Abstract
Collaborative (Co-) teaching is an increasingly popular model of instructional used to improve inclusive education outcomes. The woefully under theorized and researched arrangement involves multiple certified teachers—a general and special educator—sharing a classroom space and increased spectrum of student learning needs. Our multiyear Design-Based investigation of and intervention with co-teachers revealed the need to view co-teaching as an activity system. The focus of this paper includes the emergent themes uncovered and theoretical findings from the investigation, including the advancement of a novel sociocultural-oriented co-teaching framework, the Co-Teaching Implementation Framework. Also discussed is the key role of psychological safety and risk-taking within co-teaching teams and their capacity for learning to successfully implement instructional changes. Participants emphasized how performance is undermined if the risk of voicing disagreement or a deviation in the curriculum is too great, leading to silence, confusion, and resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achinstein, B. (2002). Conflict amid community: The micropolitics of teacher collaboration. Teachers College Record, 104(3), 421–455.
Akkerman, S. F., & Bakker, A. (2011). Boundary crossing and boundary objects. Review of Educational Research, 81(2), 132–169.
Antonioni, D. (1998). Relationship between the Big Five personality factors and conflict management styles. International Journal of Conflict Management, 9, 336–355.
Argyris, C. (1993). On organizational learning. Cambridge, MA: Blackwell Publishers.
Armenakis, A. A., & Bedeian, A. G. (1999). Organizational change: A review of theory and research in the 1990s. Journal of Management, 25(3), 293–315.
Artiles, A. J., Kozleski, E. B., Trent, S. C., Osher, D., & Ortiz, A. (2010). Justifying and explaining disproportionality, 1968–2008: A critique of underlying views of culture. Exceptional Children, 76(3), 279–299.
Bacharach, N. L., Heck, T. W., & Dahlberg, K. R. (2011). What makes co-teaching work? Identifying the essential elements. College Teaching Methods & Styles Journal (CTMS), 4(3), 43–48.
Banks, J. A. (1996). Multicultural education, transformative knowledge, and action: Historical and contemporary perspectives. New York: Teachers College Press.
Barron, B. (2003). When smart groups fail. Journal of the Learning Sciences, 12(3), 307–359.
Bawens, J., & Hourcade, J. (1995). Cooperative teaching: Rebuilding the schoolhouse for all students. Austin, TX: ProEd.
Behfar, K. J., Peterson, R. S., Mannix, E. A., & Trochim, W. M. K. (2008). The critical role of conflict resolution in teams: A close look at the links between conflict type, conflict management strategies, and team outcomes. Journal of Applied Psychology, 93, 170–188.
Bell, P. (2004). On the theoretical breadth of design-based research in education. Educational psychologist, 39(4), 243–253.
Benedict, A. E., Park, Y., Brownell, M. T., Lauterbach, A. A., & Kiely, M. T. (2013). Using lesson study to align elementary literacy instruction within the RTI framework. Teaching Exceptional Children, 45(5), 22–31.
Bradley, B. H., Postlethwaite, B. E., Klotz, A. C., Hamdani, M. R., & Brown, K. G. (2012). Reaping the benefits of task conflict in teams: The critical role of team psychological safety climate. Journal of Applied Psychology, 97(1), 151–158.
Brown, A. L. (1992). Design experiments: Theoretical and methodological challenges in creating complex interventions in classroom settings. The Journal of the Learning Sciences, 2(2), 141–178.
Bunderson, J. S., & Boumgarden, P. (2009). Structure and learning in self-managed teams: Why “bureaucratic” teams can be better learners. Organization Science, 21(3), 609–624.
Cook, L., & Friend, M. (1995). Co-teaching: Guidelines for creating effective practices. Focus on Exceptional Children, 28(3), 1–16.
Cook, B. G., McDuffie-Landrum, K. A., Oshita, L., & Cothren Cook, S. (2011). Co-teaching for students with disabilities: A critical analysis of the empirical literature. In J. Kauffman & D. P. Hallahan (Eds.), Handbook of special education (pp. 147–159). New York, NY: Routledge.
