Abstract
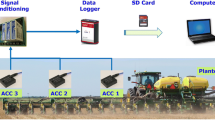
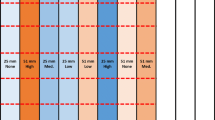
Uniform plant stand, herein understood as an outcome of plant spacing and seeding-depth uniformity, requires proper selection of downforce control across varying field conditions, especially when planting at faster ground speeds. Thus, objectives of this study were (1) to assess the effect of ground speed and downforce settings on plant spacing and seeding depth, and (2) evaluate the relationship of planting speed and row-unit vibration. A 12-row planter was used to plant corn on no-till and strip-tilled fields. Treatment factors were downforce setting with two levels: 620 and 980 N, and ground speed with four levels: 7.2, 9.7, 12.1, and 16.1 km h−1. The planter was programmed to plant corn at 51 mm seeding depth at a seeding rate of 84,000 seeds ha−1, equivalent to a theoretical plant spacing of 178 mm. No significant downforce effect was observed at either field on plant spacing, although the low downforce setting resulted in lower plant spacing variability. Higher variability in spacing was observed with increasing ground speed. Target seeding depth on the no-till field was achieved with high downforce and slower ground speed, while deeper than the target seeding depth on the strip-tilled field was observed with a high downforce setting. Finally, both downforce settings revealed increasing row-unit acceleration as ground speed increased.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badua, S. A., Sharda, A., Flippo, D., & Ciampitti, I. (2018). Real-time gauge wheel load variability of a row-crop planter during field operation. Transactions of the ASABE, 61(5), 1517–1527. https://doi.org/10.13031/trans.12511.
Benson, G. O. (1990). Corn replant decisions: A review. Journal of Production Agriculture, 3, 180–184. https://doi.org/10.2134/jpa1990.0180.
Brandelero, E. M., Adami, P. F., Modolo, A. J., Baesso, M. M., & Fabian, A. J. (2015). Seeder performance under different speeds and its relation to soybean cultivars yield. Journal of Agronomy, 14(3), 139–145.
Brune, P. F., Ryan, B. J., Technow, F., & Myers, D. B. (2018). Relating planter downforce and soil strength. Soil and Tillage Research, 184, 243–252.
Buchholz, D. D., Palm, E. W., Thomas, G., & Pfost, D. L. (1993). No-till planting systems. University of Missouri Extension, USA. Retrieved 24/11/2020 from https://extension.missouri.edu/publications/g4080.
Carlson, G., Doerge, T., & Clay, D. (2002). Estimating corn yield losses from unevenly spaced planting. Site-specific Management guidelines, SSMG-37. Retrieved 24/11/2020 from http://www.nue.okstate.edu/CORN/Corn_YieldLoss.pdf.
Da Silva, R. P., Corá, J. E., Filho, A. C., Lopes, A., & Furlani, C. E. A. (2004). Effect of press wheels submitted to vertical loads in depths of sowing on corn crop development. Engenharia Agrícola, 24(2), 396–404. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-69162004000200019.
Da Silveira, J. C. M., Fernandes, H. C., Modolo, A. J., de Lima Silva, S., & Trogello, E. (2011). Furrow depth, soil disturbance area and draft force of a seeder-fertilizer at different seeding speeds. Revista Ceres, 58(3), 293–298.
Duncan, S., Fjell, D., & Vanderlip, R. (2007). Growth and development. Corn production handbook. Kansas State University, USA. Retrieved 27/02/2020 from https://bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/c560.pdf.
Egli, D. B., & Rucker, M. (2012). Seed vigor and the uniformity of emergence of corn seedlings. Crop Science, 52(6), 2774–2782.
Elmore, R., Al-Kaisi, M., & Hanna, M. (2014). Corn seeding depth: Back to the basics. Agronomy News, 5(1), 1–3.
Fallahi, S., & Raoufat, M. H. (2008). Row-crop planter attachments in a conservation tillage system: A comparative study. Soil and Tillage Research, 98(1), 27–34.
Fancelli, A. L. (2000). Crop physiology and basic aspects of management for high yield. In I. Santini & A. L. Fancelli (Eds.), Maize crop: management strategies for the south region (pp. 103–106). Guarapuava, Brazil: Fundação Agrária de Pesquisa Agro-Pecuaria.
Fulton, J., Poncet, A., McDonald, T., Knappenberger, T., Shaw, J., Bridges, R., et al. (2015). Considerations for site-specific implementation of active downforce and seeding depth technologies on row-crop planters. Downforce by depth settings influence seeding depth. In: VDI-Berichte Nr. 2251, LAND.TECHNIK AgEng 2015, Innovations in agricultural engineering for efficient farming, agricultural engineering, Düsseldorf, Germany: VDI Verlag GmbH, pp 139–145.
Grassbaugh, E. M., & Bennett, M. A. (1998). Factors affecting vegetable stand establishment. Scientia Agricola, 55(1), 116–120. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90161998000500021.
Gratton, J., Chen, Y., & Tessier, S. (2003). Design of a spring-loaded downforce system for a no-till seed opener. Canadian Biosystems Engineering, 45, 29–35.
Hanna, H. M., Steward, B. L., & Aldinger, L. (2010). Soil loading effects of planter depth-gauge wheels on early corn growth. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 26(4), 551–556. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.32058.
Hanna, H. M. (2009). Planter Set-up and Adjustments for Accurate Seeding of Corn and Soybean. Retrieved 24/11/2020 from www.agry.purdue.edu/CCA/2009/CCA%202009/Proceedings/Hanna%20CCA%20Proceedings%202009-2%20Final%20Version%2011-24.pdf.
