Abstract
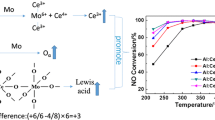
A novel Ti-doped Ce– Sn mixed oxide (Ce–Sn–Ti) catalysts were developed for the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx with NH3. The addition of titanium could improve SCR activity at a low-temperature window. By optimizing the element proportions, the NOx conversion of Ce0.6Sn2.4Ti2 catalysts could reach more than 90% in a wide-operating temperature window (200 –450 °C). The appropriate doping Ti formed Sn–O-Ti, Sn–O-Ce and Ti–O-Ce structures, which could increase the content of Ce3+ through electrons transfer from Sn or Ti to Ce (Ce3+ + Ti4+ ↔ Ce4+ + Ti3+ and 2Ce4+ + Sn2+ ↔ 2Ce3+ + Sn4+). The solid solution structure increased specific surface areas, active sites (Ce3+), and Lewis acid sites over the Ce0.6Sn2.4Ti2 catalysts. According to DRIFTS results, only bidentate nitrate could react with adsorbed NH3 species. However, adsorbed NH3 species could quickly react with the gaseous NO. The NH3-SCR reaction mechanism over Ce0.6Sn2.4Ti2 catalysts mainly followed the Eley –Rideal mechanism.
Graphic Abstract
The electron transfer between tin, cerium, and titanium elements led to generate more active sites (Ce3+) used for NH3 and NOx activation/oxidation, which improved SCR activity. The NH3-SCR reaction mechanism over Ce0.6Sn2.4Ti2 catalyst mainly followed the Eley−Rideal mechanism, in which adsorbed NH3 species could quickly react with the gaseous NO to generate N2 and H2O.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Busca G, Lietti L, Ramis G, Berti F (1998) Chemical and mechanistic aspects of the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by ammonia over oxide catalysts: A review. Appl Catal B 18:1–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(98)00040-X
Li JH, Chang HZ, Ma L, Hao JM, Yang RT (2011) Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over metal oxide and zeolite catalysts-A review. Catal Today 175:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2011.03.034
Lai JK, Wachs IE (2018) A Perspective on the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) of NO with NH3 by Supported V2O5–WO3/TiO2 Catalysts. ACS Catal 8:6537–6551. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b01357
Liu FD, He H, Ding Y, Zhang CB (2009) Effect of manganese substitution on the structure and activity of iron titanate catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Appl Catal B 93:194–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.09.029
Xu Q, Fang Z, Chen Y, Guo Y, Guo Y, Wang L, Wang Y, Zhang J, Zhan W (2020) Titania-Samarium-Manganese Composite Oxide for the Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3. Environ Sci Technol 54:2530–2538. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b06701
Han L, Cai S, Gao M, Hasegawa JY, Wang P, Zhang J, Shi L, Zhang D (2019) Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3 by Using Novel Catalysts: State of the Art and Future Prospects. Chem Rev 119:10916–10976. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00202
Guo MY, Zhao PP, Liu QL, Liu CX, Han JF, Ji N, Song CF, Ma DG, Lu XB, Liang XY, Li ZG (2019) Improved low-temperature activity and H2O resistance of Fe-doped Mn−Eu catalysts for NO removal by NH3-SCR. ChemCatChem 11:4954–4965
Kong J, Xiang Z, Li G, An T (2020) Introduce oxygen vacancies into CeO2 catalyst for enhanced coke resistance during photothermocatalytic oxidation of typical VOCs. Appl Catal B 269:118755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118755
Pushkarev VV, Kovalchuk VI, d’Itri JL (2004) Probing defect sites on the CeO2 surface with dioxygen. Phys Chem B 108:5341–5348. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0311254
Ma L, Seo CY, Nahata M, Chen XY, Li JH, Schwank JW (2018) Shape dependence and sulfate promotion of CeO2 for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Appl Catal B 232:246–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.03.065
Wei L, Cui SP, Guo HX, Ma XY, Zhang LJ (2016) DRIFT and DFT study of cerium addition on SO2 of manganese-based catalysts for low temperature SCR. J Mol Catal A 421:102–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2016.05.013
Wu ZH, Zeng YQ, Song FJ, Zhang SL, Zhong Q (2019) Active sites assembly effect on CeO2-WO3-TiO2 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Mol Catal 479:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2019.110549
Ding S, Liu F, Sh IX, Liu K, Lian Z, Xie L, He H (2015) Significant promotion effect of Mo additive on a novel Ce-Zr mixed oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:9497–9506
Liu C, Xian H, Jiang Z, Wang LH, Zhang J, Zheng LR, Tan YS, Li XG (2015) Insight into the improvement effect of the Ce doping into the SnO2 catalyst for the catalytic combustion of methane. Appl Catal B 176:542–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.04.042
Zhu YG, Wang Y, Xie J, Cao GS, Zhu TJ, Zhao XB, Yang HY (2015) Effects of graphene oxide function groups on SnO2/graphene nanocomposites for lithium storage application. Electrochim Electrochim Acta 154:338–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.12.065
Zhao Y, Teng BT, Yang ZX, Zhao Y, Zhao LH, Luo MF (2011) Density functional theory study of Sn adsorption on the CeO2 surface. J Phys Chem C 115:16461–16466. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp203640f
Zhou Y, Xie Z, Jiang J, Wang J, Song X, He Q, Ding W, Wei Z (2020) Lattice-confined Ru clusters with high CO tolerance and activity for the hydrogen oxidation reaction. Nat Catal 3:454–462. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-020-0446-9
Geng Y, Chen XL, Yang SJ, Liu FD, Shan WP (2017) Promotional Effects of Ti on a CeO2-MoO3 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:16952–16959. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b05380
