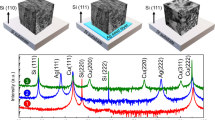
Abstract
The size of silicon nanowires (SiNWs) plays an important role for their application in nanoelectronic and nanophotonic systems. Therefore, it is of great interest to study the synthesis conditions of SiNWs in order to grow SiNWs with well-controlled manner to be integrated into a device. This paper includes a systematic study of the dependence of diameter and length of the SiNWs on the growth conditions. SiNWs were synthesized via vapor–liquid–solid (VLS) mechanism using a catalyst film of Sn nanoparticles on stainless steel (SS) substrate. The morphology and microstructure of SiNWs synthesized at different parameters were investigated with scanning electron microscopy and Raman spectroscopy. In this study, we have observed that there exists a minimum size of the catalyst to initiate the growth of SiNWs for a given set of process parameters. Furthermore, this work also addresses the difficulties associated with the growth of long SiNWs. Effect of filament temperature on the morphology of SiNWs has also been studied. It is observed that their dimensions and geometrical orientation are greatly influenced by the filament temperature. At filament temperatures between 1400 and 1600 °C, short SiNWs with random distributions are observed. Long and vertical SiNWs are found if the filament temperature was raised to 1800–1950 °C.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi MM, Karim KS (2013) Core–shell homoepitaxial silicon nanowires. Chem Phys Lett 583:141–145
Adachi MM, Anantram MP, Karim KS (2010) Optical properties of crystalline amorphous core -Sshell silicon nanowires. Nano Lett 10:4093–4098
Bootsma G, Gassen H (1971) A quantitative study on the growth of silicon whiskers from silane and germanium whiskers from germane. J Cryst Growth 10:223–234
Brockhoff AM, van der Weg WF, Habraken FHPM (2001) The effects of hotwire atomic hydrogen on amorphous silicon. J Appl Phys 89:2993–3000
Chaudhari P, Singh A, Topkar A, Dusane RO (2012) Hot wire chemical vapor deposited boron carbide thin film/crystalline silicon diode for neutron detection application. Solid State Electronics 78:156–158
Chen Z, Cao C (2006) Effect of size in nanowires grown by the vapor-liquid-solidmechanism. Appl Phys Lett 88:143118
Choi JW, Donough JM, Jeong S, Yoo JS, Chan CK, Cui Y (2010) Stepwise nanopore evolution in one-dimensional nanostructures. Nano Lett 10:1409–1413
Chong SK, Goh BT, Aspanut Z, Muhamad MR, Dee CF, Rahmana SA (2011) Radial growth of slanting-columnar nanocrystalline Si on Si nanowires. Chem Phys Lett 515:68–71
Chong SK, Goh BT, Dee CF, Rahmana SA (2012) Study on the role of filament temperature on growth of indium catalyzed silicon nanowires by the hot-wire chemical vapor deposition technique. Mater Chem Phys 135:635–643
Chong SK, Dee CF, Yahya N, Rahman SA (2013) Control growth of silicon nanocolumns’ epitaxy on silicon nanowires. J Nanopart Res 15:1–8
Cui Y, Lauhon LJ, Gudiksen MS, Wang J, Lieber CM (2001) Diameter-controlled synthesis of single-crystal silicon nanowires. Appl Phys Lett 78:2214–2216
Cui Y, Zhong Z, Wang D, Wang WU, Lieber CM (2003) High performance silicon nanowire field effect transistors. Nano Lett 3:149–152
Cui LF, Ruffo R, Chan CK, Peng H, Yi C (2008) Crystalline-amorphous core- shell silicon nanowires for high capacity and high current battery electrodes. Nano Lett 9:491–495
Cui LF, Ruffo R, Chan CK, Peng H, Yi C (2009) Crystalline-amorphous core –shell silicon nanowires for high capacity and high current battery electrodes. Nano Lett 9:491–495
Dhalluin F (2007) Critical condition for growth of silicon nanowires. Journal of Applied Physics 102: 094906
