Abstract
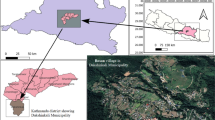
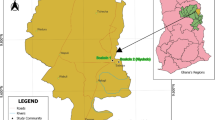
India is witnessing an increasing rate of farmers’ suicide, which has been attributed to indebtedness by most of the studies. Indebtedness can be attributed to multiple factors, including individual, household, community, climatic, institutional, and market-oriented factors. The majority of studies have related these factors with indebtedness in isolation, but the conflating effect of these factors has not been investigated. Moreover, it is observed that farmers follow different adaptation measures to deal with crop failure and socio-economic and climatic stressors, which also play a significant role in their well-being. However, the relationship of these adaptation measures toward indebtedness and farmers’ suicide was found to be missing in the existing literature, which would otherwise provide valuable information regarding how to deal with farmers’ suicide. Considering the compounding effect of these factors on farmers’ suicide, we evaluated and quantified the relationship of individual, community, climatic, credit, and market-oriented factors with adaptation and indebtedness, which were subsequently related to suicidal ideation of farmers. This complex relationship was estimated using structural equation modeling (SEM) by surveying 400 farmers across 15 villages in Vidarbha and Marathwada regions of Maharashtra. SEM results show that individual traits, i.e., age, experience, and illness of farmers; community-oriented factors, i.e., provision of lakes, wells, water tanks; credit factor, i.e., moneylenders; perception of climate change; and market factors are the primary factors contributing toward farmers’ suicidal ideation. Adaptation was found to play a vital role in reducing the indebtedness and suicidal thoughts of the farming community. Results emphasize that a combined and thorough understanding of all the factors is required before making any recommendations to the government or any other decision-making entity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abid M, Schneider UA, Scheffran J (2016) Adaptation to climate change and its impacts on food productivity and crop income: perspectives of farmers in rural Pakistan. J Rural Stud 47:254–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2016.08.005
Ainembabazi JH, Mugisha J (2014) The role of farming experience on the adoption of agricultural technologies: evidence from smallholder farmers in Uganda. J Dev Stud 50:666–679. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220388.2013.874556
Alauddin M, Sarker MAR (2014) Climate change and farm-level adaptation decisions and strategies in drought-prone and groundwater-depleted areas of Bangladesh: an empirical investigation. Ecol Econ 106:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2014.07.025
APHA (2020) American public health association. https://www.apha.org/annualmeeting
Assadi M (2006) Agrarian crisis and farmers’ suicide in India: dimension, nature and response of the state in Karnataka. Indian. J Labour Econ 49:791–811
Balachandran RP, Dhal SC (2018) Relationship between money lenders and farmers. Agr Finance Rev
Banerjee RR (2015) Farmers’ perception of climate change, impact and adaptation strategies: a case study of four villages in the semi-arid regions of India. Nat Hazards 75(3):2829–2845
Basha DPC (2018) Farmers suicide in India - causes and remedies. Int J Res Econ Soc Sci 10:279–288. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2006-2099
Bayard B, Jolly C (2007) Environmental behavior structure and socio-economic conditions of hillside farmers: a multiple-group structural equation modeling approach. Ecol Econ 62:433–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2006.07.004
Behere PB, Bhise MC (2009) Farmers’ suicide: Across culture. Indian J Psychiatry 51:242
Below TB, Mutabazi KD, Kirschke D, Franke C, Sieber S, Siebert R, Tscherning K (2012) Can farmers’ adaptation to climate change be explained by socio-economic household-level variables? Glob Environ Chang 22:223–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2011.11.012
Bhise MC, Behere PB (2016) Risk factors for farmers’ suicides in central rural India: matched case--control psychological autopsy study. Indian J Psychol Med 38:560
Bollen KA (2008) Fixed and random effects in panel data using structural equations models. California Center for Population Research, University of California. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3sr461nd
Bollen K (2010) Structural equations with latent variables, 2nd edn. Structural equations with latent variables. Wiley, New York
Census of India (2011) Census of India, 2011. http://censusindia.gov.in/2011-Common/CensusData2011.html
Dandekar A, Bhattacharya S (2017) Lives in debt. Econ Political Wkly 52(21):77
Deressa TT, Hassan RM, Ringler C, Alemu T, Yesuf M (2009) Determinants of farmers’ choice of adaptation methods to climate change in the Nile Basin of Ethiopia. Glob Environ Chang 19:248–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2009.01.002