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (2002). Overview of self-determination theory: An organismic dialectical perspective. In Handbook of self-determination research, pp. 3–33.
Decuyper, S., Dochy, F., & Van den Bossche, P. (2010). Grasping the dynamic complexity of team learning: An integrative model for effective team learning in organizations. Educational Research Review, 5(2), 111–133.
Detert, J., & Burris, E. (2007). Leadership behavior and employee voice: Is the door really open? The Academy of Management Journal Archive, 50(4), 869–884.
Detert, J. R., & Edmondson, A. C. (2007). Why employees are afraid to speak. Harvard Business Review, 85(5), 23–25.
Durlak, J. A., & DuPre, E. P. (2008). Implementation matters: A review of research on the influence of implementation on program outcomes and the factors affecting implementation. American Journal of Community Psychology, 41, 327–350.
Edelson, D. C. (2002). Design research: What we learn when we engage in design. The Journal of the Learning Sciences, 11(1), 105–121.
Edmondson, A. C. (1999). Psychological safety and learning behavior in work teams. Administrative Science Quarterly, 44(2), 350–383.
Edmondson, A. C. (2004). Psychological safety, trust, and learning in organizations: A group-level lens. In Trust and Distrust (Ed.), Organizations: dilemmas and approaches (pp. 239–272). New York: Russell Sage Foundation.
Edmondson, A. C., Higgins, M., Singer, S., & Weiner, J. (2016). Understanding psychological safety in health care and education organizations: A comparative perspective. Research in Human Development, 13(1), 65–83.
Edmondson, A. C., & Lei, Z. (2014). Psychological safety: The history, renaissance, and future of an interpersonal construct. The Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 1(1), 23–43.
Edwards, A. (2012). The role of common knowledge in achieving collaboration across practices. Learning, Culture and Social Interaction, 1(1), 22–32.
Engeström, Y. (1987). Learning by expansion. Helsinki: Orienta Konsultit.
Engeström, Y., & Sannino, A. (2010). Studies of expansive learning: Foundations, findings and future challenges. Educational Research Review, 5(1), 1–24.
Florian, L. (2014). Reimagining special education: Why new approaches are needed. In L. Florian (Ed.), The SAGE handbook of special education (2nd ed., Vol. 1, pp. 9–23). London: Sage.
Florian, L., & Linklater, H. (2010). Preparing teachers for inclusive education: Using inclusive pedagogy to enhance teaching and learning for all. Cambridge journal of education, 40(4), 369–386.
Friend, M., & Bursuck, W. D. (2011). Including students with special needs: A practical guide for classroom teachers. Allyn & Bacon, A Pearson Education Company, 75 Arlington Street, Boston, MA 02116.
Friend, M., Cook, L., Hurley-Chamberlain, D., & Shamberger, C. (2010). Co-teaching: An illustration of the complexity of collaboration in special education. Journal of Educational and Psychological Consultation, 20, 9–27.
Hackett, J., Bang, M., Goulter, A., & Battista, M. (2019). Crossing risky boundaries: Learning to authentically and equitably co-teach through design and practice. Teaching and Teacher Education, 86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2019.102889.
Higgins, M., Ishimaru, A., Holcombe, R., & Fowler, A. (2012). Examining organizational learning in schools: The role of psychological safety, experimentation, and leadership that reinforces learning. Journal of Educational Change, 13(1), 67–94.
Isherwood, R. S., & Barger-Anderson, R. (2008). Factors affecting the adoption of co-teaching models in inclusive classrooms: One school’s journey from mainstreaming to inclusion. Journal of Ethnographic & Qualitative Research, 2, 121–128.
Kessel, M., Kratzer, J., & Schultz, C. (2012). Psychological safety, knowledge sharing, and creative performance in healthcare teams. Creativity and Innovation Management, 21(2), 147–157.
King County Housing Authority. (2015). Housing development [web site]. Retrieved May 25, 2016, from http://www.kcha.org/development/greenbridge/.
Kostopoulos, K. C., & Bozionelos, N. (2011). Team exploratory and exploitative learning: Psychological safety, task conflict, and team performance. Group and Organization Management, 36(3), 385–415.
