Abstract
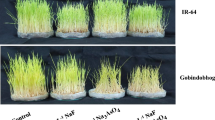
The manuscript aimed to explore the differential responses of Vigna radiata and Vigna mungo to fluoride (25 mg L−1 NaF) stress and validate the protective roles of sodium nitroprusside (SNP) (50 µM). V. radiata showed 53.5% higher bioaccumulation of fluoride compared to V. mungo. The overall growth in V. radiata was more affected (32.0%) compared with V. mungo (6.3%), which on the contrary displayed regulated fluoride entry and fluoride-adaptive phenotype. Fluoride bioaccumulation in V. radiata significantly triggered H2O2 and methylglyoxal accumulation, electrolyte leakage, chlorophyll degradation and lipid peroxidation, which accounted for its fluoride sensitivity. Exogenous SNP alleviated fluoride toxicity in both the species by synthesizing osmolytes (proline, glycine-betaine and total amino acids), non-enzymatic antioxidants (anthocyanins, flavonoids, total phenolics, carotenoids, ascorbate and glutathione) and activating antioxidative enzymes (APX, SOD, GPX, GST, GPOX and GR). Fluoride toxicity inhibited the CAT activity to a higher degree in V. radiata (51.0%) than V. mungo (31.3%). However, SNP supplementation rescued the CAT activity, lowered the fluoride uptake and membrane damage, and also alleviated oxidative stress in both the species, along with accelerated growth recovery and chlorophyll conservation. Cytotoxic methylglyoxal was efficiently detoxified in presence of SNP due to enhanced activity of the glyoxalases. Exogenous SNP also triggered endogenous NO formation along with up regulating the activity of P5CS and PAL, which stimulated proline and flavonoid biosynthesis during stress. Statistical analyses revealed that the ameliorating potential of SNP was more prominent in the susceptible species. Overall, our investigation established V. radiata and V. mungo as fluoride-sensitive and fluoride-tolerant species, respectively, and also illustrated the efficacy of SNP in abating stress-induced damages in Vigna by augmenting the defence machinery.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas ZK (2018) Sodium nitroprusside improves performance of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) under salt stress. Biosci Biotechnol Res Asia 15(3):603–10
Agarwal S, Khan S (2016) Sodium fluoride (NaF) induced changes in growth and DNA profile of Vigna radiata. Plant Sci Today 3:1–5
Banerjee A, Roychoudhury A (2019a) Structural introspection of a putative fluoride transporter in plants. 3 Biotech 9:103
Banerjee A, Roychoudhury A (2019b) Differential regulation of defence pathways in aromatic and non-aromatic indica rice cultivars towards fluoride toxicity. Plant Cell Rep 38:1217–1233
Banerjee A, Roychoudhury A (2020a) Gibberellic acid-priming promotes fluoride tolerance in a susceptible indica rice cultivar by regulating the antioxidant and phytohormone homeostasis. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10110-7
Banerjee A, Roychoudhury A (2020b) Differential lead-fluoride and nickel-fluoride uptake in co-polluted soil variably affects the overall physiome in an aromatic rice cultivar. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115504
Banerjee A, Roychoudhury A, Ghosh P (2019) Differential fluoride uptake induces variable physiological damage in a non-aromatic and an aromatic indica rice cultivar. Plant Physiol Biochem 142:143–150
Banerjee A, Singh A, Roychoudhury A (2020a) Fluoride toxicity variably affects overall physiology and grain development in three contrasting rice genotypes, representing a potential biohazard. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10604-7
Banerjee A, Samanta S, Roychoudhury A (2020b) Spermine ameliorates prolonged fluoride toxicity in soil-grown rice seedlings by activating the antioxidant machinery and glyoxalase system. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 189:109737
Banerjee A, Singh A, Sudarshan M, Roychoudhury A (2021) Silicon nanoparticle-pulsing mitigates fluoride stress in rice by fine-tuning the ionomic and metabolomics balance and refining agronomic traits. Chemosphere 262:127826
