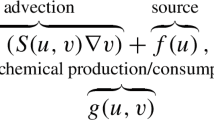Abstract
We recount and discuss some of the most important methods and blow-up criteria for analyzing solutions of Keller-Segel chemotaxis models. First, we discuss the results concerning the global existence, boundedness and blow-up of solutions to parabolic-elliptic type models. Thereafter we describe the global existence, boundedness and blow-up of solutions to parabolic-parabolic models. The numerical analysis of these models is still at a rather early stage only. We recollect quite a few of the known results on numerical methods also and direct the attention to a number of open problems in this domain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, J.: Chemotaxis in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 44, 341–356 (1975)
Ahn, J., Kang, K., Lee, J.: Eventual smoothness and stabilization of global weak solutions in parabolic-elliptic chemotaxis systems with logarithmic sensitivity. Nonlinear Anal. 49, 312–330 (2019)
Akilandeeswari, A., Tyagi, J., Nonnegative solutions to time fractional Keller-Segel system. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.6880
Akhmouch, M., Amine, M.B.: Semi-implicit finite volume schemes for a chemotaxis-growth model. Indag. Math. 27, 702–720 (2016)
Andreianov, B., Bendahmane, M., Saad, M.: Finite volume methods for degenerate chemotaxis model. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 235, 4015–4031 (2011)
Arumugam, G., Erhardt, A.H., Eswaramoorthy, I., Krishnan, B.: Existence of weak solutions to the Keller-Segel chemotaxis system with additional cross-diffusion. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 54, 103090 (2020)
Bedrossian, J.: Large mass global solutions for a class of \(L^{1}\)-critical nonlocal aggregation equations and parabolic-elliptic Patlak-Keller-Segel models. Commun. Partial Differ. Equ. 40, 1119–1136 (2015)
Bellomo, N., Winkler, M.: Finite-time blow-up in a degenerate chemotaxis system with flux limitation. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. Ser. B 4, 31–67 (2017)
Bellomo, N., Winkler, M.: A degenerate chemotaxis system with flux limitation: maximally extended solutions and absence of gradient blow-up. Commun. Partial Differ. Equ. 42, 436–473 (2017)
Bellomo, N., Bellouquid, A., Tao, Y., Winkler, M.: Toward a mathematical theory of Keller-Segel models of pattern formation in biological tissues. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 25, 1663–1763 (2015)
Bhuvaneswari, V., Shangerganesh, L., Balachandran, K.: Global existence and blow up of solutions of quasilinear chemotaxis system. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 38, 3738–3746 (2015)
Biler, P.: Global solutions to some parabolic-elliptic systems of chemotaxis. Adv. Math. Sci. Appl. 9, 347–359 (1999)
Biler, P., Woyczynski, W.A.: Global and exploding solutions for nonlocal quadratic evolution problems. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 59, 845–869 (1998)
Biler, P., Zienkiewicz, J.: Existence of solutions for the Keller-Segel model of chemotaxis with measures as initial data. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci., Math. 63, 41–51 (2015)
Biler, P., Zienkiewicz, J.: Blowing up radial solutions in the minimal Keller-Segel model of chemotaxis. J. Evol. Equ. 19, 71–90 (2019)
Biler, P., Karch, G., Pilarczyk, D.: Global radial solutions in classical Keller-Segel chemotaxis model. J. Differ. Equ. 267, 6352–6369 (2019)
Black, T.: Boundedness in a Keller-Segel system with external signal production. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 446, 436–455 (2017)
Black, T., Lankeit, J., Mizukami, M.: A Keller-Segel-fluid system with singular sensitivity: generalized solutions. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 42, 3002–3020 (2019)
Blanchet, A., Dolbeault, J., Perthame, B.: Two-dimensional Keller-Segel model: optimal critical mass and qualitative properties of the solutions. Electron. J. Differ. Equ. 2006, 44 (2006)
Blanchet, A., Calvez, V., Carrillo, J.A.: Convergence of the mass-transport steepest descent scheme for the subcritical Patlak-Keller-Segel model. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 46, 691–721 (2008)
Blanchet, A., Carrillo, J.A., Laurençot, P.: Critical mass for a Patlak-Keller-Segel model with degenerate diffusion in higher dimensions. Calc. Var. 35, 33–168 (2009)
Bonner, J.T.: The Cellular Slime Molds, 2nd edn. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1967)
Boon, J.P., Herpigny, B.: Model for chemotactic bacterial bands. Bull. Math. Biol. 48, 1–19 (1986)
