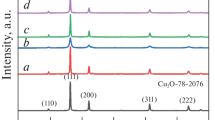
Abstract
In this paper, the precipitation method was used to synthesize CuO nanoparticles (NPs). Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide (CTAB) were used as a surfactant to modify the surface morphology of the CuO NPs. To investigate the characteristics of the CuO NPs, X-ray diffraction technique (XRD), X-Ray photoelectron spectrometry (XPS), Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and Energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDAX) were used. The catalytic activities of as prepared CuO NPs were evaluated by monitoring reduction of MB dye in the presence of NaBH4 as reducing agent. Effect of catalyst mass, concentration of NaBH4 and concentration of MB dye were investigated. The best results for the reduction of MB dye were obtained by the CuO–SDS catalyst. The results showed that 10 min of reaction time was sufficient to have the total degradation of MB dye. The reuse of the CuO–SDS catalyst for five cycles has shown interesting results via the reduction of MB dye without losing its effectiveness.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. I. Schlesinger, H. C. Brown, B. Abraham, et al. (1953). Improved Arc process for the preparation of diborane purification of diborane. J Am Chem Soc 75, 191. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01097a050.
B. D. James and M. G. H. Wallbridge, Metal tetrahydroborates. (Wiley, London, 2007), pp. 99–231.
S. C. Amendola, S. L. Sharp-Goldman, M. Saleem Janjua, et al. (2000). An ultrasafe hydrogen generator: aqueous, alkaline borohydride solutions and Ru catalyst. J Power Sources 85, 186–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7753(99)00301-8.
S. C. Amendola, S. L. Sharp-Goldman, M. S. Janjua, et al. (2000). A Safe, portable, hydrogen gas generator using aqueous borohydride solution and Ru catalyst. Int J Hydrog Energy 25, 969–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3199(00)00021-5.
T. Kamal, Y. Anwar, S. B. Khan, et al. (2016). Dye adsorption and bactericidal properties of TiO2/chitosan coating layer. Carbohydr Polym 148, 153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.04.042.
X. Li, S. Tang, D. Yuan, et al. (2019). Improved degradation of anthraquinone dye by electrochemical activation of PDS. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 177, 77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.04.015.
V. S. Munagapati, V. Yarramuthi, and D. S. Kim (2017). Methyl orange removal from aqueous solution using goethite, chitosan beads and goethite impregnated with chitosan beads. J Mol Liq 240, 329–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.05.099.
Glossman-Mitnik D (2013) Computational study of the chemical reactivity properties of the Rhodamine B molecule. In: Procedia Computer Science. Elsevier B.V., pp 816–825
C. Bruhn, H. Lenke, and H.-J. Knackmuss (1987). Nitrosubstituted aromatic compounds as nitrogen source for bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 53, 208–210.
A. Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh and M. Khorsandi (2010). Photodecolorization of eriochrome black T using NiS-P zeolite as a heterogeneous catalyst. J Hazard Mater 176, 629–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.077.
B. Nabil, E. A. Ahmida, C. Christine, et al. (2018). Polyfunctional cotton fabrics with catalytic activity and antibacterial capacity. Chem Eng J 351, 328–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.050.
T. Aditya, A. Pal, and T. Pal (2015). Nitroarene reduction: a trusted model reaction to test nanoparticle catalysts. Chem Commun 51, 9410–9431. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC01131K.
X. K. Kong, Z. Y. Sun, M. Chen, et al. (2013). Metal-free catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol by N-doped graphene. Energy Environ Sci 6, 3260–3266. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ee40918j.
X. K. Kong, Chen C. Le, and Q. W. Chen (2014). Doped graphene for metal-free catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 2841–2857.
A. Wang, H. Yin, H. Lu, et al. (2009). Catalytic activity of nickel nanoparticles in hydrogenation of p-nitrophenol to p-aminophenol. Catal Commun 10, 2060–2064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2009.07.031.
A. K. Patra, A. Dutta, and A. Bhaumik (2010). Cu nanorods and nanospheres and their excellent catalytic activity in chemoselective reduction of nitrobenzenes. Catal Commun 11, 651–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2010.01.015.
K. Kombaiah, J. J. Vijaya, L. J. Kennedy, and K. Kaviyarasu (2019). Catalytic studies of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by conventional and microwave combustion method. Mater Chem Phys 221, 11–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.09.012.
S. M. Pawar, B. S. Pawar, A. I. Inamdar, et al. (2017). In-situ synthesis of Cu(OH)2 and CuO nanowire electrocatalysts for methanol electro-oxidation. Mater Lett 187, 60–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.10.079.
