Abstract
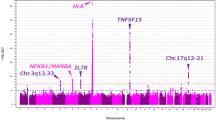
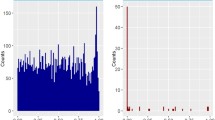
Susceptibility to primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is in part genetically determined. In our previous PBC genome-wide association study (GWAS) in 1118 Han Chinese PBC and 4036 controls, we noted that multiple SNPs in the runt-related transcription factor 3 (RUNX3) regions showed a nominally significant association. The tag SNP rs7529070 was genotyped using a TaqMan assay in a separately collected 1435 PBC and 3205 controls. A meta-analysis with a combined 2553 PBC and 7241 controls showed that rs7529070 is still nominally associated with PBC (p = 1.7 × 10–4, odds ratio (OR) = 1.18, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.08–1.28). Further analysis indicated that the risk allele of rs7529070 (G allele) is in complete linkage disequilibrium (LD) (r2 = 1) with the G allele of rs4648889, which is known to be associated with increased RUNX3 expression. Bioinformatic analysis with existing expression data showed that the expression of RUNX3 is significantly increased in PBC patients (p = 0.001) and the expression level is correlated with disease severity. Consistently, we also found significantly increased RUNX3 expression (p < 0.01) in the livers of dnTGFβRII mice (a PBC mouse model). This study suggests that the RUNX3 locus may associate with PBC in Han Chinese.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PBC:
-
Primary biliary cirrhosis
- GWAS:
-
Genome-wide association study/studies
- RUNX3:
-
Runt-related transcription factor 3
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- LD:
-
Linkage disequilibrium
- PsA:
-
Psoriatic arthritis
- AS:
-
Ankylosing spondylitis
- SLE:
-
Systematic lupus erythematosus
- SSc:
-
Systematic sclerosis
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- RAF:
-
Risk allele frequency
- CHB:
-
Chinese Han Beijing
- CHS:
-
Chinese Han South
- GEO:
-
Gene Expression Omnibus
- IL17:
-
Interleukin 17
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon gamma
- Th17:
-
T helper 17
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor beta
- IRF4:
-
Interferon regulatory factor 4
- AASLD:
-
American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases
- AMA:
-
Antimitochondrial antibody
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- HRPT:
-
Hypoxanthine–guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
References
Affandi AJ et al (2019) Low RUNX3 expression alters dendritic cell function in patients with systemic sclerosis and contributes to enhanced fibrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214991
Apel M et al (2013) Variants in RUNX3 contribute to susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis, exhibiting further common ground with ankylosing spondylitis Arthritis Rheum 65:1224–1231. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.37885
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ et al (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 21:263–265. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bth457
Boto P, Csuth TI, Szatmari I et al (2018) RUNX3-mediated immune cell development and maturation. Crit Rev Immunol 38:63–78. https://doi.org/10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2018025488
Bowes J et al (2015) Dense genotyping of immune-related susceptibility loci reveals new insights into the genetics of psoriatic arthritis. Nat. Commun 6:6046. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7046
Budu-Aggrey A, Bowes J, Barton A et al (2016) Identifying a novel locus for psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology 55:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kev273
Cho SM, Jung SH, Chung YJ et al (2017) A Variant in RUNX3 is associated with the risk of ankylosing spondylitis in Koreans. Genomics Inform 15:65–68. https://doi.org/10.5808/GI.2017.15.2.65
Coleman C et al (2016) Common polygenic variation in coeliac disease and confirmation of ZNF335 and NIFA as disease susceptibility loci. Eur J Hum Genet 24:291–297. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2015.87
Cordell HJ et al (2015) International genome-wide meta-analysis identifies new primary biliary cirrhosis risk loci and targetable pathogenic pathways. Nat Commun 6:8019. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9019
Dong M et al (2015) Multiple genetic variants associated with primary biliary cirrhosis in a Han Chinese population. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 48:316–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-015-8472-0
Ebihara T, Seo W, Taniuchi I et al (2017) Roles of RUNX complexes in immune cell development. Adv Exp Med Biol 962:395–413. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3233-2_24
Gabriel SB et al (2002) The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science (New York, NY) 296:2225–2229. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1069424
Hardie C et al (2016) Early molecular stratification of high-risk primary biliary cholangitis. EBioMedicine 14:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.11.021
Hirschfield GM et al (2009) Primary biliary cirrhosis associated with HLA, IL12A, and IL12RB2 variants. N Engl J Med 360:2544–2555. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0810440
Jeffries MA, Dozmorov M, Tang Y, Merrill JT, Wren JD, Sawalha AH et al (2011) Genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in CD4+ T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Epigenetics 6:593–601. https://doi.org/10.4161/epi.6.5.15374
Kawashima M et al (2017) Genome-wide association studies identify PRKCB as a novel genetic susceptibility locus for primary biliary cholangitis in the Japanese population. Hum Mol Genet 26:650–659. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddw406
Lim B, Ju H, Kim M, Kang C et al (2011) Increased genetic susceptibility to intestinal-type gastric cancer is associated with increased activity of the RUNX3 distal promoter. Cancer 117:5161–5171. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.26161
Lindor KD, Gershwin ME, Poupon R, Kaplan M, Bergasa NV, Heathcote EJ et al (2009) American Association for Study of Liver D. Primary biliary cirrhosis Hepatology 50:291–308. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.22906
Liu X et al (2010) Genome-wide meta-analyses identify three loci associated with primary biliary cirrhosis. Nat Genet 42:658–660. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.627
