Abstract
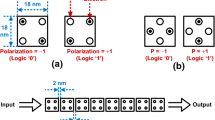
Quantum-dot cellular automata (QCA) is a computational paradigm that is based on encoding information in terms of the configuration of charge among quantum dots without requiring current switches. Mostly, QCA cells have been realized by employing the electron switching in square quantum-dot cells. In this paper, a triangular metal-dot cell with a single electron is proposed to represent ternary information. Then, an inverter chain of the proposed triangle cells is suggested through juxtaposing the cells. Additionally, wire crossing and wire fan-out are the two inseparable subjects of QCA wire. A wire-crossing method is presented for the proposed ternary wire. Wire fan-out is also dealt with in this paper by an innovative approach. The correctness of operation of proposed cells and wires are thoroughly verified by applying the physical relations.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Madan, J., Chaujar, R.: Effect of nanoscale structure on reliability of nano devices and sensors. In: Li, T., Liu, Z. (eds.) Outlook and Challenges of Nano Devices, Sensors, and MEMS, pp. 239–269. Springer, Cham (2017)
Bousari, N.B., Anvarifard, M.K., Haji-Nasiri, S.: Improving the electrical characteristics of nanoscale triple-gate junctions FinFET using gate oxide engineering. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 108, 226–234 (2019)
Martel, R., Schmidt, T., Shea, H.R., Hertel, T., Avouris, P.: Single- and multi-wall carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 2447–2449 (1998)
Matsumoto, K., Ishii, M., Segawa, K., Oka, Y., Vartanian, B.J., Harris, J.S.: Room temperature operation of a single electron transistor made by the scanning tunneling microscope nanooxidation process for the TiOx/Ti system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 68, 34–36 (1996)
Lent, C.S., Tougaw, P.D., Porod, W., Bernstein, G.H.: Quantum cellular automata. Nanotechnology. 4, 49–57 (1993)
Blair, E.P., Yost, E., Lent, C.S.: Power dissipation in clocking wires for clocked molecular quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Comput. Electron. 9, 49–55 (2010)
Dysart, T.J.: Modeling of electrostatic QCA wires. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 12, 553–560 (2013)
Angizi, S., Samadi, S., Sayedsalehi, S., Navi, K.: Design and evaluation of new majority gate-based RAM cell in quantum-dot cellular automata. Microelectron. J. 46, 43–51 (2015)
Tahmasebi, M., Mirzaee, R.F., Komleh, S.H.P.: On the design methodology of Boolean functions with quantum-dot cellular automata for reducing delay and number of wire crossings. J. Comput. Electron. 17, 1756–1770 (2018)
Kandasamy, N., Ahmad, F., Telagam, N.: Shannon logic based novel QCA full adder design with energy dissipation analysis. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 3702–3715 (2018)
Bhat, S.M., Ahmed, S.: Design of ultra-efficient reversible gate based on 1-bit full adder in QCA with power dissipation analysis. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58, 4042–4063 (2019)
Baldwin, A.T., Will, J.D., Tougaw, D.: Using the full quantum basis set to simulate quantum-dot cellular automata devices. J. Comput. Electron. 18, 982–987 (2019)
Dubrova, E.: Multiple-valued logic in VLSI: challenges and opportunities. In Proc. NORCHIP, Oslo, Norway, 99, 340–350 (1999)
Anil, D.G., Bai, Y., Choi, Y.: Performance evaluation of ternary computation in SRAM design using graphene nanoribbon field effect transistors. IEEE 8th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conf., Las Vegas, USA. 382–388 (2018)
Bajec, I.L., Zimic, N., Mraz, M.: The ternary quantum-dot cell and ternary logic. Nanotechnology. 17, 1826–1829 (2006)
Bajec, I.L., Zimic, N., Mraz, M.: Towards the bottom-up concept: extended quantum-dot cellular automata. Microelectron. Eng. 83, 1937–1942 (2006)
Tehrani, M.A., Navi, K.: A novel quantum dot cellular automata for implementation of multi-valued logic. Nano Today Conf., Singapore, Singapore. 1–8 (2009)
Lent, C.S., Isaksen, B.: Clocked molecular quantum-dot cellular automata. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices. 50, 1890–1896 (2003)
Leon, A.: Propagation of a binary signal along a chain of triangular graphane nanoclusters. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 6, 555–560 (2014)
Pulimeno, A., Graziano, M., Wang, R., Piccinini, G.: Fault tolerance analysis of a bis-ferrocene QCA wire. Workshop on Design and Test Methodologies for Emerging Technologies, Avignon, France. 1–2 (2013)
Von Neumann, J., Burks, A.W.: Theory of self-reproducing automata. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 5, 3–14 (1966)
Campos, C.A.T., Marciano, A.L., Neto, O.P.V., Torres, F.S.: USE: a universal, scalable, and efficient clocking scheme for QCA. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circ. Syst. 35, 513–517 (2016)
Amlani, I., Orlov, A.O., Snider, G.L., Lent, C.S.: Demonstration of a six-dot quantum cellular automata system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 2179–2181 (1998)
Liu, M., Lent, C.S.: High-speed metallic quantum-dot cellular automata. 3rd IEEE Conf. Nanotechnology, San Francisco, USA. 2, 465–468 (2003)
Kim, K., Wu, K., Karri, R.: Towards designing robust QCA architectures in the presence of sneak noise paths. In Proc. Design, Automation and Test in Europe, Munich, Germany. 1214–1219 (2015)
Schulhof, G., Walus, K., Jullien, G.A.: Simulation of random cell displacements in QCA. ACM J. Emerg. Technol. Comput. Syst. 2, 1–14 (2007)
Walus, K., Dysart, T.J., Jullien, G.A., Budiman, R.A.: QCADesigner: a rapid design and simulation tool for quantum-dot cellular automata. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 3, 26–31 (2004)
QCADesigner, The University of British Columbia, available at: https://waluslab.ece.ubc.ca/qcadesigner. Accessed 2020
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ronaghi, N., Faghih Mirzaee, R. & Sayedsalehi, S. Triangular Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata Wire for Standard Ternary Logic. Int J Theor Phys 59, 3821–3839 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-020-04634-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-020-04634-7