Abstract
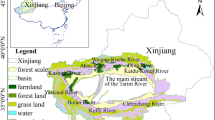
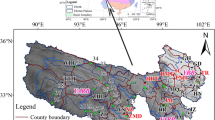
Permafrost is one of the key components of terrestrial ecosystem in cold regions. In the context of climate change, few studies have investigated resilience of social ecological system (SER) from the perspective of permafrost that restricts the hydrothermal condition of alpine grassland ecosystem. In this paper, based on the structural dynamics, we developed the numerical model for the SER in the permafrost regions of the source of Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, analyzed the spatial-temporal characteristics and sensitivity of the SER, and estimated the effect of permafrost change on the SER. The results indicate that: 1) the SER has an increasing trend, especially after 1997, which is the joint effect of precipitation, temperature, NPP and ecological conservation projects; 2) the SER shows the spatial feature of high in southeast and low in northwest, which is consistent with the variation trends of high southeast and low northwest for the precipitation, temperature and NPP, and low southeast and high northwest for the altitude; 3) the high sensitive regions of SER to the permafrost change have gradually transited from the island distribution to zonal and planar distribution since 1980, moreover, the sensitive degree has gradually reduced; relatively, the sensitivity has high value in the north and south, and low value in the south and east; 4) the thickness of permafrost active layer shows a highly negative correlation with the SER. The contribution rate of permafrost change to the SER is -4.3%, that is, once the thickness of permafrost active layer increases 1 unit, the SER would decrease 0.04 units.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adger WN (2006) Vulnerability. Global Environmental Change 16 (3): 268–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2006.02.006
Arena R, Porta PL (2012) Structural Dynamic and Economic Growth. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. pp 69–276. (https://www.cambridge.org/9781107015968, accessed on 2016-07-11)
Arnoldin JF, Loreau M, Haegeman B (2016) Resilience, reactivity and variability: A mathematical comparison of ecological stability measures. Journal of Theoretical Biology389: 47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.10.012
Asokan VA, Yarime M, Esteban M (2017) Introducing flexibility to complex, resilient socio–ecological systems: A comparative analysis of economics, flexible manufacturing systems, evolutionary biology, and supply chain management. Sustainability 9(7): 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071091
Berkes F, Colding J, Folke C (eds.) (2003) Navigating socioecological systems: building resilience for complexity and change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. pp 31–53.
Biesbroek R, Dupuis J, Wellstead A (2017) Explaining through causal mechanisms: resilience and governance of socio–ecological systems. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability 28: 64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2017.08.007
Biggs R, Schlüter M, Biggs D, et al. (2012) Toward principles for enhancing the resilience of ecosystem services. Annual Review of Environment and Resources 37: 421–448. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-environ-051211-123836
Brunner SH, Grêt–Regamey A (2016) Policy strategies to foster the resilience of mountain socio–ecological systems under uncertain global change. Environmental Science and Policy 66:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2016.09.003
Burn CR (1998) The active layer: two contrasting definitions. Permafrost and Periglacial Process 9: 411–416.
Carpenter S, Walker B, Anderies LM, et al. (2001) From Metaphor to Measurement: Resilience of What to What? Ecosystem 4(8): 765–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-001-0045-9
Cumming GS (2011) Spatial resilience: integrating landscape ecology, resilience, and sustainability. Landscape Ecology 26: 899–909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-011-9623-1
Cumming GS, Barnes G, Perz SG, et al. (2005) An exploratory framework for the empirical measurement of resilience. Ecosystem 8: 975–987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-005-0129-z
Cumming GS, Collier J (2005) Change and identity in complex systems. Ecology and Society 10(1): 29. (https://doi.org/www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol10/iss1/art29, accessed on 2015-09-16)
Davidson DJ (2010) The applicability of the concept of resilience to social systems: some sources of optimism and nagging doubts. Society and Natural Resources 23: 1135–1149. https://doi.org/10.1080/08941921003652940
Dayton P, Jarrell S, Kim S, et al. (2016) Surprising episodic recruitment and growth of Antarctic sponges: Implications for ecological resilience. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 482: 38–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2016.05.001
Fang SL (2005) Modern Control Theory and Its Practice in MATLAB. Zhejiang University Press, Hangzhou, pp 21–78 (ISBN: 9787308042291). (In Chinese)
Fang YP (2013) Managing the three–rivers headwater region, China: from ecological engineering to social Engineering. Ambio 42: 566–576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-012-0366-2
Fang YP, Liu YW, Yan X (2015) Meat production’ sensitivity and adaptation to precipitation concentration index during the growing season of grassland: Insights from rural households. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 201: 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2014.11.001
Fang YP, Qin DH, Ding YJ, et al. (2011) The impacts of permafrost change on NPP and implications: a case of the source regions of Yangtze and Yellow Rivers. Journal of Mountain Science 83: 437–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-011-1004-3
Fang YP, Zhu FB, Qiu XP, et al. (2018) Effects of natural disasters on livelihood resilience of rural residents in Sichuan. Habitat International 76: 19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2018.05.004
Farley J, Voinov A (2016) Economics, socio–ecological resilience and ecosystem services. Journal of Environmental Management 183: 389–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.07.065
Folke C (2006) Resilience: the emergence of a perspective for socioecological systems analysis. Global Environmental Change 16: 253–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2006.04.002
Folke C, Berkes F, Colding J (1998) Ecological practices and social mechanisms for building resilience and sustainability. In: Berkes F, Folke C (eds) Linking social and ecological systems. London: Cambridge University Press, London, pp 414–436.
