Abstract
Introduction
Early diagnosis of periodontitis by means of a rapid, accurate and non-invasive method is highly desirable to reduce the individual and epidemiological burden of this largely prevalent disease.
Objectives
The aims of the present systematic review were to examine potential salivary metabolic biomarkers and pathways associated to periodontitis, and to assess the accuracy of salivary untargeted metabolomics for the diagnosis of periodontal diseases.
Methods
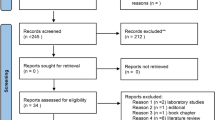
Relevant studies identified from MEDLINE (PubMed), Embase and Scopus databases were systematically examined for analytical protocols, metabolic biomarkers and results from the multivariate analysis (MVA). Pathway analysis was performed using the MetaboAnalyst online software and quality assessment by means of a modified version of the QUADOMICS tool.
Results
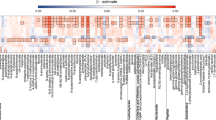
Twelve studies met the inclusion criteria, with sample sizes ranging from 19 to 130 subjects. Compared to periodontally healthy individuals, valine, phenylalanine, isoleucine, tyrosine and butyrate were found upregulated in periodontitis patients in most studies; while lactate, pyruvate and N-acetyl groups were the most significantly expressed in healthy individuals. Metabolic pathways that resulted dysregulated are mainly implicated in inflammation, oxidative stress, immune activation and bacterial energetic metabolism. The findings from MVA revealed that periodontitis is characterized by a specific metabolic signature in saliva, with coefficients of determination ranging from 0.52 to 0.99.
Conclusions
This systematic review summarizes candidate metabolic biomarkers and pathways related to periodontitis, which may provide opportunities for the validation of diagnostic or predictive models and the discovery of novel targets for monitoring and treating such a disease (PROSPERO CRD42020188482).


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Aimetti, M., Cacciatore, S., Graziano, A., & Tenori, L. (2012). Metabonomic analysis of saliva reveals generalized chronic periodontitis signature. Metabolomics, 8(3), 465–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-011-0331-2.
Arias-Bujanda, N., Regueira-Iglesias, A., Balsa-Castro, C., Nibali, L., Donos, N., & Tomás, I. (2020). Accuracy of single molecular biomarkers in saliva for the diagnosis of periodontitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 47(1), 2–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13202.
Assad, D. X., Mascarenhas, E. C. P., de Lima, C. L., de Toledo, I. P., Chardin, H., Combes, A., et al. (2020). Salivary metabolites to detect patients with cancer: A systematic review. International Journal of Clinical Oncology, 25(6), 1016–1036. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-020-01660-7.
Barnes, V. M., Teles, R., Trivedi, H. M., Devizio, W., Xu, T., Mitchell, M. W., et al. (2009). Acceleration of purine degradation by periodontal diseases. Journal of Dental Research, 88(9), 851–855. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034509341967.
Barnes, V. M., Ciancio, S. G., Shibly, O., Xu, T., Devizio, W., Trivedi, H. M., et al. (2011). Metabolomics reveals elevated macromolecular degradation in periodontal disease. Journal of Dental Research, 90(11), 1293–1297. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034511416240.
Barnes, V. M., Kennedy, A. D., Panagakos, F., Devizio, W., Trivedi, H. M., Jonsson, T., et al. (2014). Global metabolomic analysis of human saliva and plasma from healthy and diabetic subjects, with and without periodontal disease. PLoS ONE, 9(8), e105181. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0105181.
Beck, J. D., Papapanou, P. N., Philips, K. H., & Offenbacher, S. (2019). Periodontal medicine: 100 years of progress. Journal of Dental Research, 98(10), 1053–1062. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034519846113.
Beger, R. D. (2018). Interest is high in improving quality control for clinical metabolomics: setting the path forward for community harmonization of quality control standards. Metabolomics, 15(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-018-1453-6.
