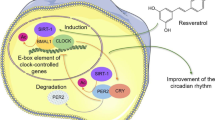
Abstract
The circadian clock is the biological mastermind governing orderly execution of bodily processes throughout the day. In recent years, an emerging topic of broad interest is clock-modulatory agents, including small molecules both of synthetic and natural origins, and their potential applications in disease models. Nobiletin is a naturally occurring flavonoid with the greatest abundance found in citrus peels. Extensive research has shown that Nobiletin is endowed with a wide range of biological activities, yet its mechanism of action remains unclear. We recently found through unbiased chemical screening that Nobiletin impinges on the clock machinery to activate temporal control of downstream processes within the cell and throughout the body. Using animal models of diseases and aging, we and others illustrate potent beneficial effects of Nobiletin on cellular energetics in both periphery and brain to promote healthy aging. Given its excellent safety profile, Nobiletin may represent a promising candidate molecule for development of nutraceutical and chronotherapeutic agents against chronic and age-related neurodegenerative diseases.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s Disease
- CI:
-
Complex I
- CIII:
-
Complex III
- CIV:
-
Complex IV
- CL:
-
cardiolipin
- SC:
-
supercomplex
- NOB:
-
Nobiletin
- TRF:
-
time-restricted feeding
References
Ben-Aziz, A. (1967) Nobiletin is main fungistat in tangerines resistant to mal secco, Science, 155, 1026-1027, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.155.3765.1026.
Walle, T. (2007) Methoxylated flavones, a superior cancer chemopreventive flavonoid subclass? Semin. Cancer Biol., 17, 354-362, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2007.05.002.
Mulvihill, E. E., Burke, A. C., and Huff, M. W. (2016) Citrus flavonoids as regulators of lipoprotein metabolism and atherosclerosis, Annu. Rev. Nutr., 36, 275-299, https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071715-050718.
Huang, H., Li, L., Shi, W., Liu, H., Yang, J., Yuan, X., and Wu, L. (2016) The multifunctional effects of nobiletin and its metabolites in vivo and in vitro, Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med., 2016, 2918796, https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2918796.
Evans, M., Sharma, P., and Guthrie, N. (2012) Bioavailability of Citrus Polymethoxylated Flavones and Their Biological Role in Metabolic Syndrome and Hyperlipidemia, InTech, pp. 1-19.
Zhang, H., Cui, J., Tian, G., DiMarco-Crook, C., Gao, W., et al. (2019) Efficiency of four different dietary preparation methods in extracting functional compounds from dried tangerine peel, Food Chem., 289, 340-350, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.03.063.
Gloston, G. F., Yoo, S. H., and Chen, Z. J. (2017) Clock-enhancing small molecules and potential applications in chronic diseases and aging, Front. Neurol., 8, 100, https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2017.00100.
Bell-Pedersen, D., Cassone, V. M., Earnest, D. J., Golden, S. S., Hardin, P. E., Thomas, T. L., and Zoran, M. J. (2005) Circadian rhythms from multiple oscillators: lessons from diverse organisms, Nat. Rev. Genet., 6, 544-556, https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1633.
Takahashi, J. S. (2017) Transcriptional architecture of the mammalian circadian clock, Nat. Rev. Genet., 18, 164-179, https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2016.150.
Green, C. B., Takahashi, J. S., and Bass, J. (2008) The meter of metabolism, Cell, 134, 728-742, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.022.
Zhang, E. E., and Kay, S. A. (2010) Clocks not winding down: unravelling circadian networks, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 11, 764-776, https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2995.
Zhang, R., Lahens, N. F., Ballance, H. I., Hughes, M. E., and Hogenesch, J. B. (2014) A circadian gene expression atlas in mammals: implications for biology and medicine, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 111, 16219-16224, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1408886111.
Mure, L. S., Le, H. D., Benegiamo, G., Chang, M. W., Rios, L., et al. (2018) Diurnal transcriptome atlas of a primate across major neural and peripheral tissues, Science, 359, eaao0318, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao0318.
Mohawk, J. A., Green, C. B., and Takahashi, J. S. (2012) Central and peripheral circadian clocks in mammals, Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 35, 445-462, https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-060909-153128.
Chen, Z., Yoo, S. H., and Takahashi, J. S. (2018) Development and therapeutic potential of small-molecule modulators of circadian systems, Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 58, 231-252, https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010617-052645.
Miller, S., and Hirota, T. (2020) Pharmacological interventions to circadian clocks and their molecular bases, J. Mol. Biol., 432, 3498-3514, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2020.01.003.
He, B., and Chen, Z. (2016) Molecular targets for small-molecule modulators of circadian clocks, Curr. Drug Metab., 17, 503-512.
He, B., Nohara, K., Park, N., Park, Y. S., Guillory, B., et al. (2016) The small molecule nobiletin targets the molecular oscillator to enhance circadian rhythms and protect against metabolic syndrome, Cell Metab., 23, 610-621, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.03.007.