Dong Y, Yu G, Alpine MC, Lu W, Lieber CM (2008) Si/a-Si core/shell nanowires as nonvolatile crossbar switches. Nano Lett 8:386–391
Doyle JR, Xu Y, Reedy R, Branz HM, Mahan AH (2008) Film stoichiometry and gas dissociation kinetics in hot-wire chemical vapor deposition of a-SiGe:H. Thin Solid Films 516:526–528
Duan HL, Bent SF (2005) The influence of filament material on radical production in hot wire chemical vapor deposition of a-Si:H. Thin Solid Films 485:126–134
Duan HL, Zaharias GA, Bent SF (2002) The effect of filament temperature on thegaseous radicals in the hot wire decomposition of silane. Thin Solid Films 395:36–41
Dusane RO (2011) Opportunities for new materials synthesis by hot wire chemical vapor process. Thin Solid Films 519:4555–4560
Friedrichs HA, Ronkow LW, Bliznjukow SA (1995) New method for simultaneous measurement of viscosity, density and surface tension of metallic melts at high temperatures. Steel research 66:509–515
Givargizov EI (1975) Fundamental aspects of VLS growth. J Cryst Growth 31:20–30
Hadjadj A, Larbi F, Gilliot M, Cabarrocas PR (2014) Etching of a-Si:H thin films by hydrogen plasma: a view from in situ spectroscopic ellipsometry. J Chem Phys 141:084708
Hannon JB, Kodambaka S, Ross FM, Tromp RM (2006) The influence of the surface migration of gold on the growth of silicon nanowires. Nature 440:69–71
Heya A, Masuda A, Matsumura H (1999) Low-temperature crystallization of amorphous silicon using atomic hydrogen generated by catalytic reaction on heated tungsten. Appl Phys Lett 74:2143–2145
Hochbaum AI, Chen R, Delgado RD, Liang W, Garnett EC, Najarian M, Majumdar A, Yang P (2008) Enhanced thermoelectric performance of rough silicon nanowires. Nature 451:163–167
Hyun YJ, Lugstein A, Steinmair M, Bertagnolli E, Pongratz P (2009) Orientation specific synthesis of kinked silicon nanowires grown by the vapour–liquid–solid mechanism. Nanotechnology 20:125606
Jangid MK, Lakhnot AS, Vemulapally A, Sonia FJ, Sinha S, Dusane RO, Mukhopadhyay A (2018) Crystalline core/amorphous shell structured silicon nanowires offer size and structure dependent reversible Na-storage. J Mater Chem A 6:3422–3434
Kikkawa J, Ohno Y, Takeda S (2005) Growth rate of silicon nanowires. Applied Physics Letters 86: 123109
Kumar R, Soam A, Dusane RO, Bhargava P (2018) Sucrose derived carbon coated silicon nanowires for supercapacitor application. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics (JMSE) 29:1947–1954
Kwak DW, Cho HY, Yang WC (2007) Dimensional evolution of silicon nanowiressynthesized by Au–Si island-catalyzed chemical vapor deposition. Physica E: Lowdimensional Systems and Nanostructures 37:153–157
Lew KK, Redwing JM (2003) Growth characteristics of silicon nanowires synthesized by vapor–liquid–solid growth in nanoporous alumina templates. J Cryst Growth 254:14–22
Masanori O, Masao K, Shunri O (1994) Selective etching of hydrogenated amorphous silicon by hydrogen plasma. Jpn J Appl Phys 33:4442
Masuda A, Izumi A, Umemoto H, Matsumura H (2002) What is the difference between catalytic CVD and plasma-enhanced CVD? Gas-phase kinetics and film properties, Vacuum 66:293–297
Misra S, Yu L, Chen W, Cabarrocas PR (2013) Wetting layer: the key player in plasma-assisted silicon nanowire growth mediated by tin. J Phys Chem C 117:17786–17790
Obreja VVN (2008) On the performance of supercapacitors with electrodes based on carbon nanotubes and carbon activated material—A review. Physica E: Low dimensional Systems and Nanostructures 40:2596–2605
Rathi SJ, Jariwala BN, Beach JD, Stradins P, Taylor PC, Weng X, Ke Y, Redwing JM, Agarwal S, Collins RT (2011) Tin-catalyzed plasma-assisted growth of silicon nanowires. J Phys Chem C 115:3833–3839
