Abstract
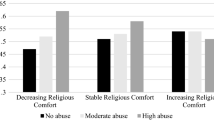
Agnew’s general strain theory has been widely tested in other countries and has received general support from most studies. To date, however, there has been limited empirical test of the theory in the Philippines. Thus, this study aims to test the core theoretical propositions of the theory that link negative life events (strains) to negative emotions that in turn encourage maladaptive behaviors or criminal coping. The study uses the Global School-based Student Health Survey (2011) data on a nationally representative sample of 5920 secondary Filipino students. In general, the results support the general strain theory: negative life events (e.g., violent experiences, discrimination, sexual harassment victimization) encourage maladaptive behaviors (i.e., suicidality, substance use, and truancy), and this link is somewhat mediated or attenuated by depression. Further, conditioning factors such as parental care and supervision, social support, and engagement in physical activities moderate the effects of negative life events and depression on maladaptive behaviors. Contrary to the theory, however, some conditioning factors intensify the effects of strain on truancy. Overall, the current findings support the theory but call for further research and theory building—delinquent acts are diverse behaviors, and thus, each may require a crime-specific model of the general strain theory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnew, R. (1992). Foundation for a general strain theory of crime and delinquency. Criminology, 30(1), 373–387.
Agnew, R. (2001). Building on the foundation of general strain theory: specifying the types of strain most likely to lead to crime and delinquency. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 38(4), 319–361.
Agnew, R. (2002). Experienced, vicarious, and anticipated strain: an exploratory study on physical victimization and delinquency. Justice Quarterly, 19(4), 603–632.
Agnew, R. (2006). General strain theory: current status and directions for further research. In F. T. Cullen, J. P. Wright, & K. Blevins (Eds.), Taking stock: the status of criminological theory—advances in criminological theory. Transaction: New Brunswick, NJ.
Agnew, R. (2010). A general strain theory of terrorism. Theoretical Criminology, 14(2), 131–153.
Agnew, R. (2013). When criminal coping is likely: an extension of general strain theory. Deviant Behavior, 34(8), 653–670.
Agnew, R. (2015a). General strain theory and delinquency. In M. D. Krohn & J. Lane (Eds.), The handbook of juvenile delinquency and juvenile justice. Chichester, West Sussex, United Kingdom: Wiley, Inc.
Agnew, R. (2015b). Using general strain theory to explain crime in Asian societies. Asian Journal of Criminology, 10(2), 131–147.
Agnew, R., & White, H. R. (1992). An empirical test of general strain theory. Criminology, 30(4), 475–499.
Agnew, R., Brezina, T., Wright, J. P., & Cullen, F. (2002). Strain, personality traits, and delinquency: extending general strain theory. Criminology, 40(1), 43–71.
Bakken, N. W., & Gunter, W. D. (2012). Self-Cutting and suicidal ideation among adolescents: gender differences in the causes and correlates of self-injury. Deviant Behavior, 33(5), 339–356.
Baron, S. W. (2006). Street youth, strain theory, and crime. Journal of Criminal Justice, 34, 209–223.
Baron, S. W. (2008). Street youth, unemployment, and crime: is it that simple? Using general strain theory to untangle the relationship. Canadian Journal of Criminology and Criminal Justice, 50, 399–433.
Baron, S. W. (2009). Street youths’ violent responses to violent personal, vicarious, and anticipated strain. Journal of Criminal Justice, 37, 442–451.
Baron, R., & Tan, J. (2012). Foster youth and crime: employing general strain theory to promote understanding. Journal of Criminal Justice, 40, 212–220.
Biddle, S. J. H., & Asare, M. (2011). Physical activity and mental health in children and adolescents: a review of reviews. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 45(11), 886–895.
Booker, C. L., Gallaher, P., Unger, J. B., Ritt-Olson, A., & Johnson, C. A. (2004). Stressful life events, smoking behavior, and intentions to smoke among a multiethnic sample of sixth graders. Ethnicity & Health, 9(4), 369–397.