Bernabe, E., Marcenes, W., Hernandez, C. R., Bailey, J., Abreu, L. G., Alipour, V., et al. (2020). Global, regional, and national levels and trends in burden of oral conditions from 1990 to 2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease 2017 study. Journal of Dental Research, 99(4), 362–373. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034520908533.
Blombach, B., Schreiner, M. E., Holátko, J., Bartek, T., Oldiges, M., & Eikmanns, B. J. (2007). L-valine production with pyruvate dehydrogenase complex-deficient Corynebacterium glutamicum. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73(7), 2079–2084. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02826-06.
Buduneli, N., & Kinane, D. F. (2011). Host-derived diagnostic markers related to soft tissue destruction and bone degradation in periodontitis. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 38(Suppl 11), 85–105. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01670.x.
Chong, J., Wishart, D. S., & Xia, J. (2019). Using metaboanalyst 4.0 for comprehensive and integrative metabolomics data analysis. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics, 68, e86. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpbi.86.
Colli, A., Fraquelli, M., Casazza, G., Conte, D., Nikolova, D., Duca, P., et al. (2014). The architecture of diagnostic research: From bench to bedside—research guidelines using liver stiffness as an example. Hepatology, 60(1), 408–418. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26948.
Dawes, C., & Wong, D. T. W. (2019). Role of saliva and salivary diagnostics in the advancement of oral health. Journal of Dental Research, 98(2), 133–141. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034518816961.
de Lima, C. L., Acevedo, A. C., Grisi, D. C., Taba, M., Jr., Guerra, E., & De Luca Canto, G. (2016). Host-derived salivary biomarkers in diagnosing periodontal disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 43(6), 492–502. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12538.
Divaris, K., Moss, K., & Beck, J. D. (2020). Biologically informed stratification of periodontal disease holds the key to achieving precision oral health. Journal of Periodontology. https://doi.org/10.1002/JPER.20-0096.
Elabdeen, H. R., Mustafa, M., Szklenar, M., Ruhl, R., Ali, R., & Bolstad, A. I. (2013). Ratio of pro-resolving and pro-inflammatory lipid mediator precursors as potential markers for aggressive periodontitis. PLoS ONE, 8(8), e70838. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070838.
Eke, P. I., Page, R. C., Wei, L., Thornton-Evans, G., & Genco, R. J. (2012). Update of the case definitions for population-based surveillance of periodontitis. Journal of Periodontology, 83(12), 1449–1454. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2012.110664.
Emwas, A.-H.M., Salek, R. M., Griffin, J. L., & Merzaban, J. (2013). NMR-based metabolomics in human disease diagnosis: Applications, limitations, and recommendations. Metabolomics, 9(5), 1048–1072. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-013-0524-y.
Fidalgo, T. K. S., Freitas-Fernandes, L. B., Angeli, R., Muniz, A. M. S., Gonsalves, E., Santos, R., et al. (2013). Salivary metabolite signatures of children with and without dental caries lesions. Metabolomics, 9(3), 657–666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-012-0484-7.
Figueira, J., Jonsson, P., Nordin Adolfsson, A., Adolfsson, R., Nyberg, L., & Öhman, A. (2016). NMR analysis of the human saliva metabolome distinguishes dementia patients from matched controls. Molecular Biosystems, 12(8), 2562–2571. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6mb00233a.
García-Villaescusa, A., Morales-Tatay, J. M., Monleón-Salvadó, D., González-Darder, J. M., Bellot-Arcis, C., Montiel-Company, J. M., et al. (2018). Using NMR in saliva to identify possible biomarkers of glioblastoma and chronic periodontitis. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188710.
Gardner, A., Parkes, H. G., So, P.-W., & Carpenter, G. H. (2019). Determining bacterial and host contributions to the human salivary metabolome. Journal of Oral Microbiology, 11(1), 1617014. https://doi.org/10.1080/20002297.2019.1617014.
