Abstract
Background
Endoscopic aqueductoplasty with aqueductal stenting is an effective surgical procedure for the treatment of isolated fourth ventricle (IFV). Due to the rarity of the underlying pathology, it can be considered a rare procedure that can be performed with different surgical techniques and approaches.
Objectives
To assess long-term functioning of permanent aqueductal stents implanted in children affected by hydrocephalus and IFV and to describe some variations of the same procedure.
Methods
We reviewed retrospectively all the patients presenting at our institution in the years 1999–2019 for symptoms of isolated fourth ventricle who underwent a surgical procedure of endoscopic aqueductoplasty and/or aqueductal stent. Surgical reports, radiological images, and surgical videos were retrospectively analyzed.
Results
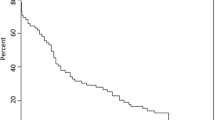
Thirty-three patients with symptomatic isolated fourth ventricle (IFV) underwent fifty (50) neuroendoscopic procedures in the period observed. The median age of the patients at the time of first surgery was 7 months, with 22 premature babies. In twenty-nine patients (87.8%), a precoronal approach was performed, while four patients received a suboccipital burr hole. Ten patients were never reoperated since. Twenty-three patients underwent further surgeries: a new aqueductoplasty with aqueductal stent was performed in 13 cases. The remaining 10 patients required a combination of other procedures for management of hydrocephalus. Long-term follow-up showed a permanent stent functioning rate of 87% at 2 years and 73% at 4 years, remaining stable afterwards at very long term (20 years).
Conclusion
Endoscopic aqueductoplasty and stenting is a reliable procedure in the long-term management of isolated fourth ventricle.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antes S, Salah M, Linsler S, Tschan CA, Breuskin D, Oertel J (2016) Aqueductal stenting with an intra-catheter endoscope--a technical note. Childs Nerv Syst 32:359–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2902-4
Cinalli G, Spennato P, Savarese L, Ruggiero C, Aliberti F, Cuomo L, Cianciulli E, Maggi G (2006) Endoscopic aqueductoplasty and placement of a stent in the cerebral aqueduct in the management of isolated fourth ventricle in children. J Neurosurg 104:21–27. https://doi.org/10.3171/ped.2006.104.1.21
Coleman CC, Troland CE (1948) Congenital atresia of the foramina of Luschka and Magendie with report of two cases of surgical cure. J Neurosurg 5:84–88. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1948.5.1.0084
Dong X, Zheng J, Xiao Q, Huang Y, Liu W, Chen G (2019) Surgical techniques and long-term outcomes of flexible neuroendoscopic aqueductoplasty and stenting in infants with obstructive hydrocephalus: a single-center study. World Neurosurg 130:98–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.06.069
Erşahin Y (2006) Endoscopic aqueductoplasty with and without stent. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 49:124–125. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-932182
Fallah A, Wang AC, Weil AG, Ibrahim GM, Mansouri A, Bhatia S (2016) Predictors of outcome following cerebral aqueductoplasty: an individual participant data meta-analysis. Neurosurgery 78:285–296. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000001024
Foltz EL, DeFeo DR (1980) Double compartment hydrocephalus--a new clinical entity. Neurosurgery 7:551–559. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-198012000-00002
Fritsch MJ, Kienke S, Manwaring KH, Mehdorn HM (2004) Endoscopic aqueductoplasty and interventriculostomy for the treatment of isolated fourth ventricle in children. Neurosurgery 55:372–377. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000130444.71677.bc
Fritsch MJ, Kienke S, Mehdorn HM (2004) Endoscopic aqueductoplasty: stent or not to stent. Childs Nerv Syst 20:137–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-003-0860-8
Gallo P, Szathmari A, Simon E, Ricci-Franchi A-C, Rousselle C, Hermier M, Mottolese C (2012) The endoscopic trans-fourth ventricle aqueductoplasty and stent placement for the treatment of trapped fourth ventricle: long-term results in a series of 18 consecutive patients. Neurol India 60:271–277. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.98507
Guida L, Beccaria K, Benichi S, Chivet A, de Saint DT, James S, Paternoster G, Zerah M, Puget S, Blauwblomme T (2020) Endoscopic aqueductal stenting in the management of pediatric hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg Pediatr 26:346–352. https://doi.org/10.3171/2020.4.PEDS20144
Harter DH (2004) Management strategies for treatment of the trapped fourth ventricle. Childs Nerv Syst 20:710–716. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-004-1004-5
Hubbard JL, Houser OW, Laws ER (1987) Trapped fourth ventricle in an adult: radiographic findings and surgical treatment. Surg Neurol 28:301–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/0090-3019(87)90310-7
Lapras C, Bret P, Patet JD, Huppert J, Honorato D (1986) Hydrocephalus and aqueduct stenosis. Direct surgical treatment by interventriculostomy (aqueduct canulation). J Neurosurg Sci 30:47–53
Marx S, Baldauf J, Matthes M, Gaab MR, Schroeder HWS (2019) Long-term reliability of neuroendoscopic aqueductoplasty in idiopathic aqueductal stenosis-related hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 85:91–95. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyy219
Mohanty A, Manwaring K (2018) Isolated fourth ventricle: to shunt or stent. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown) 14:483–493. https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opx136
Ogiwara H, Morota N (2013) Endoscopic transaqueductal or interventricular stent placement for the treatment of isolated fourth ventricle and pre-isolated fourth ventricle. Childs Nerv Syst 29:1299–1303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2112-x
Oi S, Abbott R (2004) Loculated ventricles and isolated compartments in hydrocephalus: their pathophysiology and the efficacy of neuroendoscopic surgery. Neurosurg Clin N Am 15:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1042-3680(03)00072-X
Peraio S, Amen MM, Ali NM, Zaher A, Mohamed Taha AN, Tamburrini G (2018) Endoscopic management of pediatric complex hydrocephalus. World Neurosurg 119:e482–e490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.07.187
Raouf A, Zidan I (2013) Suboccipital endoscopic management of the entrapped fourth ventricle: technical note. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 155:1957–1963. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1843-5
Spennato P, Mirone G, Ruggiero C, Parlato RS, Cinalli G (2018) Septostomy and other advanced procedures. In: Cinalli G, Ozek M, Sainte-Rose C (eds) Pediatric Hydrocephalus. Springer, Cham
Thakker R, Mohanty A (2019) Reversible progressive multiple cranial nerve paresis in the isolated fourth ventricle following placement of fourth ventricle shunt: case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Neurosurg 54:405–410. https://doi.org/10.1159/000503088
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imperato, A., Almaguer Ascencio, L.M., Ruggiero, C. et al. Endoscopic aqueductoplasty and stenting in the treatment of isolated fourth ventricle in children: 20-year institutional experience. Childs Nerv Syst 37, 1587–1596 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-05024-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-05024-4