Abstract
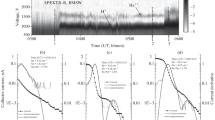
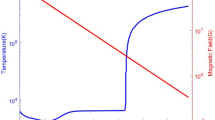
The variations in the parameters of twice ionized helium ions He++ of solar wind plasma during the passage of the front of the interplanetary shock are studied. Data taken from measurements by the Bright Monitor of Solar Wind (BMSW) installed onboard SPEKTR-R satellite were used to calculate the parameters of the He++ ions: the speed, temperature, and absolute and relative density (helium abundance). It was found that the absolute density of He++ ions behind the front of the interplanetary shock increases and that the relative density decreases. The average helium abundance behind the shock front was slightly less (by 9%) than that in the unperturbed region. The change in helium abundance correlated with the parameter θBn: the lower the θBn value is, the higher helium abundance decrease behind the front of the interplanetary shock.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Borodkova, N.L., Vaisberg, O.L., and Zastenker, G.N., Interplanetary shock waves in the post solar maximum year period (January–July, 1981), Adv. Space Res., 1986, vol. 6, no. 6, pp. 327–330.
Borrini, G., Gosling, J.T., Bame, S.J., and Feldman, W.C., An analysis of shock wave disturbances observed at 1 AU from 1971 through 1978, J. Geophys. Res., 1982, vol. 87, no. A6, pp. 4365–4373.
Ermolaev, Yu.I., Observations of He++ ions in the solar wind, Kosm. Issled., 1994, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 93–125.
Eselevich, V.G., Borodkova, N.L., Eselevich, M.V., Zastenker, G.N., Šafránkova, J., Němeček, Z., and Přech, L., Fine structure of the interplanetary shock front according to measurements of the ion flux of the solar wind with high time resolution, Cosmic Res., 2017, vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 30–55.
Formisano, V., Palmiotto, F., and Moreno, G., α-particle observations in the solar wind, Sol. Phys., 1970, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 479–498.
Gosling, J.T., Asbridge, J.R., Bame, S.J., and Paschmann, G., and Sckopke, N., Observation of two distinct population of bow shock ions in the upstream solar wind, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1978, vol. 5, pp. 957–960.
Němeček, Z., Šafránkova, J., Goncharov, O., Přech, L., and Zastenker, G.N., Ion scales of quasi-perpendicular interplanetary shocks, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2013, vol. 40, no. 16, pp. 4133–4137. https://doi.org/10.1002/grl.50814
Ogilvie, K.W. and Wilkerson, T.D., Helium abundance in the solar wind, Sol. Phys., 1969, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 435–449.
Šafránkova, J., Němeček, Z., Přech, L., et al., Fast solar wind monitor (BMSW): Description and first results, Space Sci. Rev., 2013, vol. 175, nos. 1–4, pp. 165–182.
Scholer, M., Diffusions at quasi-parallel collisionless shocks: simulations, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1990, vol. 17, pp. 1821–1824.
Scholer, M. and Terasawa, T., Ion reflection and dissipation at quasiparallel collisionless shocks, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1990, vol. 17, pp. 119–122.
Trattner, K.J. and Scholer, M., Diffuse alpha particles upstream of simulated quasi-parallel supercritical collisionless shocks, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1991, vol. 18, no. 10, pp. 1817–1820.
Volkmer, P.M. and Neubauer, F.M., Statistical properties of fast magnetoacoustic shock waves in the solar wind between 0.3 AU and 1 AU: Helios-1, 2 observations, Ann. Geophys., 1985, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 1–12.
Zastenker, G.N., Šafránkova, J., Němeček, Z., et al., Fast measurements of parameters of the solar wind using the BMSW instrument, Cosmic Res., 2013, vol. 51, no. 2, pp. 78–89.
8. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to the National Aeronautics and Space Administration Coordinated Data Analysis Web (NASA CDAWeb) for the opportunity to use data on plasma and magnetic field parameters measured by the WIND and Cluster satellites.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, grant no. 16-12-10062.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sapunova, O.V., Borodkova, N.L., Zastenker, G.N. et al. Behavior of He++ Ions at the Front of an Interplanetary Shock. Geomagn. Aeron. 60, 708–713 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793220060122
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793220060122