Braess, D.: Finite Elements, Theory, Fast Solvers, and Applications in Solid Mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1997)
Brenner, S., Scott, R.: The Mathematical Theory of Finite Element Methods. Springer, New York (2008)
Budd, C., González, R.C., Russell, R.: Precise computations of chemotactic collapse using moving mesh methods. J. Comput. Phys. 202, 463–487 (2005)
Burgerand, M., Carrillo, J.A., Wolfram, T.: A mixed finite element method for nonlinear diffusion equations. Kinet. Relat. Models 3, 59–83 (2010)
Calvez, V., Carrillo, J.A.: Volume effects in the Keller-Segel model: energy estimates preventing blow-up. J. Math. Pures Appl. 86, 155–175 (2006)
Calvez, V., Corrias, L.: The parabolic-parabolic Keller-Segel model in \(\mathbb{R}^{2}\). Commun. Math. Sci. 6, 417–447 (2008)
Carrillo, J.A., Hittmeir, S., Jüngel, A.: Cross diffusion and nonlinear diffusion preventing blow up in the Keller-Segel model. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 22, 1250041 (2012)
Chatard, M.B., Jüngel, A.: A finite volume scheme for a Keller-Segel model with additional cross-diffusion. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 34, 96–122 (2014)
Chavanis, P-H.: A stochastic Keller-Segel model of chemotaxis. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15, 60–70 (2010)
Chen, Z.: Finite Element Methods and Their Applications. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Chertock, A., Kurganov, A.: A second-order positivity preserving central-upwind scheme for chemotaxis and haptotaxis models. Numer. Math. 111, 169–205 (2008)
Chertock, A., Epshteyn, Y., Hu, H., Kurganov, A.: High-order positivity-preserving hybrid finite-volume-finite-difference methods for chemotaxis systems. Adv. Comput. Math. 44, 327–350 (2018)
Childress, S., Percus, J.K.: Nonlinear aspects of chemotaxis. Math. Biosci. 56, 217–237 (1981)
Chiyoda, Y., Mizukami, M., Yokota, T.: Finite-time blow-up in a quasilinear degenerate chemotaxis system with flux limitation. Acta Appl. Math. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10440-019-00275-z
Ciarlet, P.G.: The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1988)
Ciélak, T., Winkler, M.: Finite-time blow-up in a quasilinear system of chemotaxis. Nonlinearity 21, 1057–1076 (2008)
Cieślak, T., Stinner, C.: Finite-time blowup and global-in-time unbounded solutions to a parabolic-parabolic quasilinear Keller-Segel system in higher dimensions. J. Differ. Equ. 252, 5832–5851 (2012)
Cieslak, T., Winkler, M.: Global bounded solutions in a two-dimensional quasilinear Keller-Segel system with exponentially decaying diffusivity and subcritical sensitivity. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 35, 1–19 (2017)
Cong, W., Liu, J-G.: A degenerate \(p-\) Laplacian Keller-Segel model. Kinet. Relat. Models 9, 687–714 (2016)
Corrias, L., Escobedo, M., Matos, J.: Existence, uniqueness and asymptotic behavior of the solutions to the fully parabolic Keller-Segel system in the plane. J. Differ. Equ. 257, 1840–1878 (2014)
DiPietro, D.A., Ern, A.: Mathematical Aspects of Discontinuous Galerkin Methods. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Eisenbach, M.: Chemotaxis. Imperial College Press, London (2004)
Epshteyn, Y.: Upwind-difference potentials method for Patlak-Keller-Segel chemotaxis model. Numer. Math. 111, 169–205 (2008)
Epshteyn, Y.: Discontinuous Galerkin methods for the chemotaxis and haptotaxis models. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 224, 168–181 (2009)
Epshteyn, Y., Izmirlioglu, A.: Fully discrete analysis of a discontinuous finite element method for the Keller-Segel chemotaxis model. J. Sci. Comput. 40, 211–256 (2009)
Epshteyn, Y., Kurganov, A.: New interior penalty discontinuous Galerkin methods for the Keller-Segel chemotaxis model. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47, 386–408 (2008)
Epshteyn, Y., Xia, Q.: Efficient numerical algorithms based on difference potentials for chemotaxis systems in 3D. J. Sci. Comput. 80, 26–59 (2019)
Espejo, E., Winkler, M.: Global classical solvability and stabilization in a two-dimensional chemotaxis-Navier-Stokes system modeling coral fertilization. Nonlinearity 31, 1227–1259 (2018)
Filbet, F.: A finite volume scheme for the Patlak-Keller-Segel chemotaxis model. Numer. Math. 104, 457–488 (2006)
Freitag, M.: Global existence and boundedness in a chemorepulsion system with superlinear diffusion. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. 38, 5943–5961 (2018)
Fuest, M.: Finite-time blow-up in a two-dimensional Keller-Segel system with an environmental dependent logistic source. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 52, 103022 (2020)
