M, Shi H, Gao S, Xie G, Zhu M, Wu M, Chen J, Niu Z (2018) Integration of cell-penetrating peptides with rod-like bionanoparticles: virus-inspired gene-silencing technology. Nano Lett 18:5453–5460. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b01805
Verchot-Lubicz J, Ye CM, Bamunusinghe D (2007) Molecular biology of potexviruses: recent advances. J Gen Virol 88:1643–1655. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.82667-0
Yamaji Y, Maejima K, Komatsu K, Shiraishi T, Okano Y, Himeno M, Sugawara K, Neriya Y, Minato N, Miura C, Hashimoto M (2012) Lectin-mediated resistance impairs plant virus infection at the cellular level. Plant Cell 24:778–793. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.093658
Zhang H, Wang L, Hunter D, Voogd C, Joyce N, Davies K (2013) A Narcissus mosaic viral vector system for protein expression and flavonoid production. Plant Methods 9:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-4811-9-28
Acknowledgments
Mention of trade names or commercial products in this publication is solely for providing specific information and does not imply recommendation by the U. S. Department of Agriculture. We thank Dr. Hugh Mason at Arizona State University for providing the pBYR2eK2M-GFP plasmid. Figure 1 in this manuscript was created using Biorender.com.
Funding
This work was funded by internal USDA-ARS project 8042-22000-295-00D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RWH, JH, and PA conceived the research. PA designed vectors, conducted experiments, and analyzed data, with input from JH and RWH. PA wrote the manuscript with feedback from JH and RWH. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 533 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abrahamian, P., Hammond, J. & Hammond, R.W. Development and optimization of a pepino mosaic virus-based vector for rapid expression of heterologous proteins in plants. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 627–645 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-11066-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-11066-0