Abstract
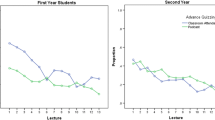
Learning management systems (LMS) offer quiz tools that help students prepare for examinations. The purpose of this study is to investigate quiz tracking variables typically reported by LMS in relation to student achievement, motivation and learning strategies. The data from 143 undergraduate students comprised quiz tracking variables (number of attempts, completion time, and score), exam scores and responses to the Need for Cognition Scale (NfC), and selected components from the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire and the Achievement Goal Questionnaire. We hypothesized students retrieving information from memory while taking a quiz would complete the quiz in less time than students who searched for answers in the textbook, and consequently, quiz completion time would correlate with exam performance and key motivational and self-regulatory factors. We found quiz completion time correlated positively with performance-avoidance goal orientation. It correlated negatively with exam performance, NfC, self-efficacy, and effort regulation. The results indicated completion time of low stakes quizzes is associated with achievement-related motivations and reliably predicts achievement on summative exams. We attribute these links to the use of retrieval practice by students who successfully regulate their effort and learning strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angus, S. D., & Watson, J. (2009). Does regular online testing enhance student learning in the numerical sciences? Robust evidence from a large data set. British Journal of Educational Technology,40(2), 255–272. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2008.00916.x.
Aron, A., Coups, E. J., & Aron, E. (2013). Statistics for psychology. London: Pearson.
Cacioppo, J. T., & Petty, R. E. (1982). The need for cognition. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,42(1), 116–131. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.42.1.116.
Cortina, J. M. (1993). What is coefficient alpha? An examination of theory and applications. Journal of Applied Psychology,78(1), 98–104. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.78.1.98.
Coutinho, S., Wiemer-Hastings, K., Skowronski, J. J., & Britt, M. A. (2005). Metacognition, need for cognition and use of explanations during ongoing learning and problem solving. Learning and Individual Differences,15(4), 321–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2005.06.001.
Credé, M., & Phillips, L. A. (2011). A meta-analytic review of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire. Learning and Individual Differences,21(4), 337–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LINDIF.2011.03.002.
Dobson, J. L. (2008). The use of formative online quizzes to enhance class preparation and scores on summative exams. Advances in Physiology Education,32(4), 297–302. https://doi.org/10.1152/advan.90162.2008.
Dopper, S. M., & Sjoer, E. (2004). Implementing formative assessment in engineering education: The use of the online assessment system Etude. European Journal of Engineering Education,29(2), 259–266. https://doi.org/10.1080/0304379032000157187.
Elliot, A. J., & Church, M. A. (1997). A hierarchical model of approach and avoidance achievement motivation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,72(1), 218–232. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.72.1.218.
Elliot, A. J., & McGregor, H. A. (2001). A 2 × 2 achievement goal framework. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,80(3), 501–519. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.80.3.501.
Elliot, A. J., McGregor, H. A., & Gable, S. (1999). Achievement goals, study strategies, and exam performance: A mediational analysis. Journal of Educational Psychology,91(3), 549–563. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.91.3.549.
Fenollar, P., Román, S., & Cuestas, P. J. (2007). University students’ academic performance: An integrative conceptual framework and empirical analysis. British Journal of Educational Psychology,77(4), 873–891. https://doi.org/10.1348/000709907X189118.
Gikandi, J. W., Morrow, D., & Davis, N. E. (2011). Online formative assessment in higher education: A review of the literature. Computers & Education,57(4), 2333–2351. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPEDU.2011.06.004.
Greene, B. A., & Miller, R. B. (1996). Influences on achievement: Goals, perceived ability, and cognitive engagement. Contemporary Educational Psychology,21(2), 181–192. https://doi.org/10.1006/CEPS.1996.0015.
Haigh, M. (2007). Sustaining learning through assessment: an evaluation of the value of a weekly class quiz. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education,32(4), 457–474. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602930600898593.
Harackiewicz, J. M., Barron, K. E., Tauer, J. M., Carter, S. M., & Elliot, A. J. (2000). Short-term and long-term consequences of achievement goals: Predicting interest and performance over time. Journal of Educational Psychology,92(2), 316–330. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.92.2.316.
Kang, S. H. K., & Pashler, H. (2014). Is the benefit of retrieval practice modulated by motivation? Journal of Applied Research in Memory and Cognition,3(3), 183–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jarmac.2014.05.006.
Karpicke, J. D. (2009). Metacognitive control and strategy selection: Deciding to practice retrieval during learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General,138(4), 469–486. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0017341.
Karpicke, J. D., Butler, A. C., & Roediger, H. L. (2009). Metacognitive strategies in student learning: Do students practise retrieval when they study on their own? Memory,17(4), 471–479. https://doi.org/10.1080/09658210802647009.
Khanna, M. M., & Cortese, M. J. (2016). The benefits of quizzing in content-focused versus skills-focused courses. Scholarship of Teaching and Learning in Psychology,2(1), 87–97. https://doi.org/10.1037/stl0000051.