Bhattacharya P, Samal AC (2018) Fluoride contamination in groundwater, soil and cultivated foodstuffs of India and its associated health risks: a review. Res J Recent Sci 7:36–47
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Campos FV, Oliveira JA, Pereira MG, Farnese FS (2019) Nitric oxide and phytohormone interactions in the response of Lactuca sativa to salinity stress. Planta 250:1475–1489
Chakrabarti S, Patra PK (2015) Biochemical and antioxidant responses of paddy (Oryza sativa L.) to fluoride stress. Fluoride 48:56–61
Dey U, Mondal NK, Das K, Datta JK (2012) Dual effects of fluoride and calcium on the uptake of fluoride, growth physiology, pigmentation, and biochemistry of Bengal gram seedlings (Cicer arietinum L.). Fluoride 45:389–393
Dwivedi R, Singh VP, Kumar J, Prasad SM (2015) Differential physiological and biochemical responses of two Vigna species under enhanced UV-B radiation. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 8:173–181
Esringu A, Aksakal O, Tabay D, Kara AA (2015) Effects of sodium nitroprusside (SNP) pretreatment on UV-B stress tolerance in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:589–597
Gadi BR, Verma P, Ram A (2012) Influence of NaF on seed germination, membrane stability and some biochemicals content in Vigna seedlings. J Chem Biol Phys Sci 2:1371–1378
Gautam V, Sharma P, Bakshi P, Arora S, Bhardwaj R, Paray BA, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2020) Effect of Rhododendron arboreum leaf extract on the antioxidant defense system against chromium (VI) stress in Vigna radiata plants. Plants 9:164
Ghosh P, Roychoudhury A (2018) Differential levels of metabolites and enzymes related to aroma formation in aromatic indica rice varieties: comparison with non-aromatic varieties. 3 Biotech 8:25
Hasanuzzaman M, Alam MM, Nahar K, Mohsin SM, Bhuyan MHMB, Parvin K, Nowak-Hawrylak B, Fujita M (2019) Silicon-induced antioxidant defense and methylglyoxal detoxification works coordinately in alleviating nickel toxicity in Oryza sativa L. Ecotoxicology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-019-02019-z
Hong BD, Joo RN, Lee KS, Lee DS, Rhie JH, Min SW, Song SG, Chung DY (2016) Fluoride in soil and plant. Korean J Agric Sci 43:522–536
Ismail GSM (2012) Protective role of nitric oxide against arsenic-induced damages in germinating mung bean seeds. Acta Physiol Plant 34:1303–1311
Khairy AIH, Oh MJ, Lee SM, Kim DS, Roh KS (2016) Nitric oxide overcomes Cd and Cu toxicity in in vitro-grown tobacco plants through increasing contents and activities of rubisco and rubisco activase. Biochim Open 2:41–51
Kumar KA, Varaprasad P, Rao AVB (2009) Effect of fluoride on catalase, guaiacol peroxidase and ascorbate oxidase activities in two verities of mulberry leaves (Morus alba L.). Res J Earth Sci 1:69–73
Lei Y, Yin C, Ren J, Li C (2007) Effect of osmotic stress and sodium nitroprusside pretreatment on proline metabolism of wheat seedlings. Biol Plant 51:386–390
Mostofa MG, Seraj ZI, Fujita M (2014) Exogenous sodium nitroprusside and glutathione alleviate copper toxicity by reducing copper uptake and oxidative damage in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Protoplasma 251:1373–1386
Mostofa MG, Rahman MM, Ansary MMU, Fujita M, Tran L-SP (2019) Interactive effects of salicylic acid and nitric oxide in enhancing rice tolerance to cadmium stress. Int J Mol Sci 20:5798
Parween T, Jan S, Mahmooduzzafar FT (2012) Evaluation of oxidative stress in Vigna radiata L. in response to chlorpyrifos. Int J Environ Sci Technol 9:605–612
Paul S, Roychoudhury A, Banerjee A, Chaudhuri N, Ghosh P (2017) Seed pretreatment with spermidine alleviates oxidative damages to different extent in the salt (NaCl)-stressed seedlings of three indica rice cultivars with contrasting level of salt tolerance. Plant Gene 11:112–123