Fuest, M.: Blow-up profiles in quasilinear fully parabolic Keller-Segel systems. Nonlinearity 33, 2306–2334 (2020)
Fujie, K.: Boundedness in a fully parabolic-chemotaxis system singular sensitivity. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 424, 675–684 (2015)
Fujie, K.: Study of Reaction-Diffusion Systems Modeling Chemotaxis. Doctoral thesis (2016)
Fujie, K., Yokota, T.: Boundedness in a fully parabolic chemotaxis system with strongly singular sensitivity. Appl. Math. Lett. 38, 140–143 (2014)
Fujie, K., Winkler, M., Yokota, T.: Blow-up prevention by logistic sources in a parabolic-elliptic Keller-Segel system with singular sensitivity. Nonlinear Anal. 109, 56–71 (2014)
Fujie, K., Winkler, M., Yokota, T.: Boundedness of solutions to parabolic-elliptic Keller-Segel systems with signal-dependent sensitivity. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 38, 1212–1224 (2015)
Galakhov, E., Salieva, O., Tello, J.I.: On a parabolic-elliptic system with chemotaxis and logistic type growth. J. Differ. Equ. 261, 4631–4647 (2016)
Ganesan, S., Tobiska, L.: Finite Elements: Theory and Algorithms. Cambridge-IISc Series. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2017). ISBN 9781108344159
Gao, H., Fu, S., Mohammed, H.: Existence of global solution to a two-species Keller-Segel chemotaxis model. Int. J. Biomath. 11, 1850036 (2018)
Godlewski, E., Raviart, P-A.: Numerical Approximation of Hyperbolic Systems of Conservation Laws. Springer, New York (1996)
Guo, L., Li, X.H., Yang, Y.: Energy dissipative local discontinuous Galerkin methods for Keller-Segel chemotaxis model. J. Sci. Comput. 78, 1387–1404 (2019)
Gurusamy, A., Balachandran, K.: Finite element method for solving Keller-Segel chemotaxis system with cross-diffusion. Int. J. Dyn. Control 6, 539–549 (2018)
Hashira, T., Ishida, S., Yokota, T.: Finite time blow- up for quasilinear degenerate Keller-Segel systems of parabolic-parabolic type. J. Differ. Equ. 264, 6459–6485 (2018)
Hesthaven, J.S., Warburton, T.: Nodal Discontinuous Galerkin Methods: Algorithms: Analysis, and Applications. Springer, New York (2008)
Hillen, T., Painter, K.: Global existence for a parabolic chemotaxis model with prevention of overcrowding. Adv. Appl. Math. 26, 280–301 (2001)
Hillen, T., Painter, K.J.: A user’s guide to PDE models for chemotaxis. J. Math. Biol. 58, 183–217 (2009)
Hittmeir, S., Jungel, A.: Cross diffusion preventing blow-up in the two-dimensional Keller-Segel model. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 43, 997–1022 (2011)
Horstmann, D.: The nonsymmetric case of the Keller-Segel model in chemotaxis: some recent results. Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 8, 399–423 (2001)
Horstmann, D.: From 1970 until present: the Keller-Segel model in chemotaxis and its consequences. Jahresber. Dtsch. Math.-Ver. 105, 103–165 (2003)
Horstmann, D., Wang, G.: Blow-up in a chemotaxis model without symmetry assumptions. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 12, 159–177 (2001)
Horstmann, D., Winkler, M.: Boundedness vs. blow-up in a chemotaxis system. J. Differ. Equ. 215, 52–107 (2005)
Horstmann, D., Meinlschmidt, H., Rehberg, J.: The full Keller-Segel model is well-posed on nonsmooth domains. Nonlinearity 31, 1560–1592 (2018)
Ishida, S., Yokota, T.: Global existence of weak solutions to quasilinear degenerate Keller-Segel systems of parabolic-parabolic type with small data. J. Differ. Equ. 252, 2469–2491 (2012)
Ishida, S., Yokota, T.: Global existence of weak solutions to quasilinear degenerate Keller-Segel systems of parabolic-parabolic type. J. Differ. Equ. 252, 1421–1440 (2012)
Ishida, S., Yokota, T.: Blow-up in finite or infinite time for quasilinear degenerate Keller-Segel systems of parabolic-parabolic type. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst., Ser. B 18, 2569–2596 (2013)
Ishida, S., Ono, T., Tokota, T.: Possibility of the existence of blow-up solutions to quasilinear degenerate Keller-Segel systems of parabolic-parabolic type. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 36, 745–760 (2013)
Ishida, S., Seki, K., Yokota, T.: Boundedness in quasilinear Keller-Segel systems of parabolic-parabolic type on non-convex bounded domains. J. Differ. Equ. 256, 2993–3010 (2014)
Jiang, J., Wu, H., Zheng, S.: Blow-up for a three dimensional Keller-Segel model with consumption of chemoattractant. J. Differ. Equ. 264, 5432–5464 (2018)
