Abstract
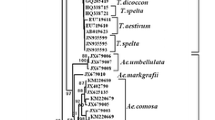
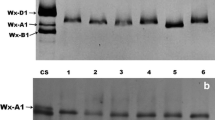
In wheat endosperm, the granule-bound starch synthase or the Waxy protein is the sole enzyme for amylose synthesis and thus determines the amylose content and ratio of amylose/amylopectin. The gene encoding this enzyme has been named as Waxy (Wx) gene. In this study, eight novel Wx alleles from four diploid species belonging to the three Triticeae genera, namely Eremopyrum, Psathyrostachys, and Henrardia have been isolated and characterized. The genetic diversity of these genes was evaluated at the molecular sequence level, and the nucleotides of these Wx genes were also compared with their homologs from wheat and its relatives. The Wx alleles of P. juncea (Fischer) Nevski, E. triticeum (Gaertn.) Nevski, E. bonaepartis (Sprengel) Nevsk, and H. persica (Boiss.) C. E. Hubbard showed obvious differences from the homologous alleles known from wheat and Aegilops as well as Taeniatherum in terms of nucleotide composition, intron length, isoelectric point, and molecular mass. Phylogenetic analysis suggested that the Wx alleles of these four species distantly related to wheat were more closely related to those of Hordeum and Secale than the other species. These Wx alleles are novel candidates with potential application in wheat breeding for modified starch properties.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baden C, Bothmer R, Flink J, Jacobsen N (1989) Intergeneric hybridization between Psathyrostachys and Hordeum. Nord J Bot 9:333–342. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1756-1051.1989.tb01008.x
Baden C (1991) A taxonomic revision of Psathyrostachys (Poaceae). Nord J Bot 11:3–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1756-1051.1991.tb01790.x
Chen N, Chen WJ, Yan H, Wang Y, Kang HY, Zhang HQ, Zhou YH, Sun GL, Sha LN, Fan X (2020) Evolutionary patterns of plastome uncover diploid-polyploid maternal relationships in Triticeae. Mol Phylogenet Evol 149:106838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2020.106838
Choi Y, Chan AP (2015) PROVEAN web server: a tool to predict the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. Bioinformatics 31:2745–2747
Dai SF, Jiang JQ, Jia YN, Xue XF, Liu DC, Wei YM, Zheng YL, Yan ZH (2016) Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of Wx genes from three Taeniatherum diploid species. Biol Plantarum 60:505–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-016-0609-3
Dai SF, Pu ZJ, Liu DC, Wei YM, Zheng YL, Hu XK, Yan ZH (2013) Characterization of novel HMW-GS in two diploid species of Eremopyrum. Gene 519:55–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.01.052
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Dvořák J, Akhunov ED (2005) Tempos of gene locus deletions and duplications and their relationship to recombination rate during diploid and polyploid evolution in the Aegilops-Triticum alliance. Genetics 171:323–332. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.105.041632
Frederiksen S (1991) Taxonomic studies in Eremopyrum (Poaceae). Nord J Bot 11:271–285. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1756-1051.1991.tb01405.x
Frederiksen S (1993) Taxonomic studies in some annual genera of the Triticeae (Poaceae). Nord J Bot 13:481–493. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1756-1051.1993.tb00086.x
Frederiksen S, Von Bothmer R (1989) Intergeneric hybridization between Taeniatherum and different genera of Triticeae, Poaceae. Nordic J Bot 9:229–240. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1756-1051.1989.tb00994.x
Gu YQ, Anderson OD, Londeore CF, Kong X, Chibbar RN, Lazo GR (2003) Structural organization of the barley D-hordein locus in comparison with its orthologous regions of wheat genomes. Genome 46:1084–1097. https://doi.org/10.1139/g03-071
Guzmán C, Alvarez JB (2016) Wheat waxy proteins: polymorphism, molecular characterization and effects on starch properties. Theor Appl Genet 129:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2595-9
Guzmán C, Caballero L, Martín LM, Alvarez JB (2012) Waxy genes from spelt wheat: new alleles for modern wheat breeding and new phylogenetic inferences about the origin of this species. Ann Bot 110:1161–1171. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcs201
Hayakawa K, Tanaka K, Nakamura T, Endo S, Hoshino T (2004) End use quality of waxy wheat flour in various grain-based foods. Cereal Chem 81:666–672. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM.2004.81.5.666
Hu XK, Dai SF, Ouellet T, Balcerzak M, Rocheleau H, Khanizadeh S, Pu ZJ, Yan ZH (2018) Characterization of novel D-hordeins from Psathyrostachys juncea. Biol Plantarum 62:369–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-018-0775-6
Huang YC, Lai HM (2010) Noodle quality affected by different cereal starches. J Food Eng 97:135–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2009.10.002
James MG, Denyer K, Myers AM (2003) Starch synthesis in the cereal endosperm. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-5266(03)00042-6
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187
