Abstract
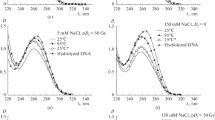
The content of damaged 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine nitrogenous bases in the blood DNA of healthy donors and patients with epidermolysis bullosa after exposure to an alternating magnetic field of 550 ± 30 A/m in the frequency range from 3 to 60 Hz in vitro was determined using an enzyme immunoassay. The degree of oxidative DNA damage in epidermolysis bullosa was almost twice as high as in healthy donors. It was shown that there was a significant increase in the level of 8-oxoguanine in the DNA of both groups after the magnetic field treatment, which depended in a complex way on the frequency. The resulting effect is explained by the generation of reactive oxygen species under the influence of a magnetic field and the disruption of DNA repair processes.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
F. I. Wolf, A. Torsello, B. Tedesco, et al., Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1743, 120 (2005).
C. A. Buckner, A. L. Buckner, S. A. Koren, et al., PLoS One 10 (4), e0124136 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124136
T. Wang, Y. Nie, S. Zhao, et al., Bioelectromagnetics 32 (6), 443 (2011).
F. Sanie-Jahromi and M. Saadat, Mol. Biol. Rep. 45, 807 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4223-7
I. Vijayalaxmi and T. J. Prihoda, Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 85, 196 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/09553000902748575
R. J. Buldak, R. Polanniak, I. Buldak, et al., Bioelectromagnetics 33, 641 (2012).
E. E. Tekutskaya, M. G. Baryshev, and G. P. Ilchenko, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med. 52 (1), 56 (2018). https://doi.org/10.21687/0233-528X-2018-52-1-56-61
A. K. Dharmadhikari, H. Bharambe, J. A. Dharmadhikari, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 138105 (2014).
V. O. Ponomarev, V. V. Novikov, A. V. Karnaukhov, and O. A. Ponomarev, Biofizika 53 (2), 197 (2008).
. V. Smirnova, S. V. Gudkov, and V. I. Bruskov, 8-Oxoguanine and Its Oxidation Products: Formation in DNA under the Impact of Heat, Uranyl Ions, and g-Radiation (Lambert Acad. Publ., Saarbrucken, 2011)
M. V. Lukina, A. A. Kuznetsova, N. A. Kuznetsov, and O. S. Fedorova, Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 43 (1), 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.7868/S0132342317010055
X. Ba, L. Aguilera-Aguirre, Q. T. Rashid, et al., Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15, 16975 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150916975
A. A. Kubanov, A. E. Karamova, V. I. Al’banova, et al., Vestn. Dermatol. Venerol. 4, 28 (2017). https://doi.org/10.25208/0042-4609-2017-0-4-22-27
E. E. Tekutskaya, M. G. Barishev, and G. P. Ilchenko, Biophysics 60 (6), 913 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S000635091506024X
G. P. Il’chenko, M. G. Baryshev, E. E. Tekutskaya, et al., Measur. Techniques 60 (6), 632 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11018-017-1247-7
S. V. Gudkov, O. E. Karp, S. A. Garmash, et al., Biophysics (Moscow) 57 (1), 1 (2012).
L. Stryer, Biochemistry (Freeman, New York, 1975; Mir, Moscow, 1985), vol. 3.
V. I. Poltev, V. M. Anisimov, C. Sanchez, et al., Biophysics (Moscow) 61 (2), 217 (2016).
M. D. Frank-Kamenetskii, A. V. Lukashin, and V. V. Anshelevich, J. Biomol. Struct. Dynam. 2, 1005 (1985).
P. Yakovchuk, E. Protozanova, and M. D. Frank-Kamenetskii, Nucleic Acids Res. 34 (2), 564 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkj454
I. N. Shtarkman, S. V. Gudkov, A. V. Chernikov, and V. I. Bruskov, Biochemistry (Moscow) 73 (4), 470 (2008).
A. A. Krasnovsky and J. B. Kozlov, J. Biomed. Photonics 3 (1), 1 (2017).
A. A. Krasnovsky, N. N. Drozdova, A. V. Ivanov, et al., Biochemistry 68, 963 (2003).
A. A. Krasnovsky, Membrane Cell Biol. 15, 530 (1998).
V. V. Novikov, E. V. Yablokova and E. E. Fesenko, Biophysics (Moscow) 63 (2), 193 (2018).
V. O. Ponomarev and V. V. Novikov, Biophysics (Moscow) 54 (2), 163 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
Laboratory diagnostic tests were performed in accordance with the mandatory compliance with the ethical standards set out in the Declaration of Helsinki of 1975 with amendments of 1983.
Additional information
Translated by E. Puchkov
Abbreviations: MF, magnetic fields; ROS, reactive oxygen species; 8-ОНdG, 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine; 8-oxoG, 8‑oxoguanine; EB, epidermolysis bullosa.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tekutskaya, E.E., Baryshev, M.G., Gusaruk, L.R. et al. Oxidative Damage to DNA under the Action of an Alternating Magnetic Field. BIOPHYSICS 65, 564–568 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350920040247
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350920040247