Sahoo MK, Kale P (2019) Integration of silicon nanowires in solar cell structure for efficiency enhancement: a review. J Mater 5:34–48
Schmidt V, Senz S, Gösele U (2007) Diameter dependence of the growth velocity ofsilicon nanowires synthesized via the vapor-liquid-solid mechanism. Physical Review B 75: 045335
Schmidt V, Wittemann JV, Senz S, Gosele U (2009) Silicon nanowires: a review on aspects of their growth and their electrical properties. Adv Mater 21:2681–2702
Schmidt V, Wittemann JV, Gosele U (2010) Growth, thermodynamics, and electrical properties of silicon nanowires. Chem Rev 110:361–388
Schropp REI (2009) Frontiers in HWCVD. Thin Solid Films 517:3415–3419
Sharma S, Kamins TI, Williams RS (2004) Diameter control of Ti-catalyzed siliconnanowires. J Cryst Growth 267:613–618
Soam A, Arya N, Meshram N, Kumbhar AK and Dusane R, (2006) Formation of Sn nanotemplate by hot-wire chemical vapor process on different substrates. Surfaces and Interfaces 8:193–198
Soam A, Arya N, Kumbhar A, Dusane R (2016) Controlling the shell microstructure in a low-temperature-grown SiNWs and correlating it to the performance of the SiNWs-based micro-supercapacitor. Appl Nanosci 6:1159–1165
Soam A, Arya N, Singh A, Dusane RO (2017) Fabrication of silicon nanowires based on-chip micro-supercapacitor. Chemical Physics Letter 678:46–50
Soam A, Parida K, Kumar R, Kavle P, Dusane R (2019) Silicon-MnO2 core-shell nanowires as electrodes for micro-supercapacitor application. Ceram Int 45:18914–18923
Tan TY, Li N, Gösele U (2003a) Is there a thermodynamic size limit of nanowiresgrown by the vapor-liquid-solid process? Appl Phys Lett 83:1199–1201
Tan TY, Li N, Gösele U (2003b) On the thermodynamic size limit of nanowires grownby the vapor-liquid-solid process. Applied Physics A 78:519–526
Tian B, Zheng X, Tempa JK, Fang Y, Yu N, Yu G, Huang J, Lieber CM (2007) Coaxial silicon nanowires as solar cells and nanoelectronic power sources. Nature 449:885–889
Wagner RS, Ellis WC (1964) Vapor-liquid-solid mechanism of single crystal growth. Appl Phys Lett 4:89–90
Wagner R, Ellis W (1965) Vapor-liquid-solid mechanism of crystal growth and its application to silicon. Bell telephone system technical publications: 5018
Wagner RS, Ooherty CJ (1968) Mechanism of branching and kinking during VLS crystal growth. J Electrochem Soc 115:93–99
Westwater J, Gosain DP, Tomiya S, Usui S (1997) Growth of silicon nanowires via gold/silane vapor–liquid–solid reaction. J Vac Sci Technol B 15:554–557
Yang HG, Zeng HC (2004) Preparation of hollow anatase TiO2 nanospheres via Ostwald ripening. J Phys Chem B 108:3492–3495
Yu L, Donnell BO, Alet PJ, Boj SC, Peiro F, Arbiol J, Cabarrocas PR (2009) Plasma-enhanced low temperature growth of silicon nanowires and hierarchical structures by using tin and indium catalysts. Nanotechnology 20:225604
Zheng W, Gallagher A (2006) Hot wire radicals and reactions. Thin Solid Films 501:21–25
Acknowledgments
SAIF, IIT Bombay is acknowledged for providing the SEM characterization facilities. FIST facility (Dual beam FIB, Carl Zeiss Microscopy) in ME & MS department was also used for this work.
Funding
Financial support for this study is provided by Crompton Greaves, Mumbai.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soam, A., Arya, N. & Dusane, R. A detailed study on the growth of silicon nanowires by hot wire chemical vapor process: concept of critical size of Sn catalyst. J Nanopart Res 22, 363 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05092-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05092-2