Shinozaki, A., Misawa, K., Ikeda, Y., Haraguchi, A., Kamagata, M., Tahara, Y., and Shibata, S. (2017) Potent effects of flavonoid nobiletin on amplitude, period, and phase of the circadian clock rhythm in PER2::LUCIFERASE mouse embryonic fibroblasts, PLoS One, 12, e0170904, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170904.
Mulvihill, E. E., Assini, J. M., Lee, J. K., Allister, E. M., Sutherland, B. G., et al. (2011) Nobiletin attenuates VLDL overproduction, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis in mice with diet-induced insulin resistance, Diabetes, 60, 1446-1457, https://doi.org/10.2337/db10-0589.
Lee, Y. S., Cha, B. Y., Choi, S. S., Choi, B. K., Yonezawa, T., Teruya, T., Nagai, K., and Woo, J. T. (2013) Nobiletin improves obesity and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced obese mice, J. Nutr. Biochem., 24, 156-162, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.03.014.
Hatori, M., Vollmers, C., Zarrinpar, A., DiTacchio, L., Bushong, E. A., et al. (2012) Time-restricted feeding without reducing caloric intake prevents metabolic diseases in mice fed a high-fat diet, Cell Metab., 15, 848-860, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.019.
Chaix, A., Zarrinpar, A., Miu, P., and Panda, S. (2014) Time-restricted feeding is a preventative and therapeutic intervention against diverse nutritional challenges, Cell Metab., 20, 991-1005, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.11.001.
Chaix, A., Lin, T., Le, H. D., Chang, M. W., and Panda, S. (2019) Time-restricted feeding prevents obesity and metabolic syndrome in mice lacking a circadian clock, Cell Metab., 29, 303-319 e304, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.08.004.
Gibson, E. M., Williams, W. P., 3rd, and Kriegsfeld, L. J. (2009) Aging in the circadian system: considerations for health, disease prevention and longevity, Exp. Gerontol., 44, 51-56, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2008.05.007.
Sato, S., Solanas, G., Peixoto, F. O., Bee, L., Symeonidi, A., et al. (2017) Circadian reprogramming in the liver identifies metabolic pathways of aging, Cell, 170, 664-677.e611, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.042.
Kondratova, A. A., and Kondratov, R. V. (2012) The circadian clock and pathology of the ageing brain, Nat .Rev. Neurosci., 13, 325-335, https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3208.
Davidson, A. J., Sellix, M. T., Daniel, J., Yamazaki, S., Menaker, M., and Block, G. D. (2006) Chronic jet-lag increases mortality in aged mice, Curr. Biol., 16, R914-916, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.058.
Kondratov, R. V., Kondratova, A. A., Gorbacheva, V. Y., Vykhovanets, O. V., and Antoch, M. P. (2006) Early aging and age-related pathologies in mice deficient in BMAL1, the core componentof the circadian clock, Genes Dev., 20, 1868-1873, https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1432206.
Inokawa, H., Umemura, Y., Shimba, A., Kawakami, E., Koike, N., et al. (2020) Chronic circadian misalignment accelerates immune senescence and abbreviates lifespan in mice, Sci. Rep., 10, 2569, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59541-y.
Nohara, K., Mallampalli, V., Nemkov, T., Wirianto, M., Yang, J., et al. (2019) Nobiletin fortifies mitochondrial respiration in skeletal muscle to promote healthy aging against metabolic challenge, Nat. Commun., 10, 3923, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11926-y.
Yang, X., Wang, H., Li, T., Chen, L., Zheng, B., and Liu, R. H. (2020) Nobiletin delays aging and enhances stress resistance of Caenorhabditis elegans, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 21, 341, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010341.
Nohara, K., Shin, Y., Park, N., Jeong, K., He, B., Koike, N., Yoo, S. H., and Chen, Z. (2015) Ammonia-lowering activities and carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (Cps1) induction mechanism of a natural flavonoid, Nutr. Metab. (Lond.), 12, 23, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12986-015-0020-7.
Nohara, K., Nemkov, T., D'Alessandro, A., Yoo, S. H., and Chen, Z. (2019) Coordinate regulation of cholesterol and bile acid metabolism by the clock modifier nobiletin in metabolically challenged old mice, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 20, 4281, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174281.
Petrenko, V., Gandasi, N. R., Sage, D., Tengholm, A., Barg, S., and Dibner, C. (2020) In pancreatic islets from type 2 diabetes patients, the dampened circadian oscillators lead to reduced insulin and glucagon exocytosis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 117, 2484-2495, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1916539117.
Qi, G., Guo, R., Tian, H., Li, L., Liu, H., Mi, Y., and Liu, X. (2018) Nobiletin protects against insulin resistance and disorders of lipid metabolism by reprogramming of circadian clock in hepatocytes, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids, 1863, 549-562, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.02.009.
Genova, M. L., and Lenaz, G. (2015) The interplay between respiratory supercomplexes and ROS in aging, Antioxid. Redox Signal., 23, 208-238, https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2014.6214.