Ren Y, Wang W, He J, Zhang L, Wei Y, Yang M (2020) Nitric oxide alleviates salt stress in seed germination and early seedling growth of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) by enhancing physiological and biochemical parameters. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 187:109785
Shi H-T, Li R-J, Cai W, Liu W, Wang C-L, Lu Y-T (2011) Increasing nitric oxide content in Arabidopsis thaliana by expressing rat neuronal nitric oxide synthase resulted in enhanced stress tolerance. Plant Cell Physiol 53:344–357
Silveira NM, Hancock JT, Frungillo L, Siasou E, Marcos FCC, Salgado I, Machado EC, Ribeiro RV (2017) Evidence towards the involvement of nitric oxide in drought tolerance of sugarcane. Plant Physiol Biochem 115:354–359
Simontacchi M, Galatro A, Ramos-Artuso F, Santa-María GE (2015) Plant survival in a changing environment: the role of nitric oxide in plant responses to abiotic stress. Front Plant Sci 6:977
Singh A, Roychoudhury A (2020) Silicon-regulated antioxidant and osmolyte defense and methylglyoxal detoxification functions co-ordinately in attenuating fluoride toxicity and conferring protection to rice seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 154:758–769
Singh A, Banerjee A, Roychoudhury A (2020a) Seed priming with calcium compounds abrogate fluoride-induced oxidative stress by upregulating defence pathways in an indica rice variety. Protoplasma 257:767–782
Singh A, Roychoudhury A, Samanta S, Banerjee A (2020b) Fluoride stress-mediated regulation of tricarboxylic acid cycle and sugar metabolism in rice seedlings in absence and presence of exogenous calcium. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10202-4
Vishwakarma A, Wany A, Pandey S, Bulle M, Kumari A, Kishorekumar R, Igamberdiev AU, Mur LAJ, Gupta KJ (2019) Current approaches to measure nitric oxide in plants. J Exp Bot 70:4333–4343
Waśkiewicz A, Beszterda M, Goliński P (2014) Nonenzymatic antioxidants in plants. In: Ahmad P (ed) Oxidative damage to plants. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 201–234
Xu Y, Sun X, Jin J, Zhou H (2010) Protective effect of nitric oxide on light-induced oxidative damage in leaves of tall fescue. J Plant Physiol 167:512–518
Xu LL, Fan ZY, Dong YJ, Kong J, Bai XY (2014) Effects of exogenous salicylic acid and nitric oxide on physiological characteristics of two peanut cultivars under cadmium stress. Biol Plant 59:171–182
Yadu B, Chandrakar V, Meena R, Sahu K (2017) Glycine betaine reduces oxidative injury and enhances fluoride stress tolerance via improving antioxidant enzymes, proline and genomic template stability in Cajanus cajan L. South Afr J Bot 111:68–75
Zhang Y, Wang L, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Wei Q, Zhang W (2006) Nitric oxide enhances salt tolerance in maize seedlings through increasing activities of proton-pump and Na+/H+ antiport in the tonoplast. Planta 224:545–555
Acknowledgements
Financial assistance from Science and Engineering Research Board, Government of India through the Grant [EMR/2016/004799] and Department of Higher Education, Science and Technology and Biotechnology, Government of West Bengal, through the Grant [264(Sanc.)/ST/P/S&T/1G-80/2017] to Dr. Aryadeep Roychoudhury is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS performed all the experiments and drafted the manuscript. AB assisted AS in chlorophyll estimation, and in Pearson’s correlation matrix and principal component analysis. Dr. AR designed all the experiments, supervised the overall work, critically drafted and reviewed the manuscript and incorporated necessary modifications.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in submitting this manuscript.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Tariq Aftab.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A., Banerjee, A. & Roychoudhury, A. Differential Responses of Vigna radiata and Vigna mungo to Fluoride-Induced Oxidative Stress and Amelioration via Exogenous Application of Sodium Nitroprusside. J Plant Growth Regul 40, 2342–2357 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10285-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10285-z