Abstract
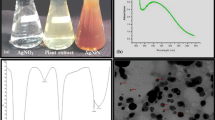
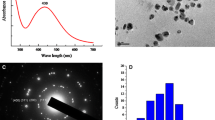
Hyperhydricity (HH) is one of the major problems in plant tissue culture. Increased frequency (75%) of HH in the cultures of. Dianthus chinensis L. cultivar telstar scarlet raised from nodal segments on agar (0.85%) gelled, benzyladenine (2.5 µM) supplemented Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium was noticed in the third subculture onwards. To reduce HH and to resume normal growth, the addition of silver nitrate is routinely recommended in the culture medium. However, the impact of biogenic silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) on HH reversion has not been well investigated. In this study, biogenic AgNPs prepared from leaf extract of D. chinensis were used to control HH in D. chinensis cultures. The characterization of bioynthesized AgNPs has been done by UV–Vis spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis, energy-dispersive X-ray spectrum, transmission electron microscopy, and atomic force microscopy. Higher water content or addition of ethylene precursor, ethephon, in culture medium induced plantlet with unhealthy, pale green, glassy shoots (HH). Due to the biological activity of Ag+ ions and water regulating mechanism, AgNPs treatment on hyperhydric explant (4 weeks) resulted in high retroversion coupled with reduced relative water content. Supplementation of 100 µg L−1 AgNPs in MS medium significantly reduced the percentage of HH to 13.3%, in contrast to control (100%). Addition of AgNPs effectively reduced hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) content (50%) characterized by green, healthy shoots with proper stomata in contrast to hyperhydric shoots. The gene expression pattern of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylase synthase (ACS1) and 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid oxidase (ACO1) showed reduced expression after the retroversion of microshoots in 100 µg L−1 AgNPs medium compared to hyperhydric shoot. The relative gene expression profile of ACS1 and ACO1 at 100 µg L−1 AgNPs treatment was 9.8 and 1.8-fold over normal shoots (1), respectively. Inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) analysis on AgNPs directed HH reverted shoots showed genetic stability thus proved safe to adopt this technique to produce true to type plants. Combined manipulation, coordination of water permeability, and anti-ethylene activity of AgNPs were responsible for effective HH reversion. These finding will put forward the future utilization of bioencapsulated AgNPs in plant tissue culture and agriculture practices.
Graphic Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghdaei M, Salehi H, Sarmast MK (2012) Effects of silver nanoparticles on Tecomella undulata (Roxb.) Seem, micropropagation. Adv Hort Sci 26:21–24. https://doi.org/10.13128/ahs-12748
Ali A, Mohammad S, Khan MA, Raja NI, Arif M, Kamil A, Mashwani Z (2019) Silver nanoparticles elicited in vitro callus cultures for accumulation of biomass and secondary metabolites in Caralluma tuberculata. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:715–724. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1577884
Anandalakshmi K, Venugobal J, Ramasamy V (2015) Characterization of silver nanoparticles by green synthesis method using Pedalium murex leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Appl Nanosci 6:399–408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-015-0449-z
Bernard F, Moghadam NN, Mirzajani F (2015) The effect of colloidal silver nanoparticles on the level of lignification and hyperhydricity syndrome in Thymus daenensis in vitro shoots: a possible involvement of bonded polyamines. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 51:546–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-015-9700-2
Bhakya S, Muthukrishnan S, Sukumaran M, Muthukumar M (2016) Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Appl Nanosci 6:755–766. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-015-0473-z
Bornet B, Branchard M (2001) Nonanchored inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers: reproducible and specific tools for genome fingerprinting. Plant Mol Biol Rep 19:209–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02772892
Castro-Gonzalez CG, Sánchez-Segura L, Gómez-Merino FC, Bello-Bello JJ (2019) Exposure of stevia (Stevia rebaudiana B.) to silver nanoparticles in vitro: transport and accumulation. Sci Rep 9:10372. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46828-y
Cvjetko P, Zovko M, Stefanic PP, Biba R, Tkalec M, Domijan A, Vrček IV, Letofsky-Papst I, Sikic S, Balen B (2018) Phytotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles in tobacco plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:5590–5602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0928-8
De D, De B (2003) Effect of ethephon on antioxidant enzymes and diosgenin production in seedlings of Trigonella foenum-graecum. Food Chem 82:211–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(02)00514-9
Desikan R, Last K, Harrett-Williams R, Tagliavia C, Harter K, Hooley R, Hancock JT, Neill SJ (2006) Ethylene-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis occurs via AtrbohF-mediated hydrogen peroxide synthesis. Plant J 47:907–916
Dimkpa CO, McLean JE, Martineau N, Britt DW, Haverkamp R, Anderson AJ (2013) Silver nanoparticles disrupt wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) growth in a sand matrix. Environ Sci Technol 47:1082–1090. https://doi.org/10.1021/es302973y
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Fernandez-Garcia N, Piqueras A, Olmos E (2008) Subcellular location of H2O2, peroxidases and pectin epitopes in control and hyperhydric shoots of carnation. Environ Exp Bot 62:168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.08.004
