Abstract
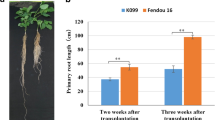
The complexity of sweetpotato genome, including hexaploidy and heterozygosity, has hindered genetic studies on agronomically important traits such as storage root formation and thickening. Ipomoea trifida (H. B. K.) G. Don. (2n = 2x = 30) is closely related to and cross-compatible with sweetpotato. The diploid I. trifida has been developed as a model plant for sweetpotato genetic research, due to its low ploidy and simple genetic background. In order to reveal the molecular mechanisms underlying storage root development in sweetpotato, F1 mapping population derived from diploid I. trifida was screened for root diameter by genotyping-by-sequencing method. A total of 11,555 raw polymorphic SNPs were identified, in which 8454 SNPs can be used in this F1 population. The SNP genotyping data was utilized to construct the genetic linkage map of I. trifida. The maternal and paternal linkage maps were produced, and 904 maternal and 2034 paternal markers resulted in 13 and 15 LGs respectively. The total length of the maternal maps covered 842.34 cM, while the paternal maps spanned 1540.98 cM. The integrated genetic map consisted of 2892 SNPs (average of 193 markers/linkage group) on 15 linkage groups (LGs) covering 1550.22 cM of the whole genome at an average inter marker distance of 0.55 cM. By using the phenotypic data obtained in this study, three significant QTL were detected for root diameter. These QTL were distributed among three LGs at three independent positions, and each QTL explained significant amount of phenotypic trait variation ranged from 6.1 to 12.0%. The qRD-2 QTL explained 12.0% of the phenotypic variation. This study results will assist in the map-based cloning of genes controlling storage root-related traits and further helps to reveal the genetic basis of root development in sweetpotato.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin DF, Huáman Z (1996) A synopsis of ipomoea (Convolvulaceae) in the Americas. Taxon 64(3):3–38
Balsalobre TWA, Pereira GDS, Margarido GRA, Gazaffi R, Barreto FZ, Anoni CO, Cardososilva CB, Costa EA, Mancini MC, Hoffmann HP (2017) GBS-based single dosage markers for linkage and QTL mapping allow gene mining for yield-related traits in sugarcane. BMC Genomics 18(1):72
Cervantes-Flores JC (2008) development of a genetic linkage map and identification of homologous linkage group in sweetpotato using multiple-dose AFLP markers. Mol Breed 21:511–532
Cervantes-Flores JC, Sosinski B, Pecota KV, Mwanga ROM, Catignani GL, Truong VD, Watkins RH, Ulmer MR, Yencho GC (2011) Identification of quantitative trait loci for dry-matter, starch, and b-carotene content in sweetpotato. Mol Breed 28:201–216
Diaz J, Schmiediche P, Austin DF (1996) Polygon of crossability between eleven species of Ipomoea: section Batatas (Convolvulaceae). Euphytica 88(3):189–200
Elshire RJ, Glaubitz JC, Sun Q, Poland JA, Kawamoto K, Buckler ES, Mitchell SE (2011) A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE 6(5):e19379. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019379
Firon N, LaBonte D, Villordon A, McGregor C, Kfir Y, Pressman E (2009). Botany and Physiology: Storage Root Formation and Development. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-9475-0_3
Gemenet DC, Pereira GDS, Boeck BD, Wood JC, Mollinari M, Olukolu BA, Diaz F, Mosquera V, Ssali RT, David M, Kitavi MN, Burgos G, Felde TZ, Ghislain M, Carey E, Swanckaert J, Coin LJM, Fei Z, Hamilton JP, Yada B, Yencho GC, Zeng ZB, Mwanga ROM, Khan A, Gruneberg WJ, Buell CR (2020) Quantitative trait loci and differential gene expressionanalyses reveal the genetic basis for negatively associated β-carotene and starch content inhexaploid sweetpotato [Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.]. Theor Appl Genet 133(1):23–36
Glaubitz JC, Casstevens TM, Lu F, Harriman J, Elshire RJ, Sun Q, Buckler ES (2014) TASSEL-GBS: a high capacity genotyping by sequencing analysis pipeline. PLoS ONE 9(2):e90346
Hirakawa H, Okada Y, Tabuchi H, Shirasawa K, Watanabe A, Tsuruoka H, Minami C, Nakayama S, Sasamoto S, Kohara M et al (2015) Survey of genome sequences in a wild sweet potato, Ipomoea trifida (HBK) G. Don. DNA Res 2(2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsv002
Huang JC, Sun M (2000) Genetic diversity and relationships of sweetpotato and its wild relatives in Ipomoea series Batatas (Convolvulaceae) as revealed by inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) and restriction analysis of chloroplast DNA. Theor Appl Genet 100(7):1050–1060
Kosambi DD (1943) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Hum Genet 12(1):172–175. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-1809.1943.tb02321.x
Kosambi DD (2011) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugenics. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-1809.1943.tb02321.x
Lai GR, Zhang J, Liu H, Dong XM, Lai JS, Huang YQ, Chen JT, Guo JJ (2017) Construction of high density genetic map via GBS technology and QTL mapping for nutritional quality traits in maize (Zea mays). J Agric Biotechnol 25(9):1400–1410. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2017.09.003
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25(16):2078–2079
Li AX, Liu QC, Wang QM, Zhang LM, Zhai H, Liu SZ (2010) Establishment of molecular linkage maps using SRAP markers in sweetpotato. Acta Agron Sin 36(8):1286–1295
