Abstract
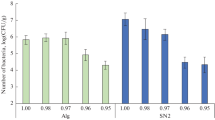
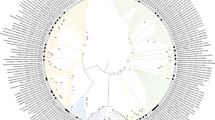
The results of the phylogenetic analysis and analysis of the physiological characteristics of metabolic activity of strains isolated from frozen sedimentary rocks collected in the Antarctic and the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago are reported in this article. A comparable abundance of cultured cells and close morphological diversity of colony morphotypes were revealed in all samples. Representatives of the Actinobacteria and Firmicutes phyla were predominant in the cultured bacterial communities. These communities were characterized by mesophilic and neutrophilic optima, as well as by the wide ranges of temperatures and pH suitable for metabolic activity. Moderate halotolerance in the presence of sodium or potassium chloride, as well as the high inhibitory effect of sodium hydrocarbonate and low inhibitory effect of magnesium sulfate, were revealed. The communities were highly resistant to the presence of 5% magnesium perchlorate in the culture medium. Strains resistant to antibiotics in the composition of the medium were revealed: The isolated strains were the most resistant to ampicillin, chloramphenicol, and cephalexin.











Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Andersson, D.I., Persistence of antibiotic resistant bacteria, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 452–456.
Bai, Y., Yang, D., Wang, J., Xu, S., Wang, X., and An, L., Phylogenetic diversity of culturable bacteria from alpine permafrost in the Tianshan Mountains, northwestern China, Res. Microbiol., 2006, vol. 157, no. 8, pp. 741–751.
Belov, A.A., Cheptsov, V.S., and Vorobyova, E.A., Soil bacterial communities of Sahara and Gibson deserts: Physiological and taxonomical characteristics, AIMS Microbiol., 2018, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 685–710.
Belov, A.A., Cheptsov, V.S., Vorobyova, E.A., Manucharova, N.A., and Ezhelev, Z.S., Stress-tolerance and taxonomy of culturable bacterial communities isolated from a central Mojave Desert soil sample, Geosciences, 2019, vol. 9, no. 4, p. 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9040166
Bulat, S.A., Microbiology of the subglacial Lake Vostok: first results of borehole-frozen lake water analysis and prospects for searching for lake inhabitants, Philos. Trans. R. Soc., A, 2016, vol. 374, no. 2059, p. 20140292.
Bull, A.T., Actinobacteria of the extremobiosphere, Extremophiles Handbook, 2011, pp. 1203–1240.
Chattopadhyay, M.K., Mechanism of bacterial adaptation to low temperature, J. Biosci., 2006, vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 157–165.
Christner, B.C., Kvitko, B.H., and Reeve, J.N., Molecular identification of bacteria and eukarya inhabiting an Antarctic cryoconite hole, Extremophiles, 2003, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 177–183.
Clark, B.C. and Van Hart, D.C., The salts of Mars, Icarus, 1981, vol. 45, no. 2, pp. 370–378.
Clarke, A., The thermal limits to life on Earth, Int. J. Astrobiol., 2014, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 141–154.
Efimenko, T.A., Efremenkova, O.V., Demkina, E.V., Petrova, M.A., Sumarukova, I.G., Vasilyeva, B.F., and El’‑Registan, G.I., Bacteria isolated from Antarctic permafrost are efficient antibiotic producers, Microbiology, 2018, vol. 87, no. 5, pp. 692–698.
Foght, J., Aislabie, J., Turner, S., Brown, C.E., Ryburn, J., Saul, D.J., and Lawson, W., Culturable bacteria in subglacial sediments and ice from two southern hemisphere glaciers, Microb. Ecol., 2004, vol. 47, no. 4, pp. 329–340.
Gilichinsky, D.A., Wilson, G.S., Friedmann, E.I., Mckay, C.P., Sletten, R.S., Rivkina, E.M., Vishnivetskaya, T.A., Erokhina, L.G., Ivanushkina, N.E., Kochkina, G.A., Shcherbakova, V.A., Soina, V.S., Spirina, E.V., Vorobyova, E.A., Fyodorov-Davydov, D.G., Hallet, B, Ozerskaya, S.M., Sorokovikov, V.A., Laurinavichyus, K.S., Shatilovich, A.V., Chanton, J.P., Ostroumov, V.E., and Tiedje, J.M., Microbial populations in Antarctic permafrost: biodiversity, state, age, and implication for astrobiology, Astrobiology, 2007, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 275–311.