ReddyBM, Khan A, Yamada Y, Kobayashi T, Loridant S, Volta JC. Structural characterization of CeO2-TiO2 and V2O5/CeO2-TiO2 catalysts by Raman and XPS techniques. J Phys Chem B 2003;107:5162–5167. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0344601
Zeng Y, Song W, Wang Y, Meng Y, Song F, Zhang S, Zhong Q (2019) The utilization of dye wastewater in enhancing catalytic activity of CeO2-TiO2 mixed oxide catalyst for NO reduction and dichloromethane oxidation. Chemosphere 235:1146–1153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.07.031
Liu C, Han JF, Bi YL, Wang J, Guo MY, Liu QL (2020) A novel Cerium-Tin composite oxide catalyst with high SO2 tolerance for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Catal Today. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2020.07.085
Li P, Xin Y, Li Q, Wang ZP, Zhang ZL, Zheng LR (2012) Ce-Ti Amorphous Oxides for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3: Confirmation of Ce-O-Ti Active Sites. Environ Sci Technol 46:9600–9605. https://doi.org/10.1021/es301661r
Yang SJ, Wang CZ, Chen JH, Peng Y, Ma L, Chang HZ, Chen L, Liu CX, Xu JY, Li JH, Yan NQ (2012) A novel magnetic Fe-Ti-V spinel catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 in a broad temperature range. Catal Sci Technol 2:915–917. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cy00459c
Gu TT, Jin RB, Liu Y, Liu HF, Weng XL, Wu ZB (2013) Promoting effect of calcium doping on the performances of MnOx/TiO2 catalysts for NO reduction with NH3 at low temperature. Appl Catal B 129:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.09.003
Li WM, Liu HD, Chen YF (2017) Promotion of transition metal oxides on the NH3-SCR performance of ZrO2-CeO2 catalyst. Front Env Sci Eng 11:6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-017-0914-x
Qu RY, Gao X, Cen KF, Li JH (2013) Relationship between structure and performance of a novel cerium-niobium binary oxide catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Appl Catal B 142:290–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.05.035
Chang H, Li J, Chen X, Ma L, Yang S, Schwank JW, Hao J (2012) Effect of Sn on MnO-CeO2 catalyst for SCR of NO by ammonia: Enhancement of activity and remarkable resistance to SO2. Catal Commun 27:54–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2012.06.022
Wang X, Wang F, Qi L, Guo R, Li B, Chen D, Zou H (2020) Orientation transition, dielectric, and ferroelectric behaviors of sol-gel derived PZT thin films deposited on Ti–Pt alloy layers: A Ti content-dependent study. Ceram Int 46:10256–10261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.01.018
Cheng LS, Yang RT, Chen N (1996) Iron oxide and chromia supported on titania-pillared clay for selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide with ammonia. J Catal 164:70–81. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcat.1996.0364
Gao X, Jiang Y, Zhong Y, Luo ZY, Cen KF (2010) The activity and characterization of CeO2-TiO2 catalysts prepared by the sol-gel method for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J Hazard Mater 174:734–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.112
Meng DM, Zhan WC, Guo Y, Guo YL, Wang L, Lu GZ (2015) A Highly Effective Catalyst of Sm-MnOx for the NH3-SCR of NOx at Low Temperature: Promotional Role of Sm and Its Catalytic Performance. Acs Catal 5:5973–5983. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.5b00747
Qi GS, Yang RT, Chang R (2004) MnOx-CeO2 mixed oxides prepared by co-precipitation for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperatures. Appl Catal B 51:93–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2004.01.023
Qi GS, Yang RT (2004) Characterization and FTIR studies of MnOx-CeO2 catalyst for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J Phys Chem B 108:15738–15747. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp048431h
Fan ZY, Shi JW, Gao C, Gao G, Wang BR, Niu CM (2017) Rationally Designed Porous MnOx-FeOx Nanoneedles for Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by NH3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:16117–16127. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b00739
Chen L, Si Z, Wu X, Weng D (2014) DRIFT study of CuO-CeO2-TiO2 mixed oxides for NOx reduction with NH3 at low temperatures. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:8134–8145. https://doi.org/10.1021/am5004969
Liu Z, Feng X, Zhou Z, Feng Y, Li J (2018) Ce-Sn binary oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO x by NH3. Appl Surf Sci 428:526–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.09.175
Liu ZM, Liu HY, Zeng H, Xu Q (2016) A novel Ce-Sb binary oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Catal Sci Technol 6:8063–8071. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cy01756h
Gao C, Shi JW, Fan ZY, Wang BR, Wang Y, He C, Wang XB, Li J, Niu CM (2018) “Fast SCR” reaction over Sm-modified MnOx-TiO2 for promoting reduction of NOx with NH3. Appl Catal A 564:102–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2018.07.017
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Fund of China (Grant No. 21507100) and Development (Air pollution causes and control technology research) Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFC0205302) and Science and Technology Project of Hebei Province(No. 206Z3702G) and National Key R&D Program of China: Technology integration & engineering demonstration of efficiently secure disposal system for municipal solid wastes (Grant Nos. 2019YFC1904102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Bi, Y., Wang, H. et al. Promotional Effects on NH3-SCR Performance of CeO2–SnO2 Catalysts Doped by TiO2: A Mechanism Study. Catal Surv Asia 25, 48–57 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10563-020-09318-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10563-020-09318-0