Jin, H.Y., Kim, Y.J., Wang, Z.A.: Boundedness, stabilization and pattern formation driven by density-suppressed motility. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 78, 1632–1657 (2018)
Jüngel, A., Leingang, O., Wang, S.: Vanishing cross-diffusion limit in a Keller-Segel system with additional cross-diffusion. Nonlinear Anal. 192, 111698 (2020)
Kang, K., Kim, K., Yoon, C.: Existence of weak and regular solutions for Keller-Segel system with degradation coupled to fluid equations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 485, 123750 (2020)
Keller, E.F., Segel, L.A.: Initiation of some mold aggregation viewed as an instability. J. Theor. Biol. 26, 399–415 (1970)
Keller, E.F., Segel, L.A.: Traveling bands of chemotactic bacteria: a theoretical analysis. J. Theor. Biol. 30, 377–380 (1971)
Keller, E.F., Segel, L.A.: Model for chemotaxis. J. Theor. Biol. 30, 225–234 (1971)
Kowalczyk, R., Szymanska, Z.: On the global existence of solutions to an aggregation model. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 343, 379–398 (2008)
Kozono, H., Sugiyama, Y.: The Keller-Segel system of parabolic-parabolic type with initial data in weak \(L^{n/2}(\mathbb{R}^{n})\) and its application to self-similar solutions. Indiana Univ. Math. J. 57, 1467–1500 (2008)
Kozono, H., Sugiyama, Y.: Global strong solution to the semi-linear Keller-Segel system of parabolic-parabolic type with small data in scale invariant spaces. J. Differ. Equ. 247, 1–32 (2009)
Kozono, H., Miura, M., Sugiyama, Y.: Existence and uniqueness theorem on mild solutions to the Keller-Segel system coupled with the Navier-Stokes fluid. J. Funct. Anal. 270, 1663–1683 (2016)
Lai, Y., Xiao, Y.: Existence and asymptotic behavior of global solutions to chemorepulsion systems with nonlinear sensitivity. Electron. J. Differ. Equ., 254 (2017)
Lankeit, J.: Eventual smoothness and asymptotics in a three-dimensional chemotaxis system with logistic source. J. Differ. Equ. 258, 1158–1191 (2015)
Lankeit, J.: New approach toward boundedness in a two-dimensional parabolic chemotaxis system with singular sensitivity. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 39, 394–404 (2016)
Lankeit, J.: Locally bounded global solutions to a chemotaxis consumption model with singular sensitivity and nonlinear diffusion. J. Differ. Equ. 262, 4052–4084 (2017)
Lankeit, E., Lankeit, J.: On the global generalized solvability of a chemotaxis model with signal absorption and logistic growth terms. Nonlinearity 32, 1569–1596 (2019)
Lankeit, E., Lankeit, J.: Classical solutions to a logistic chemotaxis model with singular sensitivity and signal absorption. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 46, 421–445 (2019)
Lankeit, J., Winkler, M.: A generalized solution concept for the Keller-Segel system with logarithmic sensitivity: global solvability for large nonradial data. Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 24, 24–49 (2017)
Lankeit, J., Winkler, M.: Facing low regularity in chemotaxis systems. Jahresber. Dtsch. Math.-Ver. 122, 35–64 (2020)
Laurençot, P., Mizoguchi, N.: Finite time blowup for the parabolic-parabolic Keller-Segel system with critical diffusion. Ann. Inst. Henri Poincaré A, Phys. Théor. 34, 197–220 (2017)
Li, X.: On a fully parabolic chemotaxis system with nonlinear signal secretion. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 49, 24–44 (2019)
Li, X.: Global classical solutions in a Keller-Segel(-Navier)-Stokes system modeling coral fertilization. J. Differ. Equ. 267, 6290–6315 (2019)
Li, Y.: Finite-time blow-up in quasilinear parabolic-elliptic chemotaxis system with nonlinear signal production. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 480(1), 123376 (2019)
Li, Y.: On a Keller-Segel-Stokes system with logistic type growth: blow-up prevention enforced by sublinear signal production. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 70, 157 (2019)
Li, H., Zhao, K.: Initial-boundary value problems for a system of hyperbolic balance laws arising from chemotaxis. J. Differ. Equ. 258, 302–308 (2015)
Li, D., Li, T., Zhao, K.: On a hyperbolic-parabolic system modeling chemotaxis. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 21, 1631–1650 (2011)
Li, X.H., Shu, C.-W., Yang, Y.: Local discontinuous Galerkin method for the Keller-Segel chemotaxis model. J. Sci. Comput. 73, 943–967 (2017)
Lina, K., Mub, C., Zhong, H.: A blow-up result for a quasilinear chemotaxis system with logistic source in higher dimensions. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 464, 435–455 (2018)
Liu, J-G., Wang, J.: A note on \(L^{\infty }\)-bound and uniqueness to a degenerate Keller-Segel model. Acta Appl. Math. 142, 173–188 (2016)
