Abstract
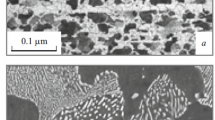
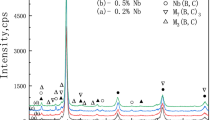
The structure and the mechanical properties of a cast high-nitrogen austenitic steel are studied after hot and cold deformation. The as-cast steel contains the FeCrB and BN phases. During hot deformation, the B13N13C74 phase forms. This phase has a layered structure and is easily deformed during hot or cold rolling. The existence of the B13N13C74 phase only slightly changes the strength and the ductility, but it substantially decreases the impact toughness of the steel as compared to that of similar boron-free Cr–Mn–Ni high-nitrogen austenitic steels.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. Kulka, D. Mikolajczak, N. Makuch, P. Dziarski, and A. Miclaszewski, “Wear resistance improvement of austenitic 316L steel by laser alloying with boron,” Surf. Coat. Technol. 291, 292–313 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.02.058
J. R. Cruz, S. L. Henke, Anderson G. M. Pukasiewicz, and Ana Sofia C. M. d’Oliveira, “The effect of boron on cavitation resistance of FeCrMnSiB austenitic stainless steels,” Wear 436–437, 203041 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear2019.203041
I. Akkurt, A. Calik, and H. Akyildirim, “The boronizing effect on the radiation shielding and magnetization properties of AISI 316L austenitic stainless steel,” Nucl. Eng. Des. 241 (1), 55–58 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucengdes.2010.10.009
T. Okita, W. G. Wolfer, F. A. Garner, and N. Sekimura, “Influence of boron on void swelling in model austenitic steels,” J. Nucl. Mater. 329–333 (Part B), 1013–1016 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2004.04.126
F. L. Serafini, M. Peruzzo, I. Krindges, M. F. C. Ordoñez, D. Rodrigues, R. M. Souza, and M. C. M. Farias, “Microstructure and mechanical behavior of 316L liquid phase sintered stainless steel with boron addition,” Mater. Char. 152, 253–264 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2019.04.009
M. Peruzzo, T. D. Beux, M. F. C. Ordoñez, R. M. Sonza, and M. C. M. Farias, “High-temperature oxidation of sintered austenitic stainless steel containing boron or yttria,” Cor. Sci. 129, 26–37 (2017).
L. G. Rigina, “Study and development of the technology of EShP and EShPD chromium–manganese steels alloyed with nitrogen,” Cand. Sci. (Eng.) Dissertation, Moscow, NPO TsNIITMASh, 2005.
I. O. Bannykh, “Structural features and perspectives of applying high-nitrogen austenitic steels,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 5, 22–29 (2019).
L. R. Botvina, V. M. Blinov, M. R. Tyutin, I. O. Bannykh, and E. V. Blinov, “Fracture of high-nitrogen 05KH20G10N3AMF steel during impact loading,” Russ. Metall. (Metally), No. 3, 239–247 (2012).
Funding
This work is supported by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation, state assignment no. 075-00947-20-00.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by Yu. Ryzhkov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bannykh, I.O., Bannykh, O.A., Rigina, L.G. et al. Structure, Phase Composition, and Mechanical Properties of a Boron-Containing High-Nitrogen Austenitic Steel Made by Induction Melting. Russ. Metall. 2020, 1439–1445 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S003602952012006X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S003602952012006X