Folke C, Carpenter S, Elmquist T, et al. (2002) Resilience and sustainable development: building adaptive capacity in a world of transformations. Ambio 312(5): 437–440. https://doi.org/10.1579/0044-7447-31.5.437
Folke C, Carpenter SR, Walker B, et al. (2010) Resilience thinking: integrating resilience, adaptability and transformability. Ecology and Society 15(4):20. (https://doi.org/www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol15/iss4/art20/, accessed on 2016-04-18)
Folke C, Colding J, Berkes F (2003) Building resilience and adaptive capacity in social–ecological systems. In: Berkes F, Colding J, Folke C (eds.), Navigating Socio–ecological systems: Building Resilience for Complexity and Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge pp 352–387.
Fraccascia L, Vito Albino IG (2017) Rethinking resilience in industrial symbiosis: Conceptualization and measurements. Ecological Economics 137: 148–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2017.02.026
Gunderson LH (2000) Ecological resilience–in theory and application. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 31: 425–439. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.31.1.425
Gunderson L, Holling CS (eds.) (2001) Panarchy: Understanding Transformations in Human and Natural Systems. Washington (DC): Island Press.
Hodbod J, Adger WN (2014) Integrating social–ecological dynamics and resilience into energy systems research. Energy Research & Social Science 1: 226–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2014.03.001
Holling CS (1973) Resilience and stability of ecological systems. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 4: 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.es.04.110173.000245
Holling CS (1986) The resilience of terrestrial ecosystems: local surprise and global change. In: Clark WC, Munn RE (eds.), Sustainable development of the biosphere, Cambridge University Press, London. pp 292–317.
Holling CS (1996) Engineering resilience versus ecological resilience. In: Schulze P (eds.), Engineering within Ecological Constraints. National Academies Press, Washington, D.C. pp 31–44.
Holling CS (2001) Understanding the complexity of economic, ecological and social systems. Ecosystem 4(5): 390–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-001-0101-5
Jiang C, Li DQ, Wang DW, et al. (2016) Quantification and assessment of changes in ecosystem service in the Three–River Headwaters Region, China as a result of climate variability and land cover change. Ecological Indictor 66: 199–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.01.051
Jiang C, Zhang LB (2016) Ecosystem change assessment in the Three–river Headwater Region, China: Patterns, causes, and implications. Ecological Engineering 93: 24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.05.011
Jorgensen SE (1992) Integration of Ecosystem Theories: A Pattern. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 18–38
Jorgenson MT, Romanovsky V, Harden J, et al. (2010) Resilience and vulnerability of permafrost to climate change. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 40(7): 1219–1236. https://doi.org/10.1139/X10-060
Knapp AK, Heisler–White J, Smith MD, et al. (2008) Climate change and grasslands: unexpected consequences of extreme rainfall patterns. (https://www.researchgate.net/publication/255608574, accessed on 2016-10-06)
Kosmas C, Karamesouti M, Kounalaki K, et al. (2016) Land degradation and long–term changes in agro–pastoral systems: An empirical analysis of ecological resilience in Asteroussia–Crete (Greece). Catena 147: 196–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.07.018
Kotzee I, Reyers B (2016) Piloting a social–ecological index for measuring flood resilience: A composite index approach. Ecological Indicator 60: 45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.06.018
Kraus MK, Park JW (2017) The structural dynamics of social class. Current Opinion in Psychology 18: 55–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2017.07.029
Kröel–Dulay G, Ransijn J, Schmidt IK, et al. (2015) Increased sensitivity to climate change in disturbed ecosystems. Nature Communications 6: 6682. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7682vaueftbyusbuzwqsbdycysxczbfa
Li YN, Zhao XQ, Wang SP, et al. (2007) Impact assessment of climate warming upon primary productivity in Yellow River source region. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology 28(4): 374–377. (In Chinese)
Li YN, Zhao XQ, Zhou HK, et al. (2008) The dynamic features of ecosystem environment and plant productivity in the source regions of the Changjiang River and Yellow River. Journal of Mountain Science 26(6): 678–683. (In Chinese)
Ludwig D, Walker B, Holling CS (1997) Sustainability, stability and resilience. Conservation Ecology 1(1). (https://doi.org/www.consecol.org/vol1/iss1/art7, accessed on 2017-06-08)
Müller F, Bergmann M, Dannowski R, et al. (2016) Assessing resilience in long–term ecological data sets. Ecological Indicator 65: 10–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.10.066
Nelson DR, Adger WN, Brown K (2007) Adaptation to environmental change: contributions of a resilience framework. Annual Review of Environment and Resources 32: 395–419. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.energy.32.051807.090348
Parsons M, Thoms MC (2018) From academic to applied: Operationalising resilience in river systems. Geomorphology 305: 242–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.08.04
Perz SG, Munoz–Carpena R, Kiker G, et al. (2013) Evaluating ecological resilience with global sensitivity and uncertainty analysis. Ecological Modelling 263: 174–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2013.04.024
Pimm SL (1991) The Balance of Nature? Ecological Issues in the Conservation of Species and Communities. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. p13.