Booker, C. L., Unger, J. B., Azen, S. P., Baezconde-Garbanati, L., Lickel, B., & Johnson, C. A. (2008). A longitudinal analysis of stressful life events, smoking behaviors, and gender differences in a multicultural sample of adolescents. Substance Use & Misuse, 43, 1509–1531.
Botchkovar, E., & Broidy, L. (2013). Accumulated strain, negative emotions, and crime: a test of general strain theory in Russia. Crime & Delinquency, 59(6), 837–860.
Botchkovar, E. V., Tittle, C. R., & Antonaccio, O. (2009). General strain theory: additional evidence using cross-cultural data. Criminology, 47(1), 131–176.
Capowich, G. E., Mazerolle, P., & Piquero, A. (2001). General strain theory, situational anger, and social networks: an assessment of conditioning influences. Journal of Criminal Justice, 2001, 445–461.
CDC & WHO (2011). Global School-based student health survey: Philippines 2011 fact sheet. Center for Disease Control and Prevention and World Health organization. Retrieved on July 5, 2015, from http://www.who.int/chp/gshs/philippines/en/
CDC & WHO. (2013). 2013 GSHS data user’s guide. Center for Disease Control and Prevention and World Health Organization. Retrieved on July 5, 2015, from http://www.cdc.gov/gshs/pdf/gshs-data-users-guide.pdf
Chaiton, M. O., Cohen, J. E., O’Loughlin, J., & Rehm, J. (2009). A systematic review of longitudinal studies on the association between depression and smoking in adolescents. BMC Public Health, 9(1), 1–11.
Chiodo, D., Wolfe, D. A., Crooks, C., Hughes, R., & Jaffe, P. (2009). Impact of sexual harassment victimization by peers on subsequent adolescent victimization and adjustment: a longitudinal study. Journal of Adolescent Health, 45, 246–252.
Conger, A. J. (1974). A revised definition for suppressor variables: a guide to their identification and interpretation. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 34(1), 35–46.
Conroe, R. (2007). Gender, obesity, and education. Sociology of Education, 80(3), 241–260.
Eime, R. M., Young, J. A., Harvey, J. T., Charity, M. J., & Payne, W. R. (2013). A systematic review of the psychological and social benefits of participation in sport for children and adolescents: informing development of a conceptual model of health through sport. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 10(98), 1–21.
Eitle, D. (2002). Exploring a source of deviance-producing strain for females: perceived discrimination and general strain theory. Journal of Criminal Justice, 30, 429–442.
Estanislao, S. (2001). Development of a tool to assess suicide potential among Filipino youth. Philippine Journal of Psychology, 34(1), 77–110.
Farrington, D. P., & Loeber, R. (2000). Some benefits of dichotomization in psychiatric and criminological research. Criminal Behavior and Mental Health, 10(2), 100–122.
Fergus, S., & Zimmerman, M. A. (2005). Adolescent resiliency: a framework for understanding healthy development in the face of risk. Annual Review of Public Health, 26, 399–419.
Froggio, G. (2007). Strain and juvenile delinquency: a critical review of Agnew’s general strain theory. Journal of Loss and Trauma, 12, 383–418.
Froggio, G., & Agnew, R. (2007). The relationship between crime and “objective” versus “subjective” strains. Journal of Criminal Justice, 35, 81–87.
Gao, Y., Dennis, S.W., & Yu, Y. (2014). Maltreatment and delinquency in china: examining and extending the intervening process of general strain theory. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology, 1–24. doi: 10.1177/0306624X14547495
Garisch, J. A., & Wilson, M. S. (2010). Vulnerabilities to deliberate self-harm among adolescents: the role of alexithymia and victimization. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 49, 151–162.
Garry, E. M. (1996). Truancy: first step to a lifetime of problems. Washington D.C: U.S. Department of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention.
Gold, D. R., Wang, X., Wypij, D., Speizer, F. E., Ware, J. H., & Dockery, D. W. (1995). Effects of cigarette smoking on lung function in adolescent boys and girls. New England Journal of Medicine, 335(13), 931–937.