Guo, R., Zong, S., Wu, M., Gu, J., and Yang, M. (2017) Architecture of human mitochondrial respiratory megacomplex I2III2IV2, Cell, 170, 1247-1257.e1212, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.050.
Mileykovskaya, E., and Dowhan, W. (2014) Cardiolipin-dependent formation of mitochondrial respiratory supercomplexes, Chem. Phys. Lipids, 179, 42-48, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2013.10.012.
Mileykovskaya, E., Penczek, P. A., Fang, J., Mallampalli, V. K., Sparagna, G. C., and Dowhan, W. (2012) Arrangement of the respiratory chain complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae supercomplex III2IV2 revealed by single particle cryo-electron microscopy, J. Biol. Chem., 287, 23095-23103, https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.367888.
Pfeiffer, K., Gohil, V., Stuart, R. A., Hunte, C., Brandt, U., Greenberg, M. L., and Schagger, H. (2003) Cardiolipin stabilizes respiratory chain supercomplexes, J. Biol. Chem., 278, 52873-52880, https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M308366200.
Azuma, K., Ikeda, K., and Inoue, S. (2020) Functional mechanisms of mitochondrial respiratory chain supercomplex assembly factors and their involvement in muscle quality, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 21, 3182, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093182.
Ghosh, S., Iadarola, D. M., Ball, W. B., and Gohil, V. M. (2019) Mitochondrial dysfunctions in Barth syndrome, IUBMB Life, 71, 791-801, https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.2018.
Nohara, K., Kim, E., Wirianto, M., Mileykovskaya, E., Dowhan, W., Chen, Z., and Yoo, S.-H. (2020) Cardiolipin synthesis in skeletal muscle is rhythmic and modifiable by age and diet, Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev., 2020, 5304768, https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5304768.
Gile, J., Scott, B., and Eckle, T. (2018) The period 2 enhancer nobiletin as novel therapy in murine models of circadian disruption resembling delirium, Crit. Care Med., 46, e600-e608, https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000003077.
Jojua, N., Sharikadze, N., Zhuravliova, E., Zaalishvili, E., and Mikeladze, D. G. (2015) Nobiletin restores impaired hippocampal mitochondrial bioenergetics in hypothyroidism through activation of matrix substrate-level phosphorylation, Nutr. Neurosci., 18, 225-231, https://doi.org/10.1179/1476830514Y.0000000120.
Nakajima, A., Ohizumi, Y., and Yamada, K. (2014) Anti-dementia activity of nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid: a review of animal studies, Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci., 12, 75-82, https://doi.org/10.9758/cpn.2014.12.2.75.
Nakajima, A., Aoyama, Y., Shin, E. J., Nam, Y., Kim, H. C., et al. (2015) Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, improves cognitive impairment and reduces soluble Abeta levels in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease (3XTg-AD), Behav. Brain Res., 289, 69-77, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2015.04.028.
Seki, T., Kamiya, T., Furukawa, K., Azumi, M., Ishizuka, S., et al. (2013) Nobiletin-rich Citrus reticulata peels, a kampo medicine for Alzheimer’s disease: a case series, Geriatr. Gerontol. Int., 13, 236-238, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-0594.2012.00892.x.
Bass, J., and Takahashi, J. S. (2010) Circadian integration of metabolism and energetics, Science, 330, 1349-1354, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1195027.
Nohara, K., Yoo, S. H., and Chen, Z. J. (2015) Manipulating the circadian and sleep cycles to protect against metabolic disease, Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne), 6, 35, https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2015.00035.
Cederroth, C. R., Albrecht, U., Bass, J., Brown, S. A., Dyhrfjeld-Johnsen, J., et al. (2019) Medicine in the fourth dimension, Cell Metab., 30, 238-250, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.06.019.
Montaigne, D., Marechal, X., Modine, T., Coisne, A., Mouton, S., et al. (2018) Daytime variation of perioperative myocardial injury in cardiac surgery and its prevention by Rev-Erbalpha antagonism: a single-centre propensity-matched cohort study and a randomised study, Lancet, 391, 59-69, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32132-3.
Chen, Z. (2017) What’s next for chronobiology and drug discovery, Expert Opin. Drug Discov., 12, 1181-1185, https://doi.org/10.1080/17460441.2017.1378179.
Funding
The following authors wish to acknowledge financial support of their laboratories: S.-H. Y. – The Welch Foundation (grant AU-1971-20180324), NIH/NIGMS (grant R01GM114424) and NIH/NIA (grant R03AG063286); W. D. – NIH/NIGMS (grant R01GM115969) and John S. Dunn Research Foundation Grant; Z. C. – The Welch Foundation (grant AU-1731-20190330) and NIH/NIA (grants R01AG045828, RF1AG061901, R56AG063746, and R01AG065984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interest in financial or any other sphere. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mileykovskaya, E., Yoo, SH., Dowhan, W. et al. Nobiletin: Targeting the Circadian Network to Promote Bioenergetics and Healthy Aging. Biochemistry Moscow 85, 1554–1559 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629792012007X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629792012007X