Marrocco, A.: Numerical simulation of chemotactic bacteria aggregation via mixed finite elements. Modél. Math. Anal. Numér. 4, 617–630 (2003)
Mimura, Y.: The variational formulation of the fully parabolic Keller-Segel system with degenerate diffusion. J. Differ. Equ. 263, 1477–1521 (2017)
Mizoguchi, N.: Type II blowup in the doubly parabolic Keller-Segel system in the two dimension. J. Funct. Anal. 271, 3323–3347 (2016)
Mizoguchi, N., Souplet, P.: Nondegeneracy of blow-up points for the parabolic Keller-Segel system. Ann. Inst. Henri Poincaré A, Phys. Théor. 31, 851–875 (2014)
Mizukami, M.: Determination of blowup type in the parabolic-parabolic Keller-Segel system. Math. Ann. 376, 39–60 (2020)
Mizukami, M., Yokota, T.: A unified method for boundedness in fully parabolic chemotaxis systems with signal-dependent sensitivity. Math. Nachr. 290, 1–13 (2017)
Mizukami, M., Ono, T., Yokota, T.: Extensibility criterion ruling out gradient blow-up in a quasilinear degenerate chemotaxis system. Preprint. arXiv:1903.00124
Mu, C., Wang, L., Zheng, P., Zhang, Q.: Global existence and boundedness of classical solutions to a parabolic-parabolic chemotaxis system. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 14, 1634–1642 (2013)
Murray, J.D.: Mathematical Biology II. Spatial Models and Biomedical Applications. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Nagai, T.: Global existence of solutions to a parabolic system for chemotaxis in two space dimensions. Nonlinear Anal., Theory Methods Appl. 30, 5381–5388 (1997)
Nagai, T.: Global existence and blow-up of solutions to a chemotaxis system. Nonlinear Anal. 47, 777–787 (2001)
Nakaguchi, E., Yagi, Y.: Fully discrete approximation by Galerkin Runge-Kutta methods for quasilinear parabolic systems. Hokkaido Math. J. 31, 385–429 (2002)
Nanjundiah, V.: Chemotaxis, signal relaying and aggregation morphology. J. Theor. Biol. 42, 63–105 (1973)
Nasreddine, E.: Global existence of solutions to a parabolic-elliptic chemotaxis system with critical degenerate diffusion. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 417, 144–163 (2014)
Negreanu, M., Tello, J.I.: On a parabolic-elliptic system with gradient dependent chemotactic coefficient. J. Differ. Equ. 265, 733–751 (2018)
Negreanu, M., Tello, J.I.: Global existence and asymptotic behavior of solutions to a Predator-Prey chemotaxis system with two chemicals. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 474, 1116–1131 (2019)
Painter, K.J.: Mathematical models for chemotaxis and their applications in self-organisation phenomena. J. Theor. Biol. 481, 162–182 (2019)
Painter, K., Hillen, T.: Volume-filling and quorum-sensing in models for chemosensitive movement. Can. Appl. Math. Q. 10, 501–543 (2001)
Patlak, C.S.: Random walk with persistence and external bias. Bull. Math. Biophys. 15, 311–338 (1953)
Payne, L.E., Song, J.C.: Blow-up and decay criteria for a model of chemotaxis. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 367, 1–6 (2010)
Payne, L.E., Song, J.C.: Lower bounds for blow-up in a model of chemotaxis. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 385, 672–676 (2012)
Payne, L.E., Straughan, B.: Decay for a Keller-Segel chemotaxis model. Stud. Appl. Math. 123, 337–360 (2009)
Prudhomme, S., Pascal, F., Oden, J.T., Romkes, A.: Review of a priori error estimation for discontinuous Galerkin Methods. Technical report, TICAM Report 00-27, Texas Institute for Computational and Applied Mathematics, Austin, TX (2000)
Riviere, B.: Discontinuous Galerkin Methods for Solving Elliptic and Parabolic Equations: Theory and Implementation. SIAM, Philadelphia (2008)
Saito, N.: Conservative upwind finite element method for a simplified Keller-Segel system modelling chemotaxis. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 27, 332–365 (2007)
Saito, N.: Conservative numerical schemes for the Keller-Segel system and numerical results. RIMS Kôkyûroku Bessatsu 15, 125–146 (2009)
Saito, N.: Error analysis of a conservative finite-element approximation for the Keller-Segel system of chemotaxis. Commun. Pure Appl. Anal. 11, 339–364 (2012)
Saito, N., Suzuki, T.: Notes on finite difference schemes to a parabolic-elliptic system modelling chemotaxis. Appl. Math. Comput. 171, 72–90 (2005)
Salako, R.B., Shen, W.: Global existence and asymptotic behavior of classical solutions to a parabolic-elliptic chemotaxis system with logistic source on \(\mathbb{R}^{N}\). J. Differ. Equ. 262, 5635–5690 (2017)