N. Dasineh Khiavi, R. Katal, S. Kholghi Eshkalak, et al. (2019). Visible light driven heterojunction photocatalyst of CuO–Cu2O thin films for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Nanomaterials 9, 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9071011.
L. Zeng, B. Wan, R. Huang, et al. (2018). Catalytic oxidation of arsenite and reaction pathways on the surface of CuO nanoparticles at a wide range of pHs. Geochem Trans 19, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12932-018-0058-3.
X. M. Miao, R. Yuan, Y. Q. Chai, et al. (2008). Direct electrocatalytic reduction of hydrogen peroxide based on Nafion and copper oxide nanoparticles modified Pt electrode. J Electroanal Chem 612, 157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2007.09.026.
Y. Bai, X. Bian, and W. Wu (2019). Catalytic properties of CuO/CeO 2 -Al 2 O 3 catalysts for low concentration NO reduction with CO. Appl Surf Sci 463, 435–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.229.
A. Mekki, A. Mokhtar, M. Hachemaoui, et al. (2021). Fe and Ni nanoparticles-loaded zeolites as effective catalysts for catalytic reduction of organic pollutants. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 310, 110597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110597.
S. P. Meshram, P. V. Adhyapak, U. P. Mulik, and D. P. Amalnerkar (2012). Facile synthesis of CuO nanomorphs and their morphology dependent sunlight driven photocatalytic properties. Chem Eng J 204–205, 158–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.07.012.
H. Sekkiou, B. Boukoussa, R. Ghezini, et al. (2016). Enhanced hydrogen storage capacity of copper containing mesoporous silicas prepared using different methods. Mater Res Express 3, 85501. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/3/8/085501.
H. Hadj Mokhtar, B. Boukoussa, R. Hamacha, et al. (2015). CuCO3–CuO nanocomposite as a novel and environmentally friendly catalyst for triazole synthesis. RSC Adv 5, 93438–93446. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA17224A.
J. Hong, J. Li, and Y. Ni (2009). Urchin-like CuO microspheres: synthesis, characterization, and properties. J Alloys Compd 481, 610–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.03.043.
Y. K. Kim, D. H. Riu, S. R. Kim, and B. I. Kim (2002). Preparation of shape-controlled copper oxide powders from copper-containing solution. Mater Lett 54, 229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(01)00568-7.
Z. Yang, J. Xu, W. Zhang, et al. (2007). Controlled synthesis of CuO nanostructures by a simple solution route. J Solid State Chem 180, 1390–1396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2007.02.008.
M. Qasem, R. El Kurdi, and D. Patra (2020). Green synthesis of curcumin conjugated CuO nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of methylene blue. ChemistrySelect 5, 1694–1704. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201904135.
G. Manjari, S. Saran, T. Arun, et al. (2017). Catalytic and recyclability properties of phytogenic copper oxide nanoparticles derived from Aglaia elaeagnoidea flower extract. J Saudi Chem Soc 21, 610–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2017.02.004.
M. Hachemaoui, A. Mokhtar, A. Mekki, et al. (2020). Composites beads based on Fe3O4@MCM-41 and calcium alginate for enhanced catalytic reduction of organic dyes. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.128.
Q. Zhang, D. A. Blom, and H. Wang (2014). Nanoporosity-enhanced catalysis on subwavelength Au nanoparticles: a plasmon-enhanced spectroscopic study. Chem Mater 26, 5131–5142. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm502508d.
M. A. Farrukh, P. Tan, and R. Adnan (2012). Influence of reaction parameters on the synthesis of surfactant-assisted tin oxide nanoparticles. Turk J Chem. https://doi.org/10.3906/kim-1108-36.
Park J-Y, Lee Y-J, Jun K-W, et al (2006) Chemical synthesis and characterization of highly oil dispersed MgO nanoparticles. Korean Society of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry / 한국공업화학회
S. Jadhav, S. Gaikwad, M. Nimse, and A. Rajbhoj (2011). Copper oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and their antibacterial activity. J Clust Sci 22, 121–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-011-0349-7.
M. R. Quirino, G. L. Lucena, J. A. Medeiros, et al. (2018). CuO rapid synthesis with different morphologies by the microwave hydrothermal method. Mater Res 21, 20180227. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-mr-2018-0227.
V. E. D. Prakash, U. K. Niyogi, and R. K. Diwan (2015). Characterization of synthesized copper oxide nanopowders and their use in nanofluids for enhancement of thermal conductivity. Indian J Pure Appl Phys 53, 753–758.