Gao H, Xia X, An L, Xin X, Liang Y (2017) Reversion of hyperhydricity in pink (Dianthus chinensis L.) plantlets by AgNO3 and its associated mechanism during in vitro culture. Plant Sci 254:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.10.008
Ge XM, Cai HL, Lei X, Zhou X, Yue M, He JM (2015) Heterotrimeric G proteinmediates ethylene-induced stomatal closure via hydrogen peroxide synthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 82:138–150. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12799
Hassanein AM, Salem JM, Faheed FA, El-nagish A (2018) Effect of anti-ethylene compounds on isoenzyme patterns and genome stability during long term culture of Moringa oleifera. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 132:201–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1326-0
He JM, Ma XG, Zhang Y, Sun TF, Xu FF, Chen YP, Liu X, Yue M (2013) Role and interrelationship of Gα protein, hydrogen peroxide, and nitric oxide in ultraviolet B-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Physiol 161:1570–1583. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.211623
Ichimura K, Yoshioka S, Yumoto-Shimizu H (2008) Effects of silver thiosulfate complex (STS), sucrose and combined pulse treatments on the vase life of cut snapdragon flowers. Environ Control Biol 46:155–162
Ivanova M, Van Staden J (2011) Influence of gelling agent and cytokinins on the control of hyperhydricity in Aloe polyphylla. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 104:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9794-5
Jeeva K, Thiyagarajan M, Elangovan V, Geetha N, Venkatachalam P (2014) Caesalpinia coriaria leaf extracts mediated biosynthesis of metallic silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity against clinically isolated pathogens. Ind Crops Prod 52:714–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.11.037
Jo YK, Kim BH, Jung G (2009) Antifungal activity of silver ions and nanoparticles on phytopathogenic fungi. Plant Dis 93:1037–1043. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-93-10-1037
Kantia A, Kothari SL (2002) High efficiency adventitious shoot bud formation and plant regeneration from leaf explants of Dianthus chinensis L. Sci Hort 96:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4238(02)00081-X
Kim DH, Gopal J, Sivanesan I (2017) Nanomaterials in plant tissue culture: the disclosed and undisclosed. RSC Adv 7:36492–36505. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA07025J
Krishnan SRS, Siril EA (2017) Enhanced in vitro shoot regeneration in Oldenlandia umbellata L. by using quercetin: a naturally occurring auxin-transport inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:899–904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0672-0
Krishnaraj C, Jagan E, Ramachandran R, Abirami SM, Mohan N, Kalaichelvan PT (2012) Effect of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles on Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) Wettst. Plant Growth Metabol Process Biochem 47:651–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.01.006
Kumar V, Parvatam G, Ravishankar GA (2009) AgNO3 - A potential regulator of ethylene activity and plant growth modulator. Electron J Biotechnol 12:2. https://doi.org/10.2225/vol12-issue2-fulltext-1
Lee S, Seo PJ, Lee HJ, Park C (2012) A NAC transcription factor NTL4 promotes reactive oxygen species production during drought-induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant J 70:831–844. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.04932.x
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol 148:350–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(87)48036-1
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lu P, Cao J, He S, Liu J, Li H, Cheng G, Ding Y, Joyce DC (2010) Nano-silver pulse treatments improve water relations of cut rose cv. Movie Starflowers Postharvest Biol Technol 57:196–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2010.04.003
Martinez LIR, Visser RGF, Klerk GD (2010) The hyperhydricity syndrome: Waterlogging of plant tissues as a major cause. Propag Ornam Plants 10:169–175
Muthukrishnan S, Bhakya S, Kumar TS, Rao MV (2015) Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial effect of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using Ceropegia thwaitesii-an endemic species. Ind Crops Prod 63:119–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.10.022
Muthuramalingam TR, Shanmugam C, Gunasekaran D, Duraisamy N, Nagappan R, Krishnan K (2015) Bioactive bile salt-capped silver nanoparticles activity against destructive plant pathogenic fungi through in vitro system. RSC Adv 5:71174–71182. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA13306H
Nairn BJ, Furneaux RH, Stevenson TT (1995) Identification of an agar constituent responsible for hydric control in micropropagation of radiata pine. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 43:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00042665
Nair R, Varghese SH, Nair BG, Maekawa T, Yoshida Y, Kumar DS (2010) Nanoparticulate material delivery to plants. Plant Sci 179:154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.04.012
Nandwal AS, Maan A, Kundu BS, Sheokand S, Kamboj DV, Sheoran A, Kumar B, Dutta D (2000) Ethylene evolution and antioxidant defence mechanism in Cicer arietinum roots in the presence of nitrate and amino ethoxyviylglycine. Plant Physiol Biochem 38:709–715. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0981-9428(00)01174-8