Gardner, A., Carpenter, G., & So, P. W. (2020). Salivary metabolomics: From diagnostic biomarker discovery to investigating biological function. Metabolites. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10020047.
Gawron, K., Wojtowicz, W., Lazarz-Bartyzel, K., Lamasz, A., Qasem, B., Mydel, P., et al. (2019). metabolomic status of the oral cavity in chronic periodontitis. In Vivo, 33(4), 1165–1174. https://doi.org/10.21873/invivo.11587.
Gertsman, I., & Barshop, B. A. (2018). Promises and pitfalls of untargeted metabolomics. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease, 41(3), 355–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-017-0130-7.
Gluud, C., & Gluud, L. L. (2005). Evidence based diagnostics. British Medical Journal (Clinical research ed.), 330(7493), 724–726. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.330.7493.724.
Hao, J., Liebeke, M., Sommer, U., Viant, M. R., Bundy, J. G., & Ebbels, T. M. (2016). Statistical correlations between NMR spectroscopy and direct infusion FT-ICR mass spectrometry aid annotation of unknowns in metabolomics. Analytical Chemistry, 88(5), 2583–2589. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02889.
Huang, Y., Zhu, M., Li, Z., Sa, R., Chu, Q., Zhang, Q., et al. (2014). Mass spectrometry-based metabolomic profiling identifies alterations in salivary redox status and fatty acid metabolism in response to inflammation and oxidative stress in periodontal disease. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 70, 223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.02.024.
Hung, J. H. (2013). Gene Set/Pathway enrichment analysis. Methods in Molecular Biology, 939, 201–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-107-3_13.
Jaedicke, K. M., Preshaw, P. M., & Taylor, J. J. (2016). Salivary cytokines as biomarkers of periodontal diseases. Periodontology 2000, 70(1), 164–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12117.
Kc, S., Wang, X. Z., & Gallagher, J. E. (2020). Diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of host-derived salivary biomarkers in periodontal disease amongst adults: Systematic review. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 47(3), 289–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13218.
Kim, J. J., Kim, C. J., & Camargo, P. M. (2013). Salivary biomarkers in the diagnosis of periodontal diseases. Journal of the California Dental Association, 41(2), 119–124.
Kinney, J. S., Morelli, T., Braun, T., Ramseier, C. A., Herr, A. E., Sugai, J. V., et al. (2011). Saliva/pathogen biomarker signatures and periodontal disease progression. Journal of Dental Research, 90(6), 752–758. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034511399908.
Kornman, K. S., Giannobile, W. V., & Duff, G. W. (2017). Quo vadis: What is the future of periodontics? How will we get there? Periodontology, 2000(75), 353–371. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12217.
Korte, D. L., & Kinney, J. (2016). Personalized medicine: an update of salivary biomarkers for periodontal diseases. Periodontology 2000, 70(1), 26–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12103.
Kuboniwa, M., Sakanaka, A., Hashino, E., Bamba, T., Fukusaki, E., & Amano, A. (2016). Prediction of periodontal inflammation via metabolic profiling of saliva. Journal of Dental Research, 95(12), 1381–1386. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034516661142.
Lee, A., Ghaname, C. B., Braun, T. M., Sugai, J. V., Teles, R. P., Loesche, W. J., et al. (2012). Bacterial and salivary biomarkers predict the gingival inflammatory profile. Journal of Periodontology, 83(1), 79–89. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2011.110060.
Liebsch, C., Pitchika, V., Pink, C., Samietz, S., Kastenmüller, G., Artati, A., et al. (2019). The saliva metabolome in association to oral health status. Journal of Dental Research, 98(6), 642–651. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034519842853.
Liu, J., Wang, Y., Meng, H., Yu, J., Lu, H., Li, W., et al. (2019). Butyrate rather than LPS subverts gingival epithelial homeostasis by downregulation of intercellular junctions and triggering pyroptosis. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 46(9), 894–907. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13162.