Gilichinsky, D., Vishnivetskaya, T., Petrova, M., Spirina, E., Mamykin, V., and Rivkina, E., Bacteria in permafrost, Psychrophiles: From Biodiversity to Biotechnology, Margesin, R., Schinner, F., Marx, J.C., and Gerday, C., Eds., Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2008, pp. 83–102.
Goordial, J., Davila, A., Lacelle, D., Pollard, W., Marinova, M.M., Greer, C.W., DiRuggiero, J., McKay, C.P., and Whyte, L.G., Nearing the cold-arid limits of microbial life in permafrost of an upper dry valley, Antarctica, ISME J., 2016, vol. 10, no. 7, p. 1613.
Hallbeck, L., Microbial Processes in Glaciers and Permafrost. A Literature Study on Microbiology Affecting Groundwater at Ice Sheet Melting, Stockholm: Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Co, 2009.
Hartmann, D.L., Global Physical Climatology, Newnes, 2015, vol. 103.
Humphrey, J., Seitz, T., Haan, T., Ducluzeau, A.-L., and Drown, D.M., Complete genome sequence of Pantoea agglomerans TH81, isolated from a permafrost thaw gradient, Microbiol. Resour. Announc., 2019, vol. 8, no. 1, p. e01486-18. https://doi.org/10.1128/MRA.01486-18
Jansson, J.K. and Taş, N., The microbial ecology of permafrost, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2014, vol. 12, no. 6, p. 414.
Kryazhevskikh, N.A., Demkina, E.V., Manucharova, N.A., Soina, V.S., Gal’chenko, V.F., and El’-Registan, G.I., Reactivation of dormant and nonculturable bacterial forms from paleosoils and subsoil permafrost, Microbiology, 2012, vol. 81, no. 4, pp. 435–445.
Lopatina, A., Krylenkov, V., and Severinov, K., Activity and bacterial diversity of snow around Russian Antarctic stations, Res. Microbiol., 2013, vol. 164, no. 9, pp. 949–958.
Nicholson, W.L., Munakata, N., Horneck, G., Melosh, H.J., and Setlow, P., Resistance of Bacillus endospores to extreme terrestrial and extraterrestrial environments, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2000, vol. 64, no. 3, pp. 548–572.
Petrovskaya, L.E., Novototskaya-Vlasova, K.A., Spirina, E.V., Khokhlova, G.V., Rivkina, E.M., Gilichinsky, D.A., Dolgikh, D.A., and Kirpichnikov, M.P., Lipolytic enzymes of microorganisms from permafrost cryopegs, Dokl. Biol. Sci., 2012, vol. 445, no. 1, pp. 279–282.
de los Ríos, A., Ascaso, C., Wierzchos, J., Fernández-Valiente, E., and Quesada, A., Microstructural characterization of cyanobacterial mats from the McMurdo Ice Shelf, Antarctica, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 70, no. 1, pp. 569–580.
Rivkina, E., Gilichinsky, D., Wagener, S., Tiedje, J., and McGrath, J., Biogeochemical activity of anaerobic microorganisms from buried permafrost sediments, Geomicrobiol. J., 1998, vol. 15. no. 3, pp. 187–193.
Rivkina, E.M., Friedmann, E.I., McKay, C.P., and Gilichinsky, D.A., Metabolic activity of permafrost bacteria below the freezing point, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2000, vol. 66, no. 8, pp. 3230–3233.
Romero, D., Traxler, M.F., López, D., and Kolter, R., Antibiotics as signal molecules, Chem. Rev., 2011, vol. 111, no. 9, pp. 5492–5505.
Rothschild, L.J. and Mancinelli, R.L., Life in extreme environments, Nature, 2001, vol. 409, no. 6823, pp. 1092–1101.
Sepehr, S., Shahnavaz, B., Asoodeh, A., and Karrabi, M., Biodegradation of phenol by cold-tolerant bacteria isolated from alpine soils of Binaloud Mountains in Iran, J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng., 2019, vol. 54, no. 4, pp. 367–379.