Gore, F. M., Bloem, P. J., Patton, G. C., Ferguson, J., Joseph, V., Coffey, C., Sawyer, S. M., & Mathers, C. D. (2011). Global burden of disease in young people aged 10–24: a systematic analysis. The Lancet, 377(9783), 2093–2102.
Guevara, J. P. (2005). Pakikipagkapwa [sharing/merging oneself with others]. In R. M. Gripaldo (Ed.), Filipino cultural traits. Washington, D.C: The Council for Research in Values and Philosophy.
Hawton, K., Saunders, K. E. A., & O’Connor, R. C. (2012). Self-harm and suicide in adolescents. The Lancet, 379(9834), 2373–2382.
Hay, C., & Evans, M. M. (2006). Violent victimization and involvement in delinquency: examining predictions from general strain theory. Journal of Criminal Justice, 34, 261–274.
Hay, C., Meldrum, R., & Mann, K. (2010). Traditional bullying, cyber bullying, and deviance: a general strain theory approach. Journal of Contemporary Criminal Justice. doi:10.1177/1043986209359557.
Heilbrunn, J. Z. (2007). Pieces of the truancy jigsaw: a literature review. Denver, Col: National Center for School Engagement.
Heneghan, H. M., Heinberg, L., Windover, A., Rogula, T., & Schauer, P. R. (2009). Weighing the evidence for an association between obesity and suicide risk. Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases, 8(1), 98–107.
Horton, R., Rice, S. K., Piquero, N. L., & Piquero, A. R. (2012). On the variability of anger cross-culturally: an assessment of general strain theory’s primary mediator. Deviant Behavior, 33, 260–281.
Jang, S. J., & Johnson, B. R. (2003). Strain, negative emotions, and deviant coping among African Americans: a test of general strain theory. Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 19(1), 79–105.
Jang, H., Song, J., & Kim, R. (2014). Does the offline bully-victimization influence cyberbullying behavior among youths? Application of general strain theory. Computers in Human Behavior, 31, 85–93.
Jun, S., & Choi, E. (2015). Academic stress and internet addiction from general strain theory framework. Computers in Human Behavior, 49, 282–287.
Klomek, A. B., Marrocco, F., Kleinman, M., Schonfeld, I. S., & Gould, M. S. (2008). Peer victimization, depression, and suicidality in adolescents. Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior, 38(2), 166–180.
Lanza, H. I., & Huang, D. Y. (2015). Is obesity associated with school dropout? Key developmental and ethnic differences. The Journal of School Health, 85(10), 663–670.
Lanza, H. I., Grella, C. E., & Chung, P. J. (2014). Does adolescent weight status predict problematic substance use patterns? American Journal of Health Behavior, 38(5), 708–716.
Lanza, H. I., Grella, C. E., & Chung, P. J. (2015). Adolescent obesity and future substance use: incorporating the psychosocial context. Journal of Adolescence, 45, 20–30.
Lin, W., Dembo, R., Sellers, C., Cochran, J. & Mieczkowski, T. (2013). Strain, negative emotions, and juvenile delinquency: the United States versus Taiwan. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology, 1–23.
Lipton, W., & Smith, D. (1983). Explaining delinquent involvement: a consideration of suppressor effects. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 20(2), 199–213.
Liu, R. T., & Miller, I. (2014). Life events and suicidal ideation and behavior: a systematic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 34(3), 181–192.
Luppino, F. S., de Wit, L. M., Bouvy, P. F., Stijnen, T., Cuijpers, P., Penninx, B. W., & Zitman, F. G. (2010). Overweight, obesity, and depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Archives of General Psychiatry, 67(3), 220–229.
Manasse, M. E., & Ganem, N. M. (2009). Victimization as a cause of delinquency: the role of depression and gender. Journal of Criminal Justice, 37, 371–378.
Maxwell, S. R. (2001). A focus on familial strain: antisocial behavior and delinquency in Filipino society. Sociological Inquiry, 71(3), 265–292.
Mazerolle, P., & Piquero, A. (1998). Linking exposure to strain with anger: an investigation of deviant adaptations. Journal of Criminal Justice, 26(3), 195–211.
