Abstract
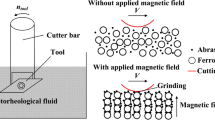
In this study a magnetic abrasive finishing (MAF) platform was developed by which an innovative MAF tool design was verified. The platform was composed of a tool per se, a linear moving table where a specimen placed on it, and a slurry supplying pump. The magnetic field was provided by two sets of NdFeB permanent magnets placed with opposite directions inside the tool. By using a C-shape and taper structure of low carbon steel, the magnetic flux generated by the magnets formed a magnetic circuit and was directed and concentrated at the opening notch of the C-shape structure where the tool tip was. A slurry composited of magnetorheological (MR) fluid, abrasive particles, and silicon oil was served as a MR abrasive slurry. The slurry was propelled to the tool tip by the slurry supplying pump and was then magnetized there to form a magnetic brush. While the table moved relative to the tool the magnetized slurry scrubbed a specimen on it. It is observed that after 2 ~ 3 hundreds of times of reciprocating motions, the magnetic brush would be stiffened and a highly efficient finishing machining process could be achieved. With aluminum specimens of initial surface roughness of Ra ~ 0.5 μm as examples, it is demonstrated that a fine surface of Ra ~ 0.06 μm could be achieved in about 2 ~ 3 min.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Dulaimi T, Khamesee MB (2017) A stationary apparatus of magnetic abrasive finishing using a rotating magnetic field. Microsyst Technol 23(11):5185–5191
Cheng HB, Yam Y, Wang YT (2009a) Experimentation on MR fluid using a 2-axis wheel tool. J Mater Process Technol 209(12–13):5254–5261
Cheng HB, Feng YP, Ren LQ, To S, Wang YT (2009b) Material removal and micro-roughness in fluid-assisted smoothing of reaction-bonded silicon carbide surfaces. J Mater Process Technol 209(9):4563–4567
Das M, Jain VK, Ghoshdastidar PS (2012) Nanofinishing of flat e workpieces using rotational–magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing (R-MRAFF) process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62(1–4):405–420
Golini D, Kordonski WI, Dumas P, Hogan SJ (1999) Magnetorheological finishing (MRF) in commercial precision optics manufacturing. Opt Manuf Test III 3782:80–91
Jha S, Jain VK (2004) Design and development of the magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing (MRAFF) process. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 44(10):1019–1029
Kordonski WI, Golini D (1999) Fundamentals of magnetorheological fluid utilization in high precision finishing. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 10(9):683–689
Kordonski WI, Jacobs SD (1996) Magnetorheological finishing. Int J Mod Phys B 10(2324):2837–2848
Kordonski WI, Shorey AB, Tricard M (2006) Magnetorheological jet (MR Jet TM) finishing technology. J Fluids Eng 128(1):20–26
Kumar S, Jain VK, Sidpara A (2015) Nanofinishing of freeform surfaces (knee joint implant) by rotational-magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing (R-MRAFF) process. Precis Eng 42:165–178
LORD (2008) MRF-140CG TECHNICAL DATA (http://www.lordmrstore.com/lord-mr-products/mrf-140cg-magneto-rheological-fluid)
Singh AK, Jha S, Pandey PM (2011) Design and development of nanofinishing process for 3D surfaces using ball end MR finishing tool. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 51(2):142–151
Singh AK, Jha S, Pandey PM (2012a) Nanofinishing of fused silica glass using ball-end magnetorheological finishing tool. Mater Manuf Process 27(10):1139–1144
Singh AK, Jha S, Pandey PM (2012b) Nanofinishing of a typical 3D ferromagnetic workpiece using ball end magnetorheological finishing process. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 63:21–31
Tricard M, Kordonski WI, Shorey AB, Evans C (2006) Magnetorheological jet finishing of conformal, freeform and steep concave optics. CIRP Ann 55(1):309–312
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the support from Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan under the grants 107-2218-E-007-036 and 107-2218-E-007-006 for the work described herein.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, PH., Chang, JY. A magnetic abrasive finishing (MAF) platform utilizing horizontal transverse magnetic field magnetized by permanent magnets. Microsyst Technol 27, 2499–2506 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-05172-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-05172-2