Lumbreras, B., Porta, M., Márquez, S., Pollán, M., Parker, L. A., & Hernández-Aguado, I. (2008). QUADOMICS: An adaptation of the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy assessment (QUADAS) for the evaluation of the methodological quality of studies on the diagnostic accuracy of ’-omics’-based technologies. Clinical Biochemistry, 41(16–17), 1316–1325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2008.06.018.
Lyman, G. H., & Moses, H. L. (2016). Biomarker tests for molecularly targeted therapies—the key to unlocking precision medicine. New England Journal of Medicine, 375(1), 4–6. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1604033.
Marchesan, J. T., Morelli, T., Moss, K., Barros, S. P., Ward, M., Jenkins, W., et al. (2015). Association of synergistetes and cyclodipeptides with periodontitis. Journal of Dental Research, 94(10), 1425–1431. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034515594779.
Marsh, P. D., & Zaura, E. (2017). Dental biofilm: ecological interactions in health and disease. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 44(Suppl 18), S12–S22. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12679.
Mikkonen, J. J., Singh, S. P., Herrala, M., Lappalainen, R., Myllymaa, S., & Kullaa, A. M. (2016). Salivary metabolomics in the diagnosis of oral cancer and periodontal diseases. Journal of Periodontal Research, 51(4), 431–437. https://doi.org/10.1111/jre.12327.
Mueller, D. C., Piller, M., Niessner, R., Scherer, M., & Scherer, G. (2014). Untargeted metabolomic profiling in saliva of smokers and nonsmokers by a validated GC-TOF-MS method. Journal of Proteome Research, 13(3), 1602–1613. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr401099r.
Murr, C., Grammer, T. B., Meinitzer, A., Kleber, M. E., März, W., & Fuchs, D. (2014). Immune activation and inflammation in patients with cardiovascular disease are associated with higher phenylalanine to tyrosine ratios: The Ludwigshafen risk and cardiovascular health study. Journal of Amino Acids, 2014, 783730. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/783730.
Nicholson, J. K., Holmes, E., Kinross, J. M., Darzi, A. W., Takats, Z., & Lindon, J. C. (2012). Metabolic phenotyping in clinical and surgical environments. Nature, 491(7424), 384–392. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11708.
Nie, A., Sun, B., Fu, Z., & Yu, D. (2019). Roles of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in immune regulation and immune diseases. Cell Death & Disease, 10(12), 901. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-2145-5.
Nociti, F. H., Jr., Casati, M. Z., & Duarte, P. M. (2015). Current perspective of the impact of smoking on the progression and treatment of periodontitis. Periodontology 2000, 67(1), 187–210. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12063.
Okuma, N., Saita, M., Hoshi, N., Soga, T., Tomita, M., Sugimoto, M., et al. (2017). Effect of masticatory stimulation on the quantity and quality of saliva and the salivary metabolomic profile. PLoS ONE, 12(8), e0183109. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0183109.
Papageorgiou, S. N., Hagner, M., Nogueira, A. V., Franke, A., Jäger, A., & Deschner, J. (2017). Inflammatory bowel disease and oral health: Systematic review and a meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 44(4), 382–393. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12698.
Papapanou, P. N., Sanz, M., Buduneli, N., Dietrich, T., Feres, M., Fine, D. H., et al. (2018). Periodontitis: Consensus report of workgroup 2 of the 2017 world workshop on the classification of periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 45(Suppl 20), S162–S170. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12946.
Parthasarathy, A., Cross, P. J., Dobson, R. C. J., Adams, L. E., Savka, M. A., & Hudson, A. O. (2018). A three-ring circus: Metabolism of the three proteogenic aromatic amino acids and their role in the health of plants and animals. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 5, 29–29. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2018.00029.
Patti, G. J., Tautenhahn, R., & Siuzdak, G. (2012). Meta-analysis of untargeted metabolomic data from multiple profiling experiments. Nature Protocols, 7(3), 508–516. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.454.