Qinghai Provincial Bureau of Statistics (2014) Qinghai Statistical Yearbook 2014. China Statistics Press, Beijing.
Romanovsky VE, Osterkamp TE (1997) Thawing of the active layer on the coastal plain of the Alaskan Arctic. Permafrost and Periglacial Processes 8(1): 1–22.
Sabatier R, Joly F, Hubert B (2017) Assessing both ecological and engineering resilience of a steppe agroecosystem using the viability theory. Agricultural System 157: 146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2017.07.009
Scazzieri R (2018) Structural dynamics and evolutionary change. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics (In press). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2018.03.007
Scheffer M, Bascompte J, Brock WA, et al. (2009) Early–warning signals for critical transitions. Nature 461: 53–59. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08227
Schlüter M, Müller B, Frank K (2013) How to use models to improve analysis and governance of socio–ecological systems–the reference frame MORE. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2037723
Schlüter M, Pahl–Wostl C (2007) Mechanisms of resilience in common–pool resource management systems: an agent–based model of water use in a river basin. Ecology and Society 12: 1–23. https://doi.org/www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol12/iss2/art4/
Shi ZH, Watanabe S, Ogawa K, et al. (2018) Reviews of resilience theories and mathematical generalization. Structural Resilience in Sewer Reconstruction. Pp 17–78.
Suzuki K, Yoshida T (2015) Ecological resilience of population cycles: A dynamic perspective of regime shift. Journal of Theoretical Biology 370: 103–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.01.026
Tilt B, Gerkey D (2016) Dams and population displacement on China’s Upper Mekong River: Implications for social capital and social–ecological resilience. Global Environmental Change 36: 153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2015.11.008
Ungaro F, Zasada I, Piorr A (2017) Turning points of ecological resilience: Geostatistical modelling of landscape change and bird habitat provision. Landscape and Urban Planning 157: 297–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2016.07.001
Walker BH, Anderies JM, Kinzig AP, et al. (2006) Exploring resilience in socio–ecological systems through comparative studies and theory development: introduction to the special issue. Ecology and Society 11 (1): 12. (https://doi.org/www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol11/iss1/art12/, accessed on 2015-12-19)
Walker B, Holling CS, Carpenter SR, et al. (2004) Resilience, adaptability and transformability in socio–ecological systems. Ecology and Society 9(2): 5. (https://doi.org/www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol9/iss2/art5/, accessed on 2017-11-21)
Walker B, Salt D (2006) Resilience thinking: sustaining ecosystems and people in a changing world. Island Press, Washington, pp 1–18
Wang GX, Li YS, Wu QB, et al. (2006) Relationship between permafrost and vegetation and its effect on alpine ecosystem in permafrost region of Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences 36(8): 743–754.
Wang XY, Yi SH, Wu QB, et al. (2016) The role of permafrost and soil water in distribution of alpine grassland and its NDVI dynamics on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Global and Planetary Change 147: 40–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2016.10.014
Westley F, Carpenter SR, Brock WA, et al. (2002) Why systems of people and nature are not just social and ecological systems. In: Gunderson LH, Holling CS (eds.), Panarchy: understanding transformations in human and natural systems. Island Press, Washington. pp 103–119.
Wu QB, Hou YD, Yun HB, et al. (2015) Changes in active–layer thickness and near–surface permafrost between 2002 and 2012 in alpine ecosystems, Qinghai–Xizang (Tibet) Plateau, China. Global and Planetary Change 124: 149–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2014.09.002
Yang ZP, Ou YH, Xu XL, et al. (2010) Effects of permafrost degradation on ecosystems. Acta Ecologica Sinica 30: 33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chnaes.2009.12.006
Yi SH, Wang X, Qin Y, et al. (2014) Responses of alpine grassland on Qinghai–Tibetan plateau to climate warming and permafrost degradation: a modeling perspective. Environmental Research Letters 9(7): 074014. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/9/7/074014
Zhang YL, Liu LS, Bai WQ, et al. (2006) Grassland degradation in the source region of the Yellow River. Acta Geographica Sinica 61(1): 3–14.
Zou JX, Yu KP (2009) Structural Dynamics (Second Edition). Harbin Institute of Technology Press, Harbin. pp19–118. (ISBN: 7560311539). (In Chinese)
Acknowledgements
The work has been supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41571523, and Grant No. 41661144038), the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2013CBA01808), the National Key Technology R&D Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2014BAC05B01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Yp., Zhu, Fb., Yi, Sh. et al. Role of permafrost in resilience of social-ecological system and its spatio-temporal dynamics in the source regions of Yangtze and Yellow Rivers. J. Mt. Sci. 16, 179–194 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5078-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5078-z