Ozturk OL, Kufrevioglu I, Demir Y (2008) In vivo and in vitro effects of ethephon on some oxidative enzymes in spinach leaves. Acta Physiol Plant 30:105–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-007-0096-4
Pal S, Tak YK, Song JM (2007) Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the Gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:1712–1720. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02218-06
Petruş-Vancea A (2018) Cell ultrastructure and chlorophyll pigments in hyperhydric and non-hyperhydric Beta vulgaris var. Conditiva plantlets, treated with deuterium depleted water. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 135:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-018-1439-0
Qian H, Peng X, Han X, Ren J, Sun L, Fu Z (2013) Comparison of the toxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver ions on the growth of terrestrial plant model Arabidopsis thaliana. J Environ Sci 25:1947–1956. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(12)60301-5
Razzaq A, Ammara R, Jhanzab HM, Mahmood T (2015) A novel nanomaterial to enhance growth and yield of wheat. J Nanosci Technol 2:55–58
Reddy NJ, Vali DN, Rani M, Rani SS (2014) Evaluation of antioxidant, antibacterial and cytotoxic effects of green synthesized silver nanoparticles by Piper longum fruit. Mater Sci Eng: C 34:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2013.08.039
Saha N, Gupta SD (2018) Promotion of shoot regeneration of Swertia chirata by biosynthesized silver nanoparticles and their involvement in ethylene interceptions and activation of antioxidant activity. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 134:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-018-1423-8
Sarmast MK, Niazi A, Salehi H, Abolimoghadam A (2015) Silver nanoparticles affect ACS expression in Tecomella undulata in vitro culture. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 1212:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0697-8
Sharma P, Bhatt D, Zaidi MGH, Saradhi PP, Khanna PK, Arora S (2012) Silver nanoparticle-mediated enhancement in growth and antioxidant status of Brassica juncea. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167:2225–2233
Sharma P, Gupta S, Arora S (2014) Effect of silver nanoparticles on antioxidant status of Brassica juncea callus. Indian J Res 8:8–18
Simms D, Cizdziel PE, Chomczynski P (1993) TRIZOTM: a new reagent for optimal single-step isolation of RNA. Focus 15:99–103
Speranza A, Crinelli R, Scoccianti V, Taddei AR, Iacobucci M, Bhattacharya P, Ke PC (2013) In vitro toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Kiwifruit pollen exhibits peculiar traits beyond the cause of silver ion release. Environ Pollut 179:258–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.04.021
Spinoso-Castillo JL, Chavez-Santoscoy RA, Bogdanchikova N, Pérez-Sato JA, Morales-Ramos V, Bello-Bello J (2017) Antimicrobial and hormetic effects of silver nanoparticles on in vitro regeneration of vanilla (Vanilla planifolia Jacks. ex Andrews) using a temporary immersion system. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 129:195–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1169-8
Sun Z, Zhang T, Su J, Chow WS, Liu J, Chen L, Li W, Peng S, Peng C (2015) A novel role of ethephon in controlling the noxious weed Ipomoea cairica (Linn.) Sweet. Sci Rep 5:11372. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11372
Tian J, Jiang F, Wu Z (2015) The apoplastic oxidative burst as a key factor of hyperhydricity in garlic plantlet in vitro. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 120:571–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0623-0
Van den Dries V, Giannì S, Czerednik A, Krens FA, De Klerk GJM (2013) Flooding of the apoplast is a key factor in the development of hyperhydricity. J Exp Bot 64:5221–5230. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert315
Vinoth A, Ravindhran R (2015) Reduced hyperhydricity in watermelon shoot cultures using silver ions. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-015-9698-5
Wang KLC, Li H, Ecker JR (2002) Ethylene biosynthesis and signaling networks. Plant Cell 14:131–151
Zuverza-Mena N, Martínez-Fernández D, Du W, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Bonila-Bird N, Lopez-Moreno M, Komarek M, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2017) Exposure of engineered nano-materials to plants: insights into the physiological and biochemical responses-a review. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:236–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.05.037
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Suhara Beevy S, Professor and Head, Department of Botany, University of Kerala, Kariavattom, Thiruvananthapuram, for providing the facilities. The first author is also thankful to the University of Kerala for financial support in the form of Junior Research Fellowship (No. AcVI(1)/715/BOT/13289/2015). One of the authors S. Muthukrishnan is thankful to the DST-SERB, New Delhi, for providing financial support through National-Post Doctoral Fellowship (N-PDF) (Ref: File No. PDF/2016/002503 dt. 28/03/2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RS and EAS formulated and designed the experiments. RS and SM performed and validated nanoparticle synthesis experiments. RS and EAS interpreted the whole data and wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Durgesh Kumar Tripathi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sreelekshmi, R., Siril, E.A. & Muthukrishnan, S. Role of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles on Hyperhydricity Reversion in Dianthus chinensis L. an In Vitro Model Culture. J Plant Growth Regul 41, 23–39 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10276-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10276-0