Pereira, J. L., Duarte, D., Carneiro, T. J., Ferreira, S., Cunha, B., Soares, D., et al. (2019). Saliva NMR metabolomics: Analytical issues in pediatric oral health research. Oral Diseases, 25(6), 1545–1554. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.13117.
Potempa, J., Banbula, A., & Travis, J. (2000). Role of bacterial proteinases in matrix destruction and modulation of host responses. Periodontology 2000, 24, 153–192. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0757.2000.2240108.x.
Pradeep, A. R., Kumar, M. S., Ramachandraprasad, M. V., & Shikha, C. (2007). Gingival crevicular fluid levels of neopterin in healthy subjects and in patients with different periodontal diseases. Journal of Periodontology, 78(10), 1962–1967. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2007.070096.
Proctor, G. B. (2016). The physiology of salivary secretion. Periodontology 2000, 70(1), 11–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12116.
Ramseier, C. A., Kinney, J. S., Herr, A. E., Braun, T., Sugai, J. V., Shelburne, C. A., et al. (2009). Identification of pathogen and host-response markers correlated with periodontal disease. Journal of Periodontology, 80(3), 436–446. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2009.080480.
Roberts, L. D., Souza, A. L., Gerszten, R. E., & Clish, C. B. (2012). Targeted metabolomics. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, 98, 30.2.1–30.2.24. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142727.mb3002s98.
Romandini, M., Laforí, A., Romandini, P., Baima, G., & Cordaro, M. (2018). Periodontitis and platelet count: A new potential link with cardiovascular and other systemic inflammatory diseases. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 45(11), 1299–1310. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13004.
Romano, F., Meoni, G., Manavella, V., Baima, G., Tenori, L., Cacciatore, S., et al. (2018). Analysis of salivary phenotypes of generalized aggressive and chronic periodontitis through nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics. Journal of Periodontology, 89(12), 1452–1460. https://doi.org/10.1002/jper.18-0097.
Romano, F., Meoni, G., Manavella, V., Baima, G., Mariani, G. M., Cacciatore, S., et al. (2019). Effect of non-surgical periodontal therapy on salivary metabolic fingerprint of generalized chronic periodontitis using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Archives of Oral Biology, 97, 208–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.10.023.
Rzeznik, M., Triba, M. N., Levy, P., Jungo, S., Botosoa, E., Duchemann, B., et al. (2017). Identification of a discriminative metabolomic fingerprint of potential clinical relevance in saliva of patients with periodontitis using 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. PLoS ONE, 12(8), e0182767. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0182767.
Sakanaka, A., Kuboniwa, M., Hashino, E., Bamba, T., Fukusaki, E., & Amano, A. (2017). Distinct signatures of dental plaque metabolic byproducts dictated by periodontal inflammatory status. Scientific Reports, 7, 42818. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42818.
Shamseer, L., Moher, D., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Liberati, A., Petticrew, M., et al. (2015). Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and explanation. British Medical Journal, 349, g7647. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g7647.
Shirasugi, M., Nakagawa, M., Nishioka, K., Yamamoto, T., Nakaya, T., & Kanamura, N. (2018). Relationship between periodontal disease and butyric acid produced by periodontopathic bacteria. Inflammation and Regeneration, 38, 23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41232-018-0081-x.
Singh, M. P., Saxena, M., Saimbi, C. S., Arif, J. M., & Roy, R. (2017). Metabolic profiling by 1H NMR spectroscopy of saliva shows clear distinction between control and diseased case of periodontitis. Metabolomics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1245-4.
Su, W., Shi, J., Zhao, Y., Yan, F., Lei, L., & Li, H. (2020). Porphyromonas gingivalis triggers inflammatory responses in periodontal ligament cells by succinate-succinate dehydrogenase–HIF–1α axis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 522(1), 184–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.11.074.