Kibble, J. (2007). Use of unsupervised online quizzes as formative assessment in a medical physiology course: Effects of incentives on student participation and performance. Advances in Physiology Education,31(3), 253–260. https://doi.org/10.1152/advan.00027.2007.
Komarraju, M., & Nadler, D. (2013). Self-efficacy and academic achievement: Why do implicit beliefs, goals, and effort regulation matter? Learning and Individual Differences,25, 67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2013.01.005.
Kupiainen, S., Vainikainen, M. P., Marjanen, J., & Hautamäki, J. (2014). The role of time on task in computer-based low-stakes assessment of cross-curricular skills. Journal of Educational Psychology,106(3), 627–638. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0035507.
Lin, Y., Durbin, J. M., & Rancer, A. S. (2016). Math anxiety, need for cognition, and learning strategies in quantitative communication research methods courses. Communication Quarterly,64(4), 390–409. https://doi.org/10.1080/01463373.2015.1103294.
Lust, G., Elen, J., & Clarebout, G. (2013). Regulation of tool-use within a blended course: Student differences and performance effects. Computers & Education,60(1), 385–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2012.09.001.
McDaniel, M. A., Agarwal, P. K., Huelser, B. J., McDermott, K. B., & Roediger, H. L. (2011). Test-enhanced learning in a middle school science classroom: The effects of quiz frequency and placement. Journal of Educational Psychology,103(2), 399–414. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0021782.
McDaniel, M. A., Anderson, J. L., Derbish, M. H., & Morrisette, N. (2007). Testing the testing effect in the classroom. European Journal of Cognitive Psychology,19(4–5), 494–513. https://doi.org/10.1080/09541440701326154.
Nicol, D. J., & Macfarlane-Dick, D. (2006). Formative assessment and self-regulated learning: A model and seven principles of good feedback practice. Studies in Higher Education,31(2), 199–218. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075070600572090.
Ozarslan, Y., & Ozan, O. (2016). Self-assessment quiz taking behaviour analysis in an online course. European Journal of Open, Distance and E-Learning,19(2), 15–31.
Pastor, D. A., Barron, K. E., Miller, B. J., & Davis, S. L. (2007). A latent profile analysis of college students’ achievement goal orientation. Contemporary Educational Psychology,32(1), 8–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEDPSYCH.2006.10.003.
Phan, H. P. (2009). Exploring students’ reflective thinking practice, deep processing strategies, effort, and achievement goal orientations. Educational Psychology,29(3), 297–313. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410902877988.
Pintrich, P. R. (2000). Multiple goals, multiple pathways: The role of goal orientation in learning and achievement. Journal of Educational Psychology,92(3), 544–555. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.92.3.544.
Pintrich, P., Smith, D., García, T., & McKeachie, W. (1991). A manual for the use of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ). Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan.
Roediger, H. L., & Butler, A. C. (2011). The critical role of retrieval practice in long-term retention. Trends in Cognitive Sciences,15(1), 20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2010.09.003.
Sadowski, C. J., & Gülgös, S. (1996). Elaborative processing mediates the relationship between need for cognition and academic performance. The Journal of Psychology,130(3), 303–307. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223980.1996.9915011.
Siemens, G. (2013). Learning analytics. American Behavioral Scientist,57(10), 1380–1400. https://doi.org/10.1177/0002764213498851.
Smith, G. (2007). How does student performance on formative assessments relate to learning assessed by exams? Journal of College Science Teaching,36(7), 28.
Winne, P. H. (2011). A cognitive and metacognitive analysis of self-regulated learning. In Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance (pp. 15–32).
Winne, P. H., & Hadwin, A. F. (1998). Studying as self-regulated learning. Metacognition in Educational Theory and Practice,93, 27–30.
Wise, S. L., & Demars, C. E. (2005). Low examinee effort in low-stakes assessment: Problems and potential solutions. Educational Assessment,10(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326977ea1001.
Wise, S. L., & Kong, X. (2005). Response time effort: A new measure of examinee motivation in computer-based tests. Applied Measurement in Education,18(2), 163–183. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15324818ame1802_2.
Wolters, C. A. (2004). Advancing achievement goal theory: Using goal structures and goal orientations to predict students’ motivation. Cognition, and Achievement,96(2), 236–250. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.96.2.236.
Woolfolk, A., Winne, P. H., & Perry, N. E. (2016). Educational Psychology, Sixth Canadian Edition, 6/E (SFU). Pearson. Retrieved June 1, 2018 from http://catalogue.pearsoned.ca/educator/product/Educational-Psychology-Sixth-Canadian-Edition-6E/9780134283609.page.
Zimmerman, T. D. (2012). Exploring learner to content interaction as a success factor in online courses. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning,13(4), 152–165.
Funding
This study was funded by the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (Grant No. 435-2012-0723).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, T.Y., Jain, M., Obaid, T. et al. What can completion time of quizzes tell us about students’ motivations and learning strategies?. J Comput High Educ 32, 389–405 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12528-019-09239-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12528-019-09239-6