Abstract
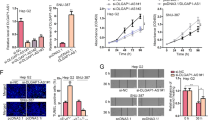
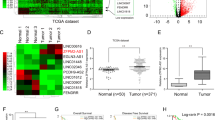
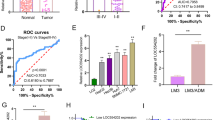
Recent studies have illustrated the role of aberrant regulatory interactions in the mediation of malignant phenotypes of cancer cells, which could potentially provide novel therapeutic targets to limit the destructive recurrence and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Herein, we clarify the oncogenic role of the long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) distal-less homeobox 6 antisense 1 (DLX6-AS1) in HCC in vivo and in vitro. To this end, we knocked down lncRNA DLX6-AS1 and manipulated the expression of miR-513c to characterize their effects in HCC cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis. Furthermore, we probed the interactions with miR-513c’s target gene Cullin4A (Cul4A) and the degradation of Annexin A10 (ANXA10) protein. Our data show that lncRNA DLX6-AS1 and Cul4A were highly expressed, while miR-513c and ANXA10 were poorly expressed in HCC tissues and cells. Moreover, the silencing of lncRNA DLX6-AS1 impeded the viability, invasion, and migration of HCC cells, while stimulating cell apoptosis. Further data indicated that lncRNA DLX6-AS1 targeted and repressed miR-513c expression, where the tumor-inhibiting effects of lncRNA DLX6-AS1 silencing was achieved by elevating miR-513c expression. Importantly, the lncRNA DLX6-AS1 upregulated the expression of Cul4A through sponging of miR-513c. The silencing of Cul4A restricted the malignant phenotypes of HCC cells by repressing the ubiquitination-mediated degradation of ANXA10. In vivo experiments verified that lncRNA DLX6-AS1 promoted the progression of HCC through the miR-513c/Cul4A/ANXA10 axis. Thus, the silencing of lncRNA DLX6-AS1 impaired miR-513c-dependent Cul4A inhibition and subsequently elevated ubiquitination-mediated degradation of ANXA10, thereby preventing the occurrence and development of HCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun L, Wang Y, Cen J, Ma X, Cui L, Qiu Z, et al. Modelling liver cancer initiation with organoids derived from directly reprogrammed human hepatocytes. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21:1015–26.
Jiang Y, Sun A, Zhao Y, Ying W, Sun H, Yang X, et al. Proteomics identifies new therapeutic targets of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 2019;567:257–61.
Ringelhan M, Pfister D, O’Connor T, Pikarsky E, Heikenwalder M. The immunology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Immunol. 2018;19:222–32.
Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018;391:1301–14.
European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address eee, European Association for the Study of the L. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018;69:182–236.
Chisari FV, Klopchin K, Moriyama T, Pasquinelli C, Dunsford HA, Sell S, et al. Molecular pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Cell. 1989;59:1145–56.
El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2557–76.
Huang JL, Zheng L, Hu YW, Wang Q. Characteristics of long non-coding RNA and its relation to hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2014;35:507–14.
Yang Y, Chen L, Gu J, Zhang H, Yuan J, Lian Q, et al. Recurrently deregulated lncRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14421.
Zhang L, He X, Jin T, Gang L, Jin Z. Long non-coding RNA DLX6-AS1 aggravates hepatocellular carcinoma carcinogenesis by modulating miR-203a/MMP-2 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;96:884–91.
Wu DM, Zheng ZH, Zhang YB, Fan SH, Zhang ZF, Wang YJ, et al. Down-regulated lncRNA DLX6-AS1 inhibits tumorigenesis through STAT3 signaling pathway by suppressing CADM1 promoter methylation in liver cancer stem cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:237.
Zhang K, Zhao Z, Yu J, Chen W, Xu Q, Chen L. LncRNA FLVCR1-AS1 acts as miR-513c sponge to modulate cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119:6045–56.
Xia HL, Lv Y, Xu CW, Fu MC, Zhang T, Yan XM, et al. MiR-513c suppresses neuroblastoma cell migration, invasion, and proliferation through direct targeting glutaminase (GLS). Cancer Biomark. 2017;20:589–96.
Ni W, Zhang Y, Zhan Z, Ye F, Liang Y, Huang J, et al. A novel lncRNA uc.134 represses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting CUL4A-mediated ubiquitination of sLATS1. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:91.