Sugimoto, M., Wong, D. T., Hirayama, A., Soga, T., & Tomita, M. (2010). Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry-based saliva metabolomics identified oral, breast and pancreatic cancer-specific profiles. Metabolomics, 6(1), 78–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-009-0178-y.
Sun, Y., Gao, H. Y., Fan, Z. Y., He, Y., & Yan, Y. X. (2020). Metabolomics signatures in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and integrative analysis. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgz240.
Takeda, I., Stretch, C., Barnaby, P., Bhatnager, K., Rankin, K., Fu, H., et al. (2009). Understanding the human salivary metabolome. NMR in Biomedicine, 22(6), 577–584. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1369.
Tervahartiala, T., Pirilä, E., Ceponis, A., Maisi, P., Salo, T., Tuter, G., et al. (2000). The in vivo expression of the collagenolytic matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, -8, -13, and -14) and matrilysin (MMP-7) in adult and localized juvenile periodontitis. Journal of Dental Research, 79(12), 1969–1977. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345000790120801.
Tonetti, M. S., Greenwell, H., & Kornman, K. S. (2018). Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 45(Suppl 20), S149-s161. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12945.
Tonetti, M. S., Jepsen, S., Jin, L., & Otomo-Corgel, J. (2017). Impact of the global burden of periodontal diseases on health, nutrition and wellbeing of mankind: A call for global action. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 44(5), 456–462. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12732.
Wallner-Liebmann, S., Tenori, L., Mazzoleni, A., Dieber-Rotheneder, M., Konrad, M., Hofmann, P., et al. (2016). Individual human metabolic phenotype analyzed by (1)H NMR of saliva samples. Journal of Proteome Research, 15(6), 1787–1793. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b01060.
Wei, J., Xie, G., Zhou, Z., Shi, P., Qiu, Y., Zheng, X., et al. (2011). Salivary metabolite signatures of oral cancer and leukoplakia. International Journal of Cancer, 129(9), 2207–2217. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25881.
Wishart, D. S. (2007). Current progress in computational metabolomics. Briefings in Informatics, 8(5), 279–293. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbm030.
Wishart, D. S. (2019). NMR metabolomics: A look ahead. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 306, 155–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmr.2019.07.013.
Wishart, D. S., Feunang, Y. D., Marcu, A., Guo, A. C., Liang, K., Vázquez-Fresno, R., et al. (2017). HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Research, 46(D1), D608–D617. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1089.
Wolff, L. F., Smith, Q. T., Snyder, W. K., Bedrick, J. A., Liljemark, W. F., Aeppli, D. A., et al. (1988). Relationship between lactate dehydrogenase and myeloperoxidase levels in human gingival crevicular fluid and clinical and microbial measurements. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 15(2), 110–115. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051x.1988.tb01003.x.
Yilmaz, A., Geddes, T., Han, B., Bahado-Singh, R. O., Wilson, G. D., Imam, K., et al. (2017). Diagnostic biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease as identified in saliva using 1H NMR-based metabolomics. Journal of Alzheimers Disease, 58(2), 355–359. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-161226.
Zhang, Y., Sun, J., Lin, C. C., Abemayor, E., Wang, M. B., & Wong, D. T. (2016). The emerging landscape of salivary diagnostics. Periodontology 2000, 70(1), 38–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12099.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge special gratitude to Gaia Meoni, Leonardo Tenori and the CERM institute of Florence for providing missing data and technical support for writing the manuscript.
Funding
This research was not supported by any fundings.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GB, GI and MA made substantial contributions to conception of the study. GB, NB, FC and FR contributed to the study design. GI, SG, and GB searched and collected the data. GB and GNB performed data processing and interpretation. GB and NB prepared the first draft of the manuscript. All authors have read, revised critically, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baima, G., Iaderosa, G., Citterio, F. et al. Salivary metabolomics for the diagnosis of periodontal diseases: a systematic review with methodological quality assessment. Metabolomics 17, 1 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-020-01754-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-020-01754-3