Singh, P., Singh, S.M., Singh, R.N., Naik, S., Roy, U., Srivastava, A., and Bölter, M., Bacterial communities in ancient permafrost profiles of Svalbard, Arctic, J. Basic Microbiol., 2017, vol. 57, no. 12, pp. 1018–1036.
Stetter, K.O., Fiala, G., Huber, G., Huber, R., and Segerer, A., Hyperthermophilic microorganisms, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 1990, vol. 75, no. 2–3, pp. 117–124.
Steven, B., Leveille, R., Pollard, W.H., and Whyte, L.G., Microbial ecology and biodiversity in permafrost, Extremophiles, 2006, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 259–267.
Steven, B., Pollard, W.H., Greer, C.W., and Whyte, L.G., Microbial diversity and activity through a permafrost/ground ice core profile from the Canadian high Arctic, Environ. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 10, no. 12, pp. 3388–3403.
Suzina, N.E., Esikova, T.Z., Oleinikov, R.R., Gafarov, A.B., Shorokhova, A.P., Polivtseva, V.N., Ross, D.V., Abashina, T.N., Duda, V.I., and Boronin, A.M., Comparative characteristics of free-living ultramicroscopical bacteria obtained from extremal biotopes, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 51, no. 2, pp. 159–168.
Taş, N., Prestat, E., McFarland, J.W., Wickland, K.P., Knight, R., Behre, A.A., Jorgenson, T., Waldrop, M.P., and Jansson, J.K., Impact of fire on active layer and permafrost microbial communities and metagenomes in an upland Alaskan boreal forest, ISME J., 2014, vol. 8, no. 9, p. 1904–1919.
Vishnivetskaya, T.A., Allan, J., Cheng, K., Chourey, K., Hettich, R.L., Layton, A., Liu, X., Murphy, J., Myky-tczuk, N.C., Phelps, T.J., Pfiffner, S.M., Saarunya, G., Stackhouse, B.T., Whyte, L., and Onstott, T.C., Microbial activity in active and upper permafrost layers in Axel Heiberg Island, AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, 2011.
Wagner, D., Lipski, A., Embacher, A., and Gattinger, A., Methane fluxes in permafrost habitats of the Lena Delta: effects of microbial community structure and organic matter quality, Environ. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 7, no. 10, pp. 1582–1592.
Wood, W.A. and Krieg, N.R., Methods for general and molecular bacteriology, Washington, D.C.: Am. Soc. Microbiol., 1989.
Yergeau, E., Hogues, H., Whyte, L.G., and Greer, C.W., The functional potential of high Arctic permafrost revealed by metagenomic sequencing, qPCR and microarray analyses, ISME J., 2010, vol. 4, no. 9, pp. 1206–1214.
Yergeau, E., Newsham, K.K., Pearce, D.A., and Kowalchuk, G.A., Patterns of bacterial diversity across a range of Antarctic terrestrial habitats, Environ. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 9, no. 11, pp. 2670–2682.
Zeng, Y.H., Koblížek, M., Li, Y.X., Liu, Y.P., Feng, F.Y., Ji, J.D., Jian, J.C., and Wu, Z.H., Long PCR RFLP of 16S-ITS-23S rRNA genes: a high resolution molecular tool for bacterial genotyping, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2013, vol. 114, no. 2, pp. 433–447.
Zhang, G., Ma, X., Niu, F., Dong, M., Feng, H., An, L., and Cheng, G., Diversity and distribution of alkaliphilic psychrotolerant bacteria in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau permafrost region, Extremophiles, 2007, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 415–424.
Zhu, S., Zhao, Q., Zhang, G., Jiang, Z., Sheng, H., Feng, H., and An, L., Paracoccus tibetensis sp. nov., isolated from Qinghai-Tibet Plateau permafrost, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2013, vol. 63, no. 5, pp. 1902–1905.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 18-34-00331) and by the Program of the Presidium of the Russian Academy of Sciences “Evolution of the Organic World and Planetary Processes” (Subprogram 1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by A. Panyushkina
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belov, A.A., Cheptsov, V.S., Vorobyova, E.A. et al. Culturable Bacterial Communities Isolated from Cryo-Arid Soils: Phylogenetic and Physiological Characteristics. Paleontol. J. 54, 903–912 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031030120080043
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031030120080043