Salako, R.B., Shen, W.: Parabolic-elliptic chemotaxis model with space-time dependent logistic sources on \(\mathbb{R}^{N}\). I. Persistence and asymptotic spreading. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 28, 2237–2273 (2018)
Salako, R.B., Shen, W.: Parabolic-elliptic chemotaxis model with space-time dependent logistic sources on \(\mathbb{R}^{N}\). II. Existence, uniqueness, and stability of strictly positive entire solutions. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 464, 883–910 (2018)
Salako, R.B., Shen, W.: Parabolic-elliptic chemotaxis model with space-time dependent logistic sources on \(\mathbb{R}^{N}\) III. Transition fronts (2018)
Senba, T., Suzuki, T.: Parabolic system of chemotaxis: blow-up in a finite and the infinite time. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 8, 349–367 (2001)
Shangerganesh, L., Barani Balan, N., Balachandran, K.: Existence and uniqueness of solutions of degenerate chemotaxis system. Taiwan. J. Math. 18, 1605–1622 (2014)
Souplet, P., Winkler, M.: Blow-up profiles for the parabolic-elliptic Keller-Segel system in dimensions \(n\geqslant 3\). Commun. Math. Phys. 367, 665–681 (2019)
Stinner, C., Winkler, M.: Global weak solutions in a chemotaxis system with large singular sensitivity. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 12, 3727–3740 (2011)
Strehl, R., Sokolov, A., Turek, S.: Efficient, accurate and flexible finite element solvers for chemotaxis problems. Comput. Math. Appl. 64, 175–189 (2012)
Strehl, R., Sokolov, A., Kuzmin, D., Horstmann, D., Turek, S.: A positivity-preserving finite element method for chemotaxis problems in 3D. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 239, 290–303 (2013)
Sugiyama, Y.: Global existence and decay properties of solutions for some degenerate quasilinear parabolic systems modelling chemotaxis. Nonlinear Anal. 63, 1051–1062 (2005)
Sugiyama, Y.: Global existence in sub-critical cases and finite time blow-up in super-critical cases to degenerate Keller-Segel system. Differ. Integral Equ. 19, 841–876 (2006)
Sugiyama, Y.: Time global existence and asymptotic behavior of solutions to degenerate quasi-linear parabolic systems of chemotaxis. Differ. Integral Equ. 20, 133–180 (2007)
Sugiyama, Y., Kunii, H.: Global existence and decay properties for a degenerate Keller-Segel model with a power factor in drift term. J. Differ. Equ. 227, 333–364 (2006)
Sugiyama, Y., Tsutsui, Y., Velázquez, J.J.L.: Global solutions to a chemotaxis system with non-diffusive memory. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 410, 908–917 (2014)
Tan, Z., Zhou, J.: Global existence and time decay estimate of solutions to the Keller-Segel system. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 42, 375–402 (2019)
Tao, Y., Winkler, M.: Boundedness in a quasilinear parabolic-parabolic Keller-Segel system with subcritical sensitivity. J. Differ. Equ. 252, 692–715 (2012)
Tao, Y., Winkler, M.: Boundedness and decay enforced by quadratic degradation in a three-dimensional chemotaxis-fluid system. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 66, 2555–2573 (2015)
Tao, Y., Winkler, M.: Effects of signal-dependent motilities in a Keller-Segel type reaction-diffusion system. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 27, 1645–1683 (2017)
Tao, Y., Winkler, M.: Effects of signal-dependent motilities in a Keller-Segel-type reaction-diffusion system. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 27, 1645–1683 (2017)
Tao, Y., Winkler, M.: Global smooth solvability of a parabolic-elliptic nutrient taxis system in domains of arbitrary dimension. J. Differ. Equ. 267, 388–406 (2019)
Tao, Y., Wang, L.H., Wang, Z.A.: Large-time behavior of a parabolic-parabolic chemotaxis model with logarithmic sensitivity in one dimension. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst., Ser. B 18, 821–845 (2013)
Tao, X., Zhou, S., Ding, M.: Boundedness of solutions to a quasilinear parabolic-parabolic chemotaxis model with nonlinear signal production. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 474, 733–747 (2019)
Tello, J.I., Winkler, M.: A chemotaxis system with logistic source. Commun. Partial Differ. Equ. 32, 849–877 (2007)
Thomee, V.: Galerkin Finite Element Methods for Parabolic Problems, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Viglialoro, G.: Very weak global solutions to a parabolic-parabolic chemotaxis-system with logistic source. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 439, 197–212 (2016)
Viglialoro, G., Woolley, T.E.: Solvability of a Keller-Segel system with signal-dependent sensitivity and essentially sublinear production. Appl. Anal. 99(14), 2507–2525 (2019).