Mazerolle, P., Burton, V. S., Cullen, F. T., Evans, T. D., & Payne, G. L. (2000). Strain, anger, and delinquent adaptations: specifying general strain theory. Journal of Criminal Justice, 28, 89–101.
Moon, B., & Jang, S. J. (2014). A general strain approach to psychological and physical bullying: a study of interpersonal aggression at school. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 29(12), 2147–2171.
Paternoster, R., & Mazerolle, P. (1994). General strain theory and delinquency: a replication and extension. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 31(3), 235–263.
Philippine Commission on Women. (2014). Statistics on Filipino women and men’s education. Retrieved on July 8, 2015, from http://www.pcw.gov.ph/statistics/201405/statistics-filipino-women-and-mens-education
Rebellon, C. J., Manasse, M. E., Van Gundy, K. T., & Cohn, E. S. (2012). Perceived injustice and delinquency: a test of general strain theory. Journal of Criminal Justice, 40, 230–237.
Reid, K. (2005). The causes, views and traits of school absenteeism and truancy. Research in Education, 74(1), 59–82.
Sharp, S. F., Peck, B. M., & Hartsfield, J. (2012). Childhood adversity and substance use of women prisoners: a general strain theory approach. Journal of Criminal Justice, 40, 202–211.
Sigfusdottir, I. D., Gudjonsson, G., & Sigurdsson, G. F. (2010). Bullying and delinquency. The mediating role of anger. Personality and Individual Differences, 48, 391–396.
Sigfusdottir, I. D., Kristjansson, A. L., & Agnew, R. (2012). A comparative analysis of general strain theory. Journal of Criminal Justice, 40, 117–127.
Steele, M. M., & Doey, T. (2007). Suicidal behavior in children and adolescents. Part 1: etiology and risk factors. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 52(6), 21–33.
Thapar, A., Collishaw, S., Pine, D. S., & Thapar, A. K. (2012). Depression in adolescence. The Lancet, 379(9820), 1056–1067.
Thompson, F. T., & Levine, D. U. (1997). Examples of easily explainable suppressor variables in multiple regression research. Multiple Linear Regression Viewpoints, 24(1), 11–13.
Tiangco, J. A. N. Z. (2005). Understanding the Filipino philosophy of resiliency: katatagang-loob [emotional strength/resiliency] and its phenomenological considerations. In R. M. Gripaldo (Ed.), Filipino cultural traits. Washington, D.C: The Council for Research in Values and Philosophy.
Unger, J. B., Li, Y., Johnson, C. A., Gong, J., Chen, X., Li, C. Y., Trinidad, D. R., Tran, N. T., & Lo, A. T. (2001). Stressful life events among adolescents in Wuhan, China: associations with smoking, alcohol use, and depressive symptoms. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 8(1), 1–18.
Warren, C. W., Jones, N. R., Eriksen, M. P., & Asma, S. (2006). Patterns of global tobacco use in young people and implications for future chronic disease burden in adults. The Lancet, 367(9512), 749–753.
Wasserman, D. (2016). Negative life events and suicide. In D. Wasserman (Ed.), Suicide: an unnecessary death. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Wasserman, D., Cheng, Q. I., & Jinag, G. X. (2005). Global suicide rates among young people aged 15–19. World Psychiatry, 4(2), 114–120.
Yiede, M., & Kobrin, M. (2009). Truancy literature review. Washington, D.C.: Department of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention.
Yun, I., & Lee, C. (2015). Hazardous alcohol use among South Korean police officers: examining predictions from general strain theory. International Journal of Law, Crime and Justice, 43, 194–213.
Zhang, J., Wieczorek, W., Conwell, Y., & Tu, X. M. (2011). Psychological strains and youth suicide in rural China. Social Science & Medicine, 2011, 2003–2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barrera, D.J., Gaga-a, B. & Pabayos, J. Negative Life Events and Maladaptive Behaviors Among Filipino Adolescents: an Empirical Test of the General Strain Theory. Asian Criminology 11, 265–287 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11417-016-9230-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11417-016-9230-9