Abstract
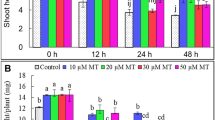
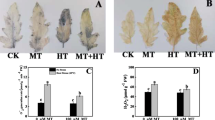
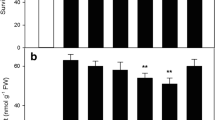
Melatonin is a signaling molecule that is involved in inducing plantsʼ abiotic stress tolerance. To determine the possible effects of the melatonin pre-treatment on thermotolerance in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.), the heat-sensitive cultivar Ventana was subjected to high temperatures (35 °C and 40 °C) for 10 h after pre-treatment with 0, 50, and 100 μM melatonin. High temperature increased malondialdehyde and H2O2 contents and reduced relative water content, carotenoid content, and catalase and ascorbate peroxidase activities, which led to a marked reduction in chlorophyll fluorescence. However, pre-treatment with melatonin at 100 μM decreased heat injury symptoms and induced antioxidant mechanisms in heat-sensitive cultivar Ventana, increasing heat tolerance. The results showed that when the melatonin pre-treated strawberry plants were exposed to high temperature (40 °C) for 2 h, the levels of FaTHsfA2a and HSP90 mRNA significantly increased, but after heat treating at 40 °C for 5 and 10 h, their mRNA levels were as similar as the control. The results support the hypothesis that melatonin acts as an important signaling molecule during heat stress to induce protective mechanisms via up-regulating the expression of defense HSF (FaTHsfA2a, FaTHSFB1a) and HSP (HSP90) genes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- APX:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- GPX:
-
Guaiacol peroxidase
- HSP:
-
Heat shock proteins
- HSF:
-
Heat shock transcription factors
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- AsA:
-
Ascorbic acid
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- RWC:
-
Relative water content
References
Ahammed GJ, Xu W, Liu A et al (2019) Endogenous melatonin deficiency aggravates high temperature-induced oxidative stress in Solanum lycopersicum L. Environ Exp Bot 161:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.06.006
Ahammed GJ, Wu M, Wang Y et al (2020) Melatonin alleviates iron stress by improving iron homeostasis, antioxidant defense and secondary metabolism in cucumber. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 265:109205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109205
AL-Huqail AA, AL-Rashed SA, Ibrahim MM et al (2017) Arsenic induced eco-physiological changes in Chickpea (Cicer arietinum) and protection by gypsum, a source of sulphur and calcium. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 217:226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.02.007
Alayafi AAM (2020) Exogenous ascorbic acid induces systemic heat stress tolerance in tomato seedlings: transcriptional regulation mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:19186–19199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06195-7
Antoniou C, Chatzimichail G, Xenofontos R et al (2017) Melatonin systemically ameliorates drought stress-induced damage in Medicago sativa plants by modulating nitro-oxidative homeostasis and proline metabolism. J Pineal Res 62:e12401. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12401
Ayyaz A, Amir M, Umer S et al (2020) Melatonin induced changes in photosynthetic efficiency as probed by OJIP associated with improved chromium stress tolerance in canola (Brassica napus L.). Heliyon 6:e04364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04364
Badek B, Napiórkowska B, Masny A, Korbin M (2014) Changes in the expression of three cold-regulated genes in “Elsanta” and “Selvik” strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) plants exposed to freezing. J Hortic Res 22:53–61. https://doi.org/10.2478/johr-2014-0022
Bagheri M, Gholami M, Baninasab B (2019) Hydrogen peroxide-induced salt tolerance in relation to antioxidant systems in pistachio seedlings. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 243:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.08.026
Baninasab B, Ghobadi C (2011) Influence of paclobutrazol and application methods on high-temperature stress injury in cucumber seedlings. J Plant Growth Regul 30:213–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-010-9188-2
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018060
Bidabadi SS, VanderWeide J, Sabbatini P (2020) Exogenous melatonin improves glutathione content, redox state and increases essential oil production in two Salvia species under drought stress. Sci Rep 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63986-6
Bose SK, Howlader P (2020) Melatonin plays multifunctional role in horticultural crops against environmental stresses: A review. Environ Exp Bot 176:104063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2020.104063
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Brown R, Wang H, Dennis M et al (2016) The effects of heat treatment on the gene expression of several heat shock protein genes in two cultivars of strawberry. Int J Fruit Sci 16:239–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/15538362.2016.1199996
Buttar ZA, Wu SN, Arnao MB et al (2020) Melatonin suppressed the heat stress-induced damage in wheat seedlings by modulating the antioxidant machinery. Plants 9:809. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9070809
Cakmak I, Marschner H (1992) Magnesium deficiency and high light intensity enhance activities of superoxide dismutase, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione reductase in bean leaves. Plant Physiol 98:1222–1227
Chen Y-E, Cui J-M, Su Y-Q et al (2015) Influence of stripe rust infection on the photosynthetic characteristics and antioxidant system of susceptible and resistant wheat cultivars at the adult plant stage. Front Plant Sci 6:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00779
Collani S, Galla G, Ramina A et al (2012) Self-incompatibility in olive: A new hypothesis on the S-locus genes controlling pollen-pistil interaction. Acta Hortic 967:133–140. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2012.967.15
Dai L, Li J, Harmens H et al (2020) Melatonin enhances drought resistance by regulating leaf stomatal behaviour, root growth and catalase activity in two contrasting rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) genotypes. Plant Physiol Biochem 149:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.01.039
Ding F, Liu B, Zhang S (2017) Exogenous melatonin ameliorates cold-induced damage in tomato plants. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 219:264–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.03.029
Gholami M, Rahemi M, Kholdebarin B, Rastegar S (2012) Biochemical responses in leaves of four fig cultivars subjected to water stress and recovery. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 148:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.09.005
Guo SH, Xu TF, Shi TC et al (2020) Cluster bagging promotes melatonin biosynthesis in the berry skins of Vitis vinifera cv Cabernet Sauvignon and Carignan during development and ripening. Food Chem 305:125502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125502
Hahn A, Bublak D, Schleiff E, Scharf K-D (2011) Crosstalk between Hsp90 and Hsp70 Chaperones and Heat Stress Transcription Factors in Tomato. Plant Cell 23:741–755. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.110.076018
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Alam MM et al (2013) Physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms of heat stress tolerance in plants. Int J Mol Sci 14:9643–9684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059643
Hassan MU, Chattha MU, Khan I et al (2020) Heat stress in cultivated plants: nature, impact, mechanisms, and mitigation strategies—a review. Plant Biosyst - An Int J Deal with all Asp Plant Biol 3:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/11263504.2020.1727987
Jahan MS, Guo S, Baloch AR et al (2020) Melatonin alleviates nickel phytotoxicity by improving photosynthesis, secondary metabolism and oxidative stress tolerance in tomato seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 197:110593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110593
Jahan MS, Shu S, Wang Y et al (2019) Melatonin alleviates heat-induced damage of tomato seedlings by balancing redox homeostasis and modulating polyamine and nitric oxide biosynthesis. BMC Plant Biol 19:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1992-7
Jannatizadeh A (2019) Exogenous melatonin applying confers chilling tolerance in pomegranate fruit during cold storage. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 246:544–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.11.027
Kamiab F (2020) Exogenous melatonin mitigates the salinity damages and improves the growth of pistachio under salinity stress. J Plant Nutr 43:1468–1484. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2020.1730898
Kosińska A, Diering S, Prim D et al (2013) Phenolic compounds profile of strawberry fruits of Charlotte cultivar. J Berry Res 3:15–23. https://doi.org/10.3233/JBR-130043
Krantev A, Yordanova R, Janda T et al (2008) Treatment with salicylic acid decreases the effect of cadmium on photosynthesis in maize plants. J Plant Physiol 165:920–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2006.11.014
Ledesma NA, Kawabata S (2016) Responses of two strawberry cultivars to severe high temperature stress at different flower development stages. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 211:319–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2016.09.007
Li SL, Li ZG, Yang LT et al (2018) Differential effects of cold Stress on chloroplasts structures and photosynthetic characteristics in cold-sensitive and cold-tolerant cultivars of sugarcane. Sugar Tech 20:11–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-017-0527-5
Liao W-Y, Lin L-F, Jheng J-L et al (2016) Identification of heat shock transcription factor genes involved in thermotolerance of octoploid cultivated strawberry. Int J Mol Sci 17:2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122130
Liu T, Zhu L, Wang J et al (2015) The genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride in soil on Vicia faba seedlings. J Hazard Mater 285:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.11.028
Liu X, Zhang S, Shanquan X, Christie P (2007) Combined toxicity of cadmium and arsenate to wheat seedlings and plant uptake and antioxidative enzyme responses to cadmium and arsenate co-contamination. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 68:305–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.11.001
Loreto F, Velikova V (2001) Isoprene produced by leaves protects the photosynthetic apparatus against ozone damage, quenches ozone products, and reduces lipid peroxidation of cellular membranes. Plant Physiol 127:1781–1787. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.010497
Luis Castañares J, Alberto Bouzo C (2019) Effect of exogenous melatonin on seed germination and seedling growth in melon (Cucumis melo L.) under salt stress. Hortic Plant J 5:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hpj.2019.01.002
McNellie JP, Chen J, Li X, Yu J (2018) Genetic mapping of foliar and tassel heat stress tolerance in maize. Crop Sci 58:2484–2493. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2018.05.0291
Medina AL, Haas LIR, Chaves FC et al (2011) Araçá (Psidium cattleianum Sabine) fruit extracts with antioxidant and antimicrobial activities and antiproliferative effect on human cancer cells. Food Chem 128:916–922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.03.119
Mirshekari A, Madani B, Yahia EM et al (2020) Postharvest melatonin treatment reduces chilling injury in sapota fruit. J Sci Food Agric 100:1897–1903. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10198
Muneer S, Park YG, Kim S, Jeong BR (2017) Foliar or subirrigation silicon supply mitigates high temperature stress in strawberry by maintaining photosynthetic and stress-responsive proteins. J Plant Growth Regul 36:836–845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-017-9687-5
Naghizadeh M, Kabiri R, Hatami A et al (2019) Exogenous application of melatonin mitigates the adverse effects of drought stress on morpho-physiological traits and secondary metabolites in Moldavian balm (Dracocephalum moldavica). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 25:881–894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-00674-4
Nievola CC, Carvalho CP, Carvalho V, Rodrigues E (2017) Rapid responses of plants to temperature changes. Temperature 4:371–405. https://doi.org/10.1080/23328940.2017.1377812
Pick T, Jaskiewicz M, Peterhänsel C, Conrath U (2012) Heat shock factor HsfB1 primes gene transcription and systemic acquired resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 159:52–55. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.191841
Priya M, Dhanker OP, Siddique KHM et al (2019) Drought and heat stress-related proteins: an update about their functional relevance in imparting stress tolerance in agricultural crops. Theor Appl Genet 132:1607–1638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03331-2
Qian Y, Cao L, Zhang Q et al (2020) SMRT and Illumina RNA sequencing reveal novel insights into the heat stress response and crosstalk with leaf senescence in tall fescue. BMC Plant Biol 20:366. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02572-4
Qian Y, Ren Q, Zhang J, Chen L (2019) Transcriptomic analysis of the maize (Zea mays L.) inbred line B73 response to heat stress at the seedling stage. Gene 692:68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.12.062
Qiao Y, Yin L, Wang B et al (2019) Melatonin promotes plant growth by increasing nitrogen uptake and assimilation under nitrogen deficient condition in winter wheat. Plant Physiol Biochem 139:342–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.03.037
Rady MM, Kuşvuran A, Alharby HF et al (2019) Pretreatment with proline or an organic bio-stimulant induces salt tolerance in wheat plants by improving antioxidant redox state and enzymatic activities and reducing the oxidative stress. J Plant Growth Regul 38:449–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-018-9860-5
Rai KK, Pandey N, Rai SP (2020) Salicylic acid and nitric oxide signaling in plant heat stress. Physiol Plant 168:241–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12958
Sable A, Rai KM, Choudhary A et al (2018) Inhibition of heat shock proteins HSP90 and HSP70 induce oxidative stress, suppressing cotton fiber development. Sci Rep 8:3620. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21866-0
Shafeiee M, Ehsanzadeh P (2019) Physiological and biochemical mechanisms of salinity tolerance in several fennel genotypes: Existence of clearly-expressed genotypic variations. Ind Crops Prod 132:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.02.042
Shi H, Tan D-X, Reiter RJ et al (2015) Melatonin induces class A1 heat-shock factors (HSFA1s) and their possible involvement of thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. J Pineal Res 58:335–342. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12219
Tang Q, Li C, Ge Y et al (2020) Exogenous application of melatonin maintains storage quality of jujubes by enhancing anti-oxidative ability and suppressing the activity of cell wall-degrading enzymes. LWT 127:109431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109431
Tiwari YK, Yadav SK (2019) High temperature stress tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.): Physiological and molecular mechanisms. J Plant Biol 62:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-018-0350-x
Vaghefi SA, Keykhai M, Jahanbakhshi F et al (2019) The future of extreme climate in Iran. Sci Rep 9:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-38071-8
Wang X, Zhang H, Xie Q et al (2020) SlSNAT interacts with HSP40, a molecular chaperone, to regulate melatonin biosynthesis and promote thermotolerance in tomato. Plant Cell Physiol 61:909–921. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcaa018
Wassie M, Zhang W, Zhang Q et al (2020) Exogenous salicylic acid ameliorates heat stress-induced damages and improves growth and photosynthetic efficiency in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 191:110206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110206
Xi Y, Han X, Zhang Z et al (2020) Exogenous phosphite application alleviates the adverse effects of heat stress and improves thermotolerance of potato (Solanum tuberosum L) seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190:110048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110048
Zahedi SM, Hosseini MS, Abadía J, Marjani M (2020) Melatonin foliar sprays elicit salinity stress tolerance and enhance fruit yield and quality in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.). Plant Physiol Biochem 149:313–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.021
Zhang J, Shi Y, Zhang X et al (2017) Melatonin suppression of heat-induced leaf senescence involves changes in abscisic acid and cytokinin biosynthesis and signaling pathways in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Environ Exp Bot 138:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2017.02.012
Zhao DQ, Li TT, Hao ZJ et al (2019) Exogenous trehalose confers high temperature stress tolerance to herbaceous peony by enhancing antioxidant systems, activating photosynthesis, and protecting cell structure. Cell Stress Chaperones 24:247–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-018-00961-1
Zhou ZS, Guo K, Elbaz AA, Yang ZM (2009) Salicylic acid alleviates mercury toxicity by preventing oxidative stress in roots of Medicago sativa. Environ Exp Bot 65:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2008.06.001
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Afazel for valuable technical helps with this experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HM carried out the experiment and performed the data analyses and reviewed the manuscript. BB was the project supervisor, designed the research, provided all the technical support during the laboratory work, and wrote the manuscript. MG helped in the design of the experiment and reviewed the manuscript. MT helped in the design of the experiment, performed gene expression analyses, and reviewed the manuscript. SK helped in the design of the experiment and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Shuxin Ren.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manafi, H., Baninasab, B., Gholami, M. et al. Exogenous Melatonin Alleviates Heat‐Induced Oxidative Damage in Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch. cv. Ventana) Plant. J Plant Growth Regul 41, 52–64 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10279-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10279-x