Wang, Y.: Global bounded weak solutions to a degenerate quasilinear chemotaxis system with rotation. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 39, 1159–1175 (2016)
Wang, J., Wang, M.: Boundedness in the higher-dimensional Keller-Segel model with signal-dependent motility and logistic growth. J. Math. Phys. 60, 011507 (2019)
Wang, Y., Xiang, Z.: Global existence and boundedness in a Keller-Segel-Stokes system involving a tensor-valued sensitivity with saturation: the 3D case. J. Differ. Equ. 261, 4944–4973 (2016)
Wang, L., Li, Y., Mu, C.: Boundedness in a parabolic-parabolic quasilinear chemotaxis system with logistic source. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. 34, 789–802 (2014)
Wang, Y., Winkler, M., Xiang, Z.: Global classical solutions in a two-dimensional chemotaxis-Navier-Stokes system with subcritical sensitivity. Ann. Sc. Norm. Super. Pisa, Cl. Sci. XVIII, 421–466 (2018)
Wang, J., Li, Y., Chen, L.: Supercritical degenerate parabolic-parabolic Keller-Segel system: existence criterion given by the best constant in Sobolev’s inequality. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 70, 71 (2019)
Wang, Y., Winkler, M., Xiang, Z.: The fast signal diffusion limit in Keller-Segel(-fluid) systems. Calc. Var. 58, 196 (2019)
Winkler, M.: Chemotaxis with logistic source: very weak global solutions and their boundedness properties. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 348, 708–729 (2008)
Winkler, M.: Aggregation vs. global diffusive behavior in the higher-dimensional Keller-Segel model. J. Differ. Equ. 248, 2889–2905 (2010)
Winkler, M.: Global solutions in a fully parabolic chemotaxis system with singular sensitivity. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 34, 176–190 (2010)
Winkler, M.: Does a ‘volume-filling effect’ always prevent chemotactic collapse? Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 33, 12–24 (2010)
Winkler, M.: Absence of collapse in a parabolic chemotaxis system with signal- dependent sensitivity. Math. Nachr. 283, 1664–1673 (2010)
Winkler, M.: Global solutions in a fully parabolic chemotaxis system with singular sensitivity. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 34, 176–190 (2011)
Winkler, M.: Finite-time blow-up in the higher-dimensional parabolic-parabolic Keller-Segel system. J. Math. Pures Appl. 100, 748–767 (2013)
Winkler, M.: Toward a mathematical theory of Keller-Segel models of pattern formation in biological tissues. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 25, 1663–1763 (2015)
Winkler, M.: Boundedness and large time behavior in a three-dimensional chemotaxis-Stokes system with nonlinear diffusion and general sensitivity. Calc. Var. 54, 3789–3828 (2015)
Winkler, M.: How far do chemotaxis-driven forces influence regularity in the Navier-Stokes system? J. Funct. Anal. 270, 1663–1683 (2016)
Winkler, M.: The two-dimensional Keller-Segel system with singular sensitivity and signal absorption: global large-data solutions and their relaxation properties. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 26, 987–1024 (2016)
Winkler, M.: Global weak solutions in a three-dimensional chemotaxis-Navier-Stokes system. Ann. Inst. Henri Poincaré 33, 1329–1352 (2016)
Winkler, M.: Emergence of large population densities despite logistic growth restrictions in fully parabolic chemotaxis systems. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst., Ser. B 22, 2777–2793 (2017)
Winkler, M.: Renormalized radial large-data solutions to the higher-dimensional Keller-Segel system with singular sensitivity and signal absorption. J. Differ. Equ. 264, 2310–2350 (2018)
Winkler, M.: Does fluid interaction affect regularity in the three-dimensional Keller-Segel system with saturated sensitivity? J. Math. Fluid Mech. 20, 1889–1909 (2018)
Winkler, M.: Finite-time blow-up in low-dimensional Keller-Segel systems with logistic-type superlinear degradation. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 69, 40 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-018-0935-8
Winkler, M.: Global mass-preserving solutions in a two-dimensional chemotaxis-Stokes system with rotational flux components. J. Evol. Equ. 18, 1267–1289 (2018)
Winkler, M.: Global solvability and stabilization in a two-dimensional cross-diffusion system modeling urban crime propagation. Ann. Inst. Henri Poincaré 36, 1747–1790 (2019)
Winkler, M.: Global classical solvability and generic infinite-time blow-up in quasilinear Keller-Segel systems with bounded sensitivities. J. Differ. Equ. 266, 8034–8066 (2019)
Winkler, M.: Can rotational fluxes impede the tendency toward spatial homogeneity in nutrient taxis(-Stokes) systems? Int. Math. Res. Not. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1093/imrn/rnz056
Winkler, M.: How unstable is spatial homogeneity in Keller-Segel systems? A new critical mass phenomenon in two-and higher-dimensional parabolic-elliptic cases. Math. Ann. 373, 1237–1282 (2019)
Winkler, M.: Does repulsion-type directional preference in chemotactic migration continue to regularize Keller-Segel systems when coupled to the Navier-Stokes equations? Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 26, 48 (2019)