Wang Y, Wen M, Kwon Y, Xu Y, Liu Y, Zhang P, et al. CUL4A induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes cancer metastasis by regulating ZEB1 expression. Cancer Res. 2014;74:520–31.
Lv J, Zhang S, Wu H, Lu J, Lu Y, Wang F, et al. Deubiquitinase PSMD14 enhances hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis by stabilizing GRB2. Cancer Lett. 2020;469:22–34.
Xu JH, Chang WH, Fu HW, Yuan T, Chen P. The mRNA, miRNA and lncRNA networks in hepatocellular carcinoma: An integrative transcriptomic analysis from Gene Expression Omnibus. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17:6472–82.
Song J, Ye A, Jiang E, Yin X, Chen Z, Bai G, et al. Reconstruction and analysis of the aberrant lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network based on competitive endogenous RNA in CESC. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119:6665–73.
Wang P, Xue L, Wang L, Tang H, Lv C, Xue Q. Long noncoding RNA DLX6-AS1 promotes migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by upregulating FUS. Panminerva Med. 2020 https://doi.org/10.23736/S0031-0808.19.03773-X.
Zhang HY, Xing MQ, Guo J, Zhao JC, Chen X, Jiang Z, et al. Long noncoding RNA DLX6-AS1 promotes neuroblastoma progression by regulating miR-107/BDNF pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:313.
Zhong ZB, Wu YJ, Luo JN, Hu XN, Yuan ZN, Li G, et al. Knockdown of long noncoding RNA DLX6-AS1 inhibits migration and invasion of thyroid cancer cells by upregulating UPF1. Eur Rev Med Pharm Sci. 2019;23:10867–73.
Lei X, Yang S, Yang Y, Zhang J, Wang Y, Cao M. Long noncoding RNA DLX6-AS1 targets miR-124-3p/CDK4 to accelerate Ewing’s sarcoma. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11:6569–76.
Fang C, Xu L, He W, Dai J, Sun F. Long noncoding RNA DLX6-AS1 promotes cell growth and invasiveness in bladder cancer via modulating the miR-223-HSP90B1 axis. Cell Cycle. 2019;18:3288–99.
Liang Y, Zhang CD, Zhang C, Dai DQ. DLX6-AS1/miR-204-5p/OCT1 positive feedback loop promotes tumor progression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2020;23:212–27.
Xu J, Sun T, Hu X. microRNA-513c suppresses the proliferation of human glioblastoma cells by repressing low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12:4403–9.
Xu Y, Wang Y, Ma G, Wang Q, Wei G. CUL4A is overexpressed in human pituitary adenomas and regulates pituitary tumor cell proliferation. J Neurooncol. 2014;116:625–32.
Hannah J, Zhou PB. The CUL4A ubiquitin ligase is a potential therapeutic target in skin cancer and other malignancies. Chin J Cancer. 2013;32:478–82.
Pan Y, Wang B, Yang X, Bai F, Xu Q, Li X, et al. CUL4A facilitates hepatocarcinogenesis by promoting cell cycle progression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17006.
Liu X, Peng X, Hu Z, Zhao Q, He J, Li J, et al. Effects of over-expression of ANXA10 gene on proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci. 2012;32:669–74.
Hung MS, Chen YC, Lin P, Li YC, Hsu CC, Lung JH et al. Cul4A modulates invasion and metastasis of lung cancer through regulation of ANXA10. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11:618.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to extend our sincere appreciation to the reviewers for their critical comments on this article.
Funding
This study was supported by the Science and Technology Project of Jiangxi Province (Social Development) (20152ACG70020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.L. and D.P. designed the study. Y.C. and Y.Z. collated the data, J.Y. and G.Z. carried out data analyses and produced the initial draft of the manuscript. X.P. and Y.M. contributed to drafting the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Peng, D., Cao, Y. et al. Upregulated lncRNA DLX6-AS1 underpins hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the miR-513c/Cul4A/ANXA10 axis. Cancer Gene Ther 28, 486–501 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00233-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00233-0
This article is cited by
-
Long noncoding RNA CERS6-AS1 modulates glucose metabolism and tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting the MDM2/p53 signaling pathway
Cell Death Discovery (2022)
-
Positive feedback between lncRNA FLVCR1-AS1 and KLF10 may inhibit pancreatic cancer progression via the PTEN/AKT pathway
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)
-
Knockdown of ANXA10 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells by down-regulating TSG101 thereby inactivating the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway
Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes (2021)
-
Research progress of DLX6-AS1 in human cancers
Human Cell (2021)