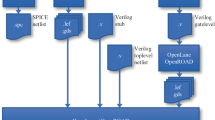
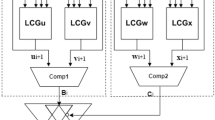
Abstract
Designing an application in hardware under inversely competing constraints such as area and performance with different objective functions such as power consumption and reliability of the circuits is a cumbersome task. Having different versions of the same resource type during the design process may ease this burden since there can be several alternative resources to meet the given constraints. In this paper, we characterize a library of some commonly used arithmetic circuits in FPGAs in terms of the speed, area, power consumption, and vulnerability to error propagation as the reliability parameter. Specifically, we implemented four well-known adders and two multipliers in an SRAM-based FPGA that is a part of Xilinx’s Zynq-7000 SoC platform. We then injected errors to the configuration bits of the circuits to evaluate the error propagation. The results show that different versions of the same resources can have different reliability values in addition to the area, latency, and power values.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alderighi M, Casini F, D’Angelo S, Pastore S, Sechi GR, Weigand R (2007) Evaluation of single event upset mitigation schemes for sram based fpgas using the flipper fault injection platform. In: Proc. 22nd IEEE international symposium on defect and fault-tolerance in VLSI systems (DFT 2007), pp 105–113
Brent RP, Kung HT (1982) A regular layout for parallel adders. IEEE Trans Comput C-31 (3):260–264
Crockett LH, Elliot RA, Enderwitz MA, Stewart RW (2014) The zynq book: Embedded processing with the arm cortex-a9 on the xilinx zynq-7000 all programmable soc. Strathclyde Academic Media, Glasgow
Daphni S, Grace KSV (2017) A review analysis of parallel prefix adders for better performance in vlsi applications. In: Proc. 2017 IEEE international conference on circuits and systems (ICCS), pp 103–106
Ghosh S, Ndai P, Roy K (2008) A novel low overhead fault tolerant kogge-stone adder using adaptive clocking. In: Proc. design, automation and test in Europe conference, pp 366–371
Graham PS, Rollins N, Wirthlin MJ, Caffrey MP (2003) Evaluating tmr techniques in the presence of single event upsets. All Faculty Publications 1:1–5
Jayanthi AN, Ravichandran CS (2013) Comparison of performance of high speed vlsi adders. In: Proc. 2013 International conference on current trends in engineering and technology (ICCTET), pp 99–104
Keshk ME, Asami K (2018) Fault injection in dynamic partial reconfiguration design based on essential bits. Journal of Aeronautics and Space Technologies 11(2):25–34
Khedhiri C, Karmani M, Hamdi B, Man KL (2011) Concurrent error detection adder based on two paths output computation. In: Proc. 2011 IEEE ninth international symposium on parallel and distributed processing with applications workshops, pp 27–32
Kogge PM, Stone HS (1973) A parallel algorithm for the efficient solution of a general class of recurrence equations. IEEE Trans Comput C-22(8):786–793
Kumar P, Sharma RK (2017) Double fault tolerant full adder design using fault localization. In: Proc. 2017 3rd international conference on computational intelligence communication technology (CICT), pp 1–6
Le R (2012) Soft error mitigation using prioritized essential bits
Machmur B, Hayek A, Boercsoek J (2013) Practical application of the reliability model for hdl in safety related systems. In: Proc. 7th WSEAS international conference CSST13, pp 226–232
Mano MM, Ciletti MD (2015) Digital