Winkler, M.: Instantaneous regularization of distributions from \((C^{0})^{*} \times L^{2}\) in the one-dimensional parabolic Keller-Segel system. Nonlinear Anal. 183, 102–116 (2019)
Winkler, M.: A three-dimensional Keller-Segel-Navier-Stokes system with logistic source: global weak solutions and asymptotic stabilization. J. Funct. Anal. 276, 1339–1401 (2019)
Winkler, M.: Does repulsion-type directional preference in chemotactic migration continue to regularize Keller-Segel systems when coupled to the Navier-Stokes equations? Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 26, 48 (2019)
Winkler, M.: Boundedness in a two-dimensional Keller-Segel-Navier-Stokes system involving a rapidly diffusing repulsive signal. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 71, 10 (2020)
Winkler, M.: Blow-up profiles and life beyond blow-up in the fully parabolic Keller-Segel system. J. Anal. Math. 141, 585–624 (2020)
Winkler, M., Djie, K.C.: Boundedness and finite-time collapse in a chemotaxis system with volume-filling effect. Nonlinear Anal. 72, 1044–1064 (2010)
Winkler, M., Yokota, T.: Stabilization in the logarithmic Keller-Segel system. Nonlinear Anal. 170, 123–141 (2018)
Wrzosek, D.: Global attractor for a chemotaxis model with prevention of overcrowding. Nonlinear Anal. 59, 1293–1310 (2004)
Wu, G., Zheng, X.: On the well-posedness for Keller-Segel system with fractional diffusion. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 34, 1739–1750 (2011)
Xiang, T.: Boundedness and global existence in the higher-dimensional parabolic-parabolic chemotaxis system with or without growth source. J. Differ. Equ. 258, 4275–4323 (2015)
Xiang, T.: How strong a logistic damping can prevent blow-up for the minimal Keller-Segel chemotaxis system? J. Math. Anal. Appl. 459, 1172–1200 (2018)
Xiang, T.: Chemotactic aggregation versus logistic damping on boundedness in the \(3D\) minimal Keller-Segel model. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 78, 2420–2438 (2018)
Xiang, T.: Sub-logistic source can prevent blow-up in the 2D minimal Keller-Segel chemotaxis system. J. Math. Phys. 59, 081502 (2018)
Xinhua, Z., Song, J.: Globally bounded in-time solutions to a parabolic-elliptic system modelling chemotaxis. Acta Math. Sci. 27, 421–429 (2007)
Yan, J., Li, Y.: Global generalized solutions to a Keller-Segel system with nonlinear diffusion and singular sensitivity. Nonlinear Anal. 176, 288–302 (2018)
Yokota, T., Yoshino, N.: Existence of solutions to chemotaxis dynamics with Lipschitz diffusion and superlinear growth. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 419, 756–774 (2014)
Yoon, C., Kim, Y-J.: Global existence and aggregation in a Keller-Segel model with Fokker-Planck diffusion. Acta Appl. Math. 149, 101–123 (2017)
Yu, H., Wang, W., Zheng, S.: Global classical solutions to the Keller-Segel-Navier-Stokes system with matrix-valued sensitivity. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 461, 1748–1770 (2018)
Zhang, R., Zhu, J., Loula, A.F.D., Yu, X.: Operator splitting combined with positivity-preserving discontinuous Galerkin method for the chemotaxis model. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 302, 312–326 (2016)
Zhang, J., Zhu, J., Zhang, R.: Characteristic splitting mixed finite element analysis of Keller-Segel chemotaxis models. Appl. Math. Comput. 278, 33–44 (2016)
Zhao, J.: Well-posedness and Gevrey analyticity of the generalized Keller-Segel system in critical Besov spaces. Ann. Mat. Pura Appl. 197, 521–548 (2018)
Zhao, X., Zheng, S.: Global existence and asymptotic behavior to achemotaxis-consumption system with singular sensitivity and logistic source. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 42, 120–139 (2018)
Zhao, J., Mu, C.L., Wang, L.C., Lin, K.: A quasilinear parabolic-elliptic chemotaxis-growth system with nonlinear secretion. Appl. Anal. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/00036811.2018.1489955
Zheng, J., Ke, Y.: Blow-up prevention by nonlinear diffusion in a 2D Keller-Segel-Navier-Stokes system with rotational flux. J. Differ. Equ. 268, 7092–7120 (2020)
Zheng, P., Mu, C., Hu, X., Tian, Y.: Boundedness of solutions in a chemotaxis system with nonlinear sensitivity and logistic source. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 424, 509–522 (2015)
Zhou, G., Saito, N.: Finite volume methods for a Keller-Segel system: discrete energy, error estimates and numerical blow-up analysis. Numer. Math. 135, 265–311 (2017)
Acknowledgement
Authors thank the referees for constructive comments which have improved the quality of the paper considerably.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The second author thanks CSIR for the financial support under the grant No. 25(0263)/17/EMR-II and partly DST-SERB under the grant MTR/2018/00096.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arumugam, G., Tyagi, J. Keller-Segel Chemotaxis Models: A Review. Acta Appl Math 171, 6 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10440-020-00374-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10440-020-00374-2