ISO 7256/1-1984(E) Standard, International Organisation for Standardization Sowing equipment-test methods—Part one, single seed drills (precision drills) (1984) 7256/1, Geneva, Switzerland: ISO
Kachman, S., & Smith, J. (1995). Alternative measures of accuracy in plant spacing for planters using single seed metering. Transactions of the ASAE, 38(2), 379–388. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.27843.
Karayel, D., & Šarauskis, E. (2011). Effect of down force on the performance of no-till disc furrow openers for clay-loam and loamy soils. Agricultural Engineering, 43, 16–24.
Knappenberger, T., & Köller, K. (2012). Spatial assessment of the correlation of seeding depth with emergence and yield of corn. Precision Agriculture, 13, 163–180.
Liu, Q., Cui, T., Zhang, D., Yang, L., Wang, Y., He, X., et al. (2018). Design and experimental study of seed precise delivery mechanism for high-speed maize planter. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 11(4), 81–87.
Liu, Q., He, X., Yang, L., Zhang, D., Cui, T., Qu, Z., et al. (2017). Effect of travel speed on seed spacing uniformity of corn seed meter. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 10(4), 98–106.
Liu, W., Tollenaar, M., Stewart, G., & Deen, W. (2004). Within-row plant spacing variability does not affect corn yield. Agronomy Journal, 96(1), 275. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2004.2750.
Mangus, D. L., Sharda, A., & Zhang, N. (2016). Development and evaluation of thermal infrared imaging system for high spatial and temporal resolution crop water stress monitoring of corn within a greenhouse. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 121, 149–159.
Molatudi, R. L., & Mariga, I. K. (2009). The effect of maize seed size and depth of planting on seedling emergence and seedling vigour. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 5(12), 2234–2237.
Moody, F. H., Hancock, J. H., & Wilkerson, J. B. (2003). Evaluating planter performance-cotton seed placement accuracy. Paper No 031146, St Joseph, MI, USA: ASAE
Morrison, J. E., & Gerik, T. J. (1985). Planter depth-control: I. Predictions and projected effects on crop emergence. Transactions of the ASAE, 28(5), 1415–1418.
Mutema, A. (2014). Effects of seed kernel size and planting depth on the germination, emergence and early growth performance of maize (zea mays). BS thesis, Bindura University of Science Education, Bindura, Zimbabwe.
Nafziger, E. D. (1996). Effects of missing and two−plant hills on corn grain yield. Journal of Production Agriculture, 9(2), 238–240. https://doi.org/10.2134/jpa1995.0391.
Nielsen, R. L. (2015). Requirements for uniform germination and emergence of corn (pp. 47907–52054). West Lafayette, IN, USA: Agronomy Department, Purdue University.
Nielsen, R. L. (1995). Planting speed effects on stand establishment and grain yield of corn. Journal of Production Agriculture, 8(3), 391–393.
Nielsen, R. L. (1993). Stand establishment variability in corn. Proceedings of the Integrated Crop Management Conference. 16. Retrieved 21/11/2020 from https://lib.dr.iastate.edu/icm/1993/proceedings/16
Ozmerzi, A., Karayel, D., & Topakei, M. (2002). Effect of sowing depth on precision seeder uniformity. Biosystems Engineering, 82(2), 227–230. https://doi.org/10.1006/bioe.2002.0057.
Poncet, A. M., Fulton, J. P., McDonald, T. P., Knappenberger, T., Shaw, J. N., & Bridges, R. W. (2018). Effect of heterogeneous field conditions on corn seeding depth accuracy and uniformity. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 34(5), 819–830.
Raper, R. L., & Kirby, J. M. (2006). Soil compaction: How to do it, undo it or avoid doing it. Agricultural Equipment Technology Conference Distinguished Lecture No. 30, St Joseph, MI, USA: ASAE.
Sharma, S., Warren, J., Lofton, J., Henry, W., & Murley, C. (2019). Optimum Planting Depth for Uniform Germination and Emergence of Corn. Oklahoma Cooperative Extension Service. PSS-2192. Stillwater, Oklahoma, USA. Retrieved 24/11/2020 from http://pods.dasnr.okstate.edu/docushare/dsweb/Get/Document-11595/PSS-2192pod.pdf
Staggenborg, S. A., Taylor, R. K., & Maddux, L. D. (2004). Effect of planter speed and seed firmers on corn stand establishment. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 20(5), 573. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.17457.
United States Department of Agriculture-National Resources Conservation Services (USDA-NRCS). (2019). Web soil survey. Retrieved 23/11/2020 from https://websoilsurvey.sc.egov.usda.gov/App/HomePage.htm.
Virk, S. S., Fulton, J. P., Porter, W. M., & Pate, G. L. (2019). Row-crop planter performance to support variable-rate seeding of maize. Precision Agriculture, 21, 603–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-019-09685-3.
Zhai, C., Long, J., Taylor, R., Weckler, P., & Wang, N. (2019). Field scale row unit vibration affecting planting quality. Precision Agriculture, 21, 589–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-019-09684-4.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to extend their great appreciation to Horsch GmbH Germany for support of the planter, and Kansas State University Biological and Agricultural Engineering Department for providing the data acquisition hardware and software, and guidance system.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badua, S.A., Sharda, A., Strasser, R. et al. Ground speed and planter downforce influence on corn seed spacing and depth. Precision Agric 22, 1154–1170 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-020-09775-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-020-09775-7