Mevel R, Draper JE, Lie ALM, Kouskoff V, Lacaud G et al (2019) RUNX transcription factors: orchestrators of development Development 146. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.148296
Oertelt S et al (2006) Anti-mitochondrial antibodies and primary biliary cirrhosis in TGF-beta receptor II dominant-negative mice. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 177:1655–1660. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.177.3.1655
Qiu F et al (2017) A genome-wide association study identifies six novel risk loci for primary biliary cholangitis 8:14828. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14828
Selmi C et al (2004) Primary biliary cirrhosis in monozygotic and dizygotic twins: genetics, epigenetics, and environment. Gastroenterology 127:485–492
Slattery ML, Lundgreen A, Herrick JS, Caan BJ, Potter JD, Wolff RK et al (2011) Associations between genetic variation in RUNX1, RUNX2, RUNX3, MAPK1 and eIF4E and riskof colon and rectal cancer: additional support for a TGF-beta-signaling pathway. Carcinog 32:318–326. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgq245
Slattery ML, Trivellas A, Pellatt AJ, Mullany LE, Stevens JR, Wolff RK, Herrick JS et al (2017) Genetic variants in the TGFbeta-signaling pathway influence expression of miRNAs in colon and rectal normal mucosa and tumor tissue. Oncotarget 8:16765–16783. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14508
Tanaka A, Leung PSC, Gershwin ME et al (2019) The genetics of primary biliary cholangitis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 35:93–98. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOG.0000000000000507
Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli B et al (2019) The challenges of primary biliary cholangitis: what is new and what needs to be done. J Autoimmun 105:102328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2019.102328
Trynka G et al (2011) Dense genotyping identifies and localizes multiple common and rare variant association signals in celiac disease. Nat Genet 43:1193–1201. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.998
Tsoi LC et al (2012) Identification of 15 new psoriasis susceptibility loci highlights the role of innate immunity. Nat Genet 44:1341–1348. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2467
Vecellio M et al (2018) Evidence for a second ankylosing spondylitis-associated RUNX3 regulatory polymorphism RMD open 4:e000628. https://doi.org/10.1136/rmdopen-2017-000628
Vecellio M, Roberts AR, Cohen CJ, Cortes A, Knight JC, Bowness P, Wordsworth BP et al (2016) The genetic association of RUNX3 with ankylosing spondylitis can be explained by allele-specific effects on IRF4 recruitment that alter gene expression. Ann Rheum Dis 75:1534–1540. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207490
Wang W et al (2015a) RUNX3 gene polymorphisms are associated with clinical features of systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese Han population. J Dermatol Sci 80:69–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2015.07.005
Wang Y et al (2014) The transcription factors T-bet and Runx are required for the ontogeny of pathogenic interferon-gamma-producing T helper 17 cells. Immunity 40:355–366.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2014.01.002
Wang YH et al (2015b) Systems biologic analysis of T regulatory cells genetic pathways in murine primary biliary cirrhosis. J Autoimmun 59:26–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2015.01.011
Webster AP et al (2018) Increased DNA methylation variability in rheumatoid arthritis-discordant monozygotic twins Genome med 10:64. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-018-0575-9
Weidinger S et al (2013) A genome-wide association study of atopic dermatitis identifies loci with overlapping effects on asthma and psoriasis. Hum Mol Genet 22:4841–4856. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt317
Wong WF, Kohu K, Chiba T, Sato T, Satake M et al (2011) Interplay of transcription factors in T-cell differentiation and function: the role of Runx Immunology 132:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03381.x
Zhang Y et al (2019) Association between RUNX3 gene polymorphisms in severe preeclampsia and its clinical features. Medicine 98:e14954. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000014954
Zhang Z, Yuan J, Tian Z, Xu J, Lu Z et al (2017) Investigation of 36 non-HLA (human leucocyte antigen) psoriasis susceptibility loci in a psoriatic arthritis cohort. Arch Dermatol Res 309:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-016-1706-z
Acknowledgments
We thank all participating members of the Jiangsu Provincial PBC Collaboration Group for providing patient samples and clinical information. We would like to thank the patients for their participation in this study.
Funding
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81870397 to X.D.L.; No. 81770381 to X.J.S.; 81620108002, 81771732, 81830016 to X.M.), from the Jiangsu Provincial Research Fund (BE2017713 to X.D.L; BL2018657 to Y.T.), Zhishan Young Scholar Program of SEU and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (X.J.S).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: X.D.L and X.J.S. Data curation, R.J, M.Z, P.J, and Q.W. Formal analysis, R.J, C.W, X.D.L, and X.J.S. Funding acquisition, X.M, X.D.L, and X.J.S. Investigation, R.J, M.Z, P.J, and Q.W. Methodology, R.J and X.D.L. Project administration, C.W and S.H.Y. Resources, L.L, W.C, Y.T, and X.M. Software, R.J and C.W. Supervision, X.D.L and X.J.S. Validation, R.J, C.W, and X.D.L. Visualization, R.J and C.W. Writing—original draft, R.J, X.D.L, and X.J.S. Writing—review and editing, M.E.G, M.F.S, and Z.X.L.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
251_2020_1192_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary file1: Fig. S1 The LD plot of significant SNPs associated with PBC in RUNX3 locus. All SNPs were analyzed by HaploView v4.2. Darker color denotes a higher correlation between markers (r2), which was defined according to the confidence interval method (Gabriel et al. 2002). The plot of pair-wise linkage disequilibrium (LD) and haplotype analysis of significant SNPs in RUNX3 was drawn by using 1118 Han Chinese PBC samples from previously genotyped GWAS data. (DOCX 28.1 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jawed, R., Zhang, M., Wang, C. et al. Replication study and meta-analysis indicate a suggestive association of RUNX3 locus with primary biliary cholangitis. Immunogenetics 72, 467–474 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-020-01192-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-020-01192-4