Deressa TT, Hassan R, Ringler C (2011) Perception of and adaptation to climate change by farmers in the Nile basin of Ethiopia 804–816. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859610000687
Deshpande RS, Prabhu N (2005) Farmers’ distress proof beyond question. Econ Pol Weekly 40:4663–4665
Dongre AR, Deshmukh PR (2012) Farmers’ suicides in the Vidarbha region of Maharashtra, India: a qualitative exploration of their causes. J Inj Violence Res 4:2–7. https://doi.org/10.5249/jivr.v4i1.68
Dushiyung Y, Patil (2010) Studies on ethnomedicine in B Uldhana district of Maharashtra (India). J Phytol 12:35–41
Fenzi M, Jarvis DI, Reyes LMA, Moreno LL, Tuxill J (2017) Longitudinal analysis of maize diversity in Yucatan, Mexico: influence of agro-ecological factors on landraces conservation and modern variety introduction. Plant Genet Resour 15:51–63
Ficiciyan A, Loos J, Sievers-Glotzbach S, Tscharntke T (2018) More than yield: ecosystem services of traditional versus modern crop varieties revisited. Sustain 10:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10082834
Garg K (2019) Depression, suicidal ideation, and resilience among rural farmers. J Neurosci Rural Pract 10:175
Gedela SPR, Prakasa R (2008) Factors responsible for agrarian crisis in Andhra Pradesh (a logistic regression analysis). World Appl Sci J 4(5):707–713
Gruère GP, Mehta-Bhatt P, Sengupta D (2008) Bt cotton and farmer suicides in India: Reviewing the evidence. Intl Food Policy Res Inst
Heidari H, Golbabaei F, Shamsipour A, Rahimi-Forushani ABBAS, Gaeini A (2015) Evaluation of heat stress among farmers using Environmenta l and biological monitoring: a study in North of Iran. International Journal of Occupational Hygiene (IJOH) 7(1):1–9
Jadhav R (2019) Just 5% of water left in Marathwada’s dams. The Hindu. 19 April 2019
Jain M, Naeem S, Orlove B, Modi V, DeFries RS (2015) Understanding the causes and consequences of differential decision-making in adaptation research: adapting to a delayed monsoon onset in Gujarat, India. Glob Environ Chang 31:98–109
Jeromi PD (2007) Farmers’ indebtedness and suicides: impact of agricultural trade liberalisation in Kerala. Econ Polit Wkly: 3241–3247
Jodha NS, Singh NP, Bantilan MCS (2012) Enhancing farmers’ adaptation to climate change in arid and semi-arid agriculture of India: evidences from indigenous practices: Developing International Public Goods from Development-oriented Projects. Working Paper Series no. 32
Judd F, Jackson H, Fraser C, Murray G, Robins G, Komiti A (2006) Understanding suicide in Australian farmers. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 41:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-005-0007-1
Kale NM (2011) Availability of subsidiary occupations and agriculture infrastructure with suicidal farmers. Karnataka J Agric Sci 24(3)
Kale NM (2013) Socio-economic, psychological and situational causes of suicides of farmers in vidarbha region of Maharashtra. Indian J Ext Educ 49:12–18
Kamthe AD (2007) Factor leading to farmers suicide in Amravati district. M. Sc. Thesis, Dr. Panjabrao Deshmukh Krishi Vidyapeeth, Akola, MS (INDIA)
Kaur L, Sharma P, Garg L (2016) Causes and cure of farmer’s suicide. Indian J Econ Dev 12(1a):305–310
Khanal U, Wilson C, Hoang V-N, Lee B (2018) Farmers’ adaptation to climate change, its determinants and impacts on rice yield in Nepal. Ecol Econ 144:139–147
Kumar RA, Raghavendra RH (2019) Farmers suicide in India: issues. Challenges and Remedies Econ Aff 64:387–394
Lakna (2020) What is the difference between HYV seeds and traditional seeds. PEDIAA 2020-06-05
Le Dang H, Li E, Nuberg I, Bruwer J (2014) Understanding farmers’ adaptation intention to climate change: A structural equation modelling study in the Mekong Delta Vietnam. Environ Sci Policy 41:11–22
Mallick S (2019) Pressure from banks pushes farmers to commit suicide. Down to Earth
Malone A (2008) The GM genocide: Thousands of Indian farmers are committing suicide after using genetically modified crops. Dly Mail:3
Manorantjtham S, Abraham S, Jacob KS (2005) Towards a national strategy to reduce suicide in India. Natl Med J India 18:118–122
Mariappan K, Zhou D (2019) A threat of farmers’ suicide and the opportunity in organic farming for sustainable agricultural development in India. Sustain 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082400
Mishra S (2006) Suicide of farmers in Maharashtra Indira Gandhi Institute of Development Research. Mumbai, Indira Gandhi Institute of Development Research, Mumbai
Mohanakumar S, Sharma RK (2006) Analysis of farmer suicides in Kerala. Econ Polit Wkly 41:1553–1558. https://doi.org/10.2307/4418114
Mohanty (2019) Farm loan waiver: Majority and poorest farmers do not benefit - a status check. Bus Today
Mondal P, Jain M, DeFries RS, Galford GL, Small C (2015) Sensitivity of crop cover to climate variability: Insights from two Indian agro-ecoregions. J Environ Manage 148:21–30
Murray Darling Basin Authority (2009) The basin plan: a concept statement. https://www.mdba.gov.au/publications/brochures-factsheets/fact-sheet-basin-plan-concept-statement