Ladson-Billings, G. (2006). From the achievement gap to the education debt: Understanding achievement in US schools. Educational Researcher, 35(7), 3–12.
Le Fevre, D. M. (2014). Barriers to implementing pedagogical change: The role of teachers’ perceptions of risk. Teaching and Teacher Education, 38, 56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2013.11.007.
Lipsky, M. (1980). Street-level bureaucracy: Dilemmas of the individual in public services. New York, NY: Russell Sage Foundation.
Marks, S. U., & Gersten, R. (1998). Engagement and disengagement between special and general educators: An application of miles and Huberman’s cross-case analysis. Learning Disability Quarterly, 21(1), 34–56.
McDermott, R., & Varenne, H. (1995). Culture as disability. Anthropology & Education Quarterly, 26(3), 324–348.
McDonald, K. M., Wachter, R. M., & Owens, D. K. (2004). Closing the quality gap: A critical analysis of quality improvement strategies. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
McKenney, S. E., & Reeves, T. C. (2012). Conducting educational research design: What, why and how. Hoboken: Taylor & Francis.
Merriam, S. B. (2009). Qualitative research: A guide to design and interpretation. San Francisco: Wiley.
Miles, M., & Huberman, A. M. (1994). Qualitative data analysis: An expanded sourcebook (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
Morrison, E. W. (2011). Employee voice behavior: Integration and directions for future research. The Academy of Management Annals, 5(1), 373–412.
Murawski, W. W. (2006). Student outcomes in co-taught secondary English classes: How can we improve? Reading & Writing Quarterly, 22(3), 227–247.
Murawski, W. W., & Dieker, L. A. (2004). Tips and strategies for co-teaching at the secondary level. Teaching Exceptional Children, 36(5), 52–59.
Naraian, S. (2010). General, special and… inclusive: Refiguring professional identities in a collaboratively taught classroom. Teaching and Teacher Education, 26(8), 1677–1686.
National Research Council. (2000). How people learn: Brain, mind, experience, and school. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Nembhard, I. M., & Edmondson, A. C. (2006). Making it safe: The effects of leader inclusiveness and professional status on psychological safety and improvement efforts in health care teams. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 27(7), 941–966.
Nembhard, I. M., & Tucker, A. L. (2016). Applying organizational learning research to accountable care organizations. Medical Care Research and Review, 73(6), 673–684.
Newman, A., Donohue, R., & Eva, N. (2017). Psychological safety: A systematic review of the literature. Human Resource Management Review, 27(3), 521–535.
Norwich, B., & Ylonen, A. (2013). Design-based research to develop the teaching of pupils with moderate learning difficulties (MLD): Evaluating lesson study in terms of pupil, teacher and school outcomes. Teaching and Teacher Education, 34(2), 162–173.
Pancsofar, N., & Petroff, J. G. (2013). Professional development experiences in co-teaching: Associations with teacher confidence, interests, and attitudes. Teacher Education and Special Education, 36(2), 83–96.
Penuel, W. R. (2014). Emerging forms of formative intervention research in education. Mind, Culture, and Activity, 21(2), 97–117.
Penuel, W. R., Fishman, B. J., Haugan Cheng, B., & Sabelli, N. (2011). Organizing research and development at the intersection of learning, implementation, and design. Educational Researcher, 40(7), 331–337.
Powell, A. E., Davies, H. T. O., Bannister, J., & Macrae, W. A. (2009). Understanding the challenges of service change—Learning from acute pain services in the UK. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 102(2), 62–68.
Rea, P. J., McLaughlin, V. L., & Walther-Thomas, C. (2002). Outcomes for students with learning disabilities in inclusive and pullout programs. Exceptional Children, 68(2), 203–222.
Reio, T. G., Jr. (2005). Emotions as a lens to explore teacher identity and change: A commentary. Teaching and Teacher Education, 21(8), 985–993.
Rice, D., & Zigmond, N. (2000). Co-teaching in secondary schools: Teacher reports of development in Australian and American classrooms. Learning Disabilities Research and Practice, 15, 190–197.