Luo M, Ding JJ, Li Y, Tang HP, Qi PF, Ma J, Wang JR, Chen GY, Pu ZE, Li W, Li ZY, Harwood W, Lan XJ, Deng M, Lu ZX, Wei YM, Zheng YL, Jiang QT (2019) A single-base change at a splice site in Wx-A1 caused incorrect RNA splicing and gene inactivation in a wheat EMS mutant line. Theor Appl Genet 132:2097–2109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03340-1
Mason-Gamer RJ, Weil CF, Kellogg EA (1998) Granule-bound starch synthase: structure, function, and phylogenetic utility. Mol Biol Evol 15:1658–1673. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a025893
Meng M, Gao X, Han LJ, Li XY, Wu D, Li HZ, Chen QJ (2014) Correlation analysis between starch properties and single nucleotide polymorphisms of waxy genes in common rye (Secale cereale L.). Genet Mol Res 13:2574–2589
Miura H, Wickramasinghe MHA, Subasinghe RM, Araki E, Komae K (2002) Development of near-isogenic lines of wheat carrying different null Wx alleles and their starch properties. Euphytica 123:353–359. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015042322687
Murai J, Taira T, Ohta D (1999) Isolation and characterization of the three waxy genes encoding the granule-bound starch synthase in hexaploid wheat. Gene 234:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00178-X
Nakamura T, Yamamori M, Hirano H, Hidaka S (1995) Production of waxy (amylose-free) wheats. Mol Gen Genet 248:253–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02191591
Niu M, Hou GG, Zhao SM (2017) Dough rheological properties and noodle-making performance of non-waxy and waxy whole-wheat flour blends. J Cereal Sci 75:261–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2017.05.002
Ørgaard M, Heslop-Harrison JS (1994) Investigations of genome relationships between Leymus, Psathyrostachys and Hordeum inferred by genomic DNA: DNA in situ Hybridization. Ann Bot 73:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.1994.1023
Ortega R, Alvarez JB, Guzmán C (2014) Characterization of the Wx gene in diploid Aegilops species and its potential use in wheat breeding. Genet Resour Crop Evol 61:369–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-013-0040-y
Pistón F, Shewry PR, Barro F (2007) D hordeins of Hordeum chilense: a novel source of variation for improvement of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 115:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-007-0542-0
Ram S, Mishra B (2008) Biochemical basis and molecular genetics of processing and nutritional quality traits of wheat. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 17:111–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03263272
Regina A, Bird A, Topping D, Bowden S, Freeman J, Barsby T, Kosar-Hashemi B, Li Z, Sadequr R, Morell M (2006) High-amylose wheat generated by RNA interference improves indices of large-bowel health in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:3546–3551. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0510737103
Šárka E, Dvořáček V (2017) Waxy starch as a perspective raw material (a review). Food Hydrocolloids 69:402–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.03.001
Tajima F (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123:585–595
Xia J, Zhu D, Wang RM, Cui Y, Yan YM (2018) Crop resistant starch and genetic improvement: a review of recent advances. Theor Appl Genet 131:2495–2511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3221-4
Yamamori M, Nakamura T, Endo TR, Nagamine T (1994) Waxy protein deficiency and chromosomal location of coding genes in common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 89:179–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225138
Yan L, Bhave M (2001) Characterization of waxy proteins and waxy genes of Triticum timopheevii and T. zhukovskyi and implications for evolution of wheat. Genome 44:582–588. https://doi.org/10.1139/g01-036
Zeng M, Morris CF, Batey IL, Wrigley CW (1997) Sources of variation for starch gelatinization, pasting, and gelation properties in wheat. Cereal Chem 74:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM.1997.74.1.63
Zhang LL, Chen H, Luo M, Zhang XW, Deng M, Ma J, Qi PF, Wang JR, Chen GY, Liu YX, Pu ZE, Li W, Lan XJ, Wei YM, Zheng YL, Jiang QT (2017) Transposon insertion resulted in the silencing of Wx-B1n in Chinese wheat landraces. Theor Appl Genet 130:1321–1330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2878-4
Acknowledgements
We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2016YFD0100502, 2017YFD0100903), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31771783, U1403185), the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Nos. 2018HH0113 and 2018HH0130), and the Key Research and Development Program of Sichuan Province (2018NZDZX0002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.H. Y coordinated the project, conceived and designed experiments. S.F. D and J.R. L conducted the experiments, and edits the manuscript. J.W. H, W.J. Y, Q.Y. L, Y.Y. Z, Z.P. S analyzed the data, J. L, and G. L planted the materials, G.Y. C and Y.M. W provide some advice on data analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, S., Li, J., Huang, J. et al. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of Wx genes of four diploid species of the Triticeae genera Eremopyrum, Psathyrostachys, and Henrardia. Genet Resour Crop Evol 68, 1389–1400 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-01069-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-01069-1