Ndamani F, Watanabe T (2016) Determinants of farmers’ adaptation to climate change: a micro level analysis in Ghana. Sci Agric 73:201–208
Negi GCS (1994) High yielding vs. traditional crop varieties: a socio-agronomic study in a Himalayan village in India. Mtn ResDev 14:251–254. https://doi.org/10.2307/3673776
Olson MB, Morris KS, Méndez VE (2012) Cultivation of maize landraces by small-scale shade coffee farmers in western El Salvador. Agric Syst 111:63–74
Paudel KP, Pandit M, Hinson R (2016) Irrigation water sources and irrigation application methods used by US plant nursery producers. Water Resour Res 52(2):698–712
Posani B (2009) Farmer suicides and the political economy of agrarian distress in India. Dev Stud Inst Work Pap. Ser 44
IMD Pune (2017) Indian Meterological department, Ministry of Earth Science. http://www.imdpune.gov.in/ndc_new/stations.html
Ranjan R (2017) Challenges to farm produce marketing: a model of bargaining between farmers and middlemen under risk. J Agr Resour Econ 42(1835-2017-2104):386–405
Rosseel Y (2012) lavaan: An R package for structural equation modeling. J Stat Softw. http://www.jstatsoft.org/v48/i02/
Sainath (2013) Farmers’ suicide rates soar above the rest. The Hindu. https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/columns/sainath/farmers-suicide-rates-soar-above-the-rest/article4725101.ece
Shamika (2018) High debt isn’t driving Indian farmers to suicide. Econ Times
Shikarwar (2019) Loan waivers to make it hard for India to achieve fiscal deficit target: Moody’s Econ In: Times
Shinge (2019) Economic Survey of Maharashtra 2018–19
Shiva BV (2004) The suicide economy of corporate globalisation. https://www.countercurrents.org/glo-shiva050404.htm
Shiva V (2009) Why are Indian farmers committing suicide and how can we stop this tragedy. VOLTAIRE Netw. URL https://www.voltairenet.org/article159305.html. Accessed 30 May 2020
Shrishail N, Rajendra P, Kunnal LB, Basvaraja H, Basavaraj B (2011) A probe into socio-economic and psychological profile of farmers’ suicide in Karnataka. Karnataka. J Agric Sci 24:157–160
Singh S, Kaur M, Kingra HS (2008) Indebtedness among farmers in Punjab. Econ Polit Wkly 43:130–136
Smit B (1993) Adaptation to climatic variability and change. University of Guelph, Dept. of Geography
Sravanth KR, Sundaram N (2019) Agricultural crisis and farmers suicides in India. Int J Innov Technol Explor Eng 8:1576–1580. https://doi.org/10.35940/ijitee.K1855.0981119
Swami D, Dave P, Parthasarathy D (2018) Agricultural susceptibility to monsoon variability: A district level analysis of Maharashtra. India Sci Total Environ:619–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.328
Swami D, Parthasarathy D (2020) A multidimensional perspective to farmers ’ decision making determines the adaptation of the farming community. J Environ Manag 264:110487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110487
The Hindu (2017) Farm suicides on rise after BJP assumed power at Centre. The Hindu
Toma L, Barnes AP, Sutherland LA, Thomson S, Burnett F, Mathews K (2018) Impact of information transfer on farmers’ uptake of innovative crop technologies: a structural equation model applied to survey data. J Technol Transf 43:864–881. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-016-9520-5
Wang YJ, Huang JK, Wang JX (2014) Household and community assets and farmers' adaptation to extreme weather event: the case of drought in China. J Integr Agric 13(4):687–697
Wang J, Tao J, Yang C, Chu M, Lam H (2017) A general framework incorporating knowledge, risk perception and practices to eliminate pesticide residues in food: a structural equation modelling analysis based on survey data of 986 Chinese farmers. Food Control 80:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.05.003
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. K. Narayanan from IIT Bombay for providing the valuable suggestions.
Funding
This work was supported by the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (DST/CC/ PR/06/2011). Centre of Excellence in Climate Studies (IITB-CECS) project of the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, India.
Data AvailabilityData can be made available on request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Deepika Swami: Writing manuscript, data modeling, data analysis;
Prashant Dave: Data modeling, Editing the manuscript, Results interpretation;
Devanathan Parthasarathy: Idea formulation, data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
NA
Consent to publish
All authors consent to publish in the journal of “Climatic Change”.
Competing interests
There are no competing interest between the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swami, D., Dave, P. & Parthasarathy, D. Understanding farmers’ suicidal ideation: a structural equation modeling study in Maharashtra, India. Climatic Change 163, 2175–2200 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-020-02935-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-020-02935-8