Ploessl D. M., & Rock, M. L. (2014). eCoaching: The effects on co-teachers’ planning and instruction. Teacher Education and Special Education: The Journal of the Teacher Education Division of the Council for Exceptional Children.
Safdar, U., Badir, Y. F., & Afsar, B. (2017). Who can I ask? How psychological safety affects knowledge sourcing among new product development team members. The Journal of High Technology Management Research, 28(1), 79–92.
Sanner, B., & Bunderson, J. S. (2015). When feeling safe isn’t enough: Contextualizing models of safety and learning in teams. Organizational Psychology Review, 5(3), 224–243.
Santamaría, L. J., & Thousand, J. A. (2004). Collaboration, co-teaching, and differentiated instruction a process-oriented approach to whole schooling. International Journal of Whole Schooling, 1(1), 13–27.
Saunders, R. (2013). The role of teacher emotions in change: Experiences, patterns and implications for professional development. Journal of Educational Change, 14(3), 303–333.
Schein, E. H., & Bennis, W. G. (1965). Personal and organizational change through group methods: The laboratory approach. New York: Wiley.
Scruggs, T. E., & Mastropieri, M. A. (2017). Making inclusion work with co-teaching. Teaching Exceptional Children, 49(4), 284–293.
Scruggs, T. E., Mastropieri, M. A., & McDuffie, K. A. (2007). Co-teaching in inclusive classrooms: A meta-synthesis of qualitative research. Exceptional Children, 73, 4.
Stake, R. E. (2003). Case studies. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The Sage handbook of qualitative research. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Tucker, A. L., Nembhard, I. M., & Edmondson, A. C. (2007). Implementing new practices: An empirical study of organizational learning in hospital intensive care units. Management Science, 53(6), 894–907.
Twyford, K., Le Fevre, D., & Timperley, H. (2017). The influence of risk and uncertainty on teachers’ responses to professional learning and development. Journal of Professional Capital and Community, 2(2), 86–100.
Tynan, R. (2005). The effects of threat sensitivity and face giving on dyadic psychological safety and upward communication. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 35(2), 223–247.
U.S. Department of Education (U.S. DOE). (2016). Office of special education programs, individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) Section 618 Data Products: State-Level Data Files. Retrieved October 20, 2016, from https://www2.ed.gov/programs/osepidea/618-data/state-level-data-files/index.html#bcc. See Digest of Education Statistics 2016, table 219.90.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind and society: The development of higher mental processes. Cambridge MA: Harvard University Press.
Walumbwa, F. O., & Schaubroeck, J. (2009). Leader personality traits and employee voice behavior: Mediating roles of ethical leadership and workgroup psychological safety. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(5), 1275–1286.
Wilkens, R., & London, M. (2006). Relationships between climate, process, and performance in continuous quality improvement groups. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 69(3), 510–523.
Yin, R. K. (1989). Case study research: Design and methods (2nd ed.). Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publication.
Funding
The funding was provided by Office of Special Education Programs, Office of Special Education and Rehabilitative Services (Grand No. Personnel Preparation Grant, 84.325D, IABS Leadership Project).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix 1
Appendix 1
See Table 2.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hackett, J., Kruzich, J., Goulter, A. et al. Tearing down the invisible walls: Designing, implementing, and theorizing psychologically safer co-teaching for inclusion. J Educ Change 22, 103–130 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10833-020-09401-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10833-020-09401-3
Keywords
- Inclusion
- Psychological safety
- Teacher learning and risk-taking
- Co-teaching implementation
- Co-teaching and Design-Based Research
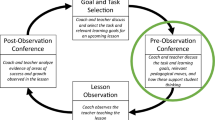
- Co-teaching should be viewed as intersecting activity systems, not sets of practices, checklists or procedures
- Psychological safety includes instructional practices and willingness to learn from mistakes
- The Co-Teaching Implementation Framework is an initial step towards a nuanced theory of co-teaching
- Participants’ practice and collaboration skills improved by co-designing this framework