A. A. Radhakrishnan and B. Baskaran Beena (2014). Structural and optical absorption analysis of CuO nanoparticles. Indian J Adv Chem Sci 2 (2), 158–161.
D. P. Dubal, D. S. Dhawale, R. R. Salunkhe, et al. (2010). Fabrication of copper oxide multilayer nanosheets for supercapacitor application. J Alloys Compd 492, 26–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.11.149.
M. Zhang, X. Su, L. Ma, et al. (2021). Promotion effects of halloysite nanotubes on catalytic activity of Co3O4 nanoparticles toward reduction of 4-nitrophenol and organic dyes. J Hazard Mater 403, 123870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123870.
S. Li, H. Li, J. Liu, et al. (2015). Highly efficient degradation of organic dyes by palladium nanoparticles decorated on 2D magnetic reduced graphene oxide nanosheets. Dalt Trans 44, 9193–9199. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5dt01036e.
A. Khalil, N. Ali, A. Khan, et al. (2020). Catalytic potential of cobalt oxide and agar nanocomposite hydrogel for the chemical reduction of organic pollutants. Int J Biol Macromol 164, 2922–2930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.140.
Z. Cherifi, B. Boukoussa, A. Mokhtar, et al. (2020). Preparation of new nanocomposite poly(GDMA)/mesoporous silica and its adsorption behavior towards cationic dye. React Funct Polym 153, 104611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2020.104611.
B. Boukoussa, R. Hamacha, A. Morsli, and A. Bengueddach (2017). Adsorption of yellow dye on calcined or uncalcined Al-MCM-41 mesoporous materials. Arab J Chem 10, S2160–S2169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.07.049.
A. Hakiki, B. Boukoussa, H. Habib Zahmani, et al. (2018). Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous silica SBA-15 functionalized by mono-, di-, and tri-amine and its catalytic behavior towards Michael addition. Mater Chem Phys 212, 415–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.12.039.
Z. Abid, A. Hakiki, B. Boukoussa, et al. (2019). Preparation of highly hydrophilic PVA/SBA-15 composite materials and their adsorption behavior toward cationic dye: effect of PVA content. J Mater Sci 54, 7679–7691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03415-w.
H. Li, D. Jiang, Z. Huang, et al. (2019). Preparation of silver-nanoparticle-loaded magnetic biochar/poly(dopamine) composite as catalyst for reduction of organic dyes. J Colloid Interface Sci 555, 460–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.08.013.
M. Zhu, C. Wang, D. Meng, and G. Diao (2013). In situ synthesis of silver nanostructures on magnetic Fe3O 4@C core-shell nanocomposites and their application in catalytic reduction reactions. J Mater Chem A 1, 2118–2125. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ta00669c.
D. Nagarajan and S. Venkatanarasimhan (2019). Copper(II) oxide nanoparticles coated cellulose sponge—an effective heterogeneous catalyst for the reduction of toxic organic dyes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 22958–22970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05419-0.
P. Saikia, A. T. Miah, and P. P. Das (2017). Highly efficient catalytic reductive degradation of various organic dyes by Au/CeO2-TiO2nano-hybrid. J Chem Sci 129, 81–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-016-1203-0.
B. K. Ghosh, S. Hazra, B. Naik, and N. N. Ghosh (2015). Preparation of Cu nanoparticle loaded SBA-15 and their excellent catalytic activity in reduction of variety of dyes. Powder Technol 269, 371–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.09.027.
M. M. Khan, J. Lee, and M. H. Cho (2014). Au@TiO2 nanocomposites for the catalytic degradation of methyl orange and methylene blue: An electron relay effect. J Ind Eng Chem 20, 1584–1590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.08.002.
R. Zhang, L. Hu, S. Bao, et al. (2016). Surface polarization enhancement: high catalytic performance of Cu/CuOx/C nanocomposites derived from Cu-BTC for CO oxidation. J Mater Chem A 4, 8412–8420. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA01199C.
P. C. Nagajyothi, P. Muthuraman, T. V. M. Sreekanth, et al. (2017). Green synthesis: In-vitro anticancer activity of copper oxide nanoparticles against human cervical carcinoma cells. Arab J Chem 10, 215–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.01.011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benhadria, N., Hachemaoui, M., Zaoui, F. et al. Catalytic Reduction of Methylene Blue Dye by Copper Oxide Nanoparticles. J Clust Sci 33, 249–260 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01950-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01950-0