Li H, Zhao N, Yu XX, Liu YX, Zhai H, He SZ, Li Q, Ma DF, Liu QC (2014) Identification of Qtls for storage root yield in sweetpotato. Sci Hortic 170(7):182–188
Li HH, Vikram P, Singh RP et al (2015) A high density GBS map of bread wheat and its application for dissecting complex disease resistance traits. BMC Genomics 16:216. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1424-5
McCormick FA (1916) Notes on the Anatomy of the Young Tuber of Ipomoea batatas Lam. Bot Gazette 61(5):388–398
Mckenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20(9):1297–1303
Nakayama H, Tanaka M, Takahata Y (2010) An AFLP-based genetic linkage map of Ipomoea trifida (H.B.K.) G. Don., a diploid relative of sweetpotato, I. batatas (L.) Lam. Trop Agric Dev 54(1):9–16
Ooijen JWV (2006) JoinMap® 4.0: software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental population. Wageningen, Kyazma BV
Ozias-Akins P (1994) Nuclear DNA content and ploidy levels in genus Ipomoea. Jamsochorticsci 119(1):110–115
Ponniah SK, Thimmapuram J, Bhide K, Kalavacharla VK, Manoharan M (2017) Comparative analysis of the root transcriptomes of cultivated sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas [L.] Lam) and its wild ancestor (Ipomoea trifida [Kunth] G. Don). BMC Plant Biol 17(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0950-x
Qi H, Wang N, Qiao W, Xu Q, Zhou H, Shi J, Yan G, Huang Q (2017) Construction of a high-density genetic map using genotyping by sequencing (GBS) for quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis of three plant morphological traits in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Euphytica 213(4):83
Rodriguez-Bonilla L, Cuevas HE, Montero-Rojas M, Bird-Pico F, Luciano-Rosario D, Siritunga D (2014) Assessment of genetic diversity of sweet potato in Puerto Rico. PLoS ONE 9(12):e116184
Tanaka M (2016) Recent progress in molecular studies on storage root formation in sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas). Jpn Agric Res Q 50(4):293–299
Tanaka M, Takahata Y, Nakatani M (2005) Analysis of genes developmentally regulated during storage root formation of sweet potato. J Plant Physiol 162(1):91–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2004.06.003
Tsuchiya T (2014) Self-incompatibility system of Ipomoea trifida, a wild-type sweet potato. In: Sawada H, Inoue N, Iwano M (eds) Sexual reproduction in animals and plants. Springer, Tokyo, pp 305–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-54589-7_25
Villordon AQ, Idit Ginzberg, Nurit Firon (2014) Root architecture and root and tuber crop productivity. Trends Plant Sci 19(7):419–425
Wallace JG, Mitchell ShE (2017) Genotyping-by-Sequencing. Curr Protocols Plant Biol 2(1):64–77
Wu Sh, Lau KH, Cao QH, Hamilton JP, Sun HH, Zhou ChX, Eserman L, Gemenet DC, Olukolu BA, Wang HY, Crisovan E, Godden GT, Jiao J, Wang X, Mercy K, Manrique-Carpintero N, Vaillancourt B, Wiegert-Rininger K, Yang XS, Bao K, Schaff J, Kreuze J, Gruneberg W, Khan A, Ghislain M, Ma DF, Jiang JM, Mwanga R, Leebens-Mack J, Coin L, Yencho C, Robin BR, Fei ZhJ (2018) Genome sequences of two diploid wild relatives of cultivated sweetpotato reveal targets for genetic improvement. Nature Commun 4580. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06983-8
Yang J, Moeinzadeh M, Kuhl H, Helmuth J, Xiao P, Haas S, Liu G, Zheng J, Sun Zh, Fan W, Deng G, Wang H, Hu F, Zhao Sh, Fernie A, Boerno S, Timmermann B, Zhang P, Vingron M (2017) Haplotype-resolved sweet potato genome traces back itshexaploidization history. Nat Plants 3:696–703
Yu M, Coyne CJ, Grusak MA, Mazourek M, Peng C, Main D, Mcgee RJ (2017) Genome-wide SNP identification, linkage map construction and QTL mapping for seed mineral concentrations and contents in pea (Pisum sativum L.). BMC Plant Biol 17(1):43
Wilson LA, Lowe SB (1973) The anatomy of the root system in West Indian sweet potato (Ipomoea Batatas (L.) Lam.) Cultivars. Ann Bot 37(151):633–643
Zhang GY, Luo XF, Lai YC, Yao BR, Lin GH, Huang SY (2009) Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with yield-related traits in the sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas). Bot Stud 50(1):43–55
Zhao N, Yu XX, Qin J, Li H, Li H, Hu J, Zhai H, He SZ, Liu QC (2013) A genetic linkage map based on AFLP and SSR markers and mapping of QTL for dry-matter content in sweetpotato. Mol Breed 32(4):807–820
Zhou Z, Zhang C, Yu Z, Hao Z, Wang Z, Xing Z, Hong D, Li M, Zhang D, Yong H (2016) Genetic dissection of maize plant architecture with an ultra-high density bin map based on recombinant inbred lines. BMC Genomics 17(1):178
Acknowledgements
Supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD1000705, 2018YFD1000700), the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-10-B1), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (31461143017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical standards
The authors declare that all studies were carried out in accordance with good laboratory practice rules and no national and international regulations and laws were violated.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, D., Wu, S., Dai, X. et al. QTL analysis of root diameter in a wild diploid relative of sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) using a SNP-based genetic linkage map generated by genotyping-by-sequencing. Genet Resour Crop Evol 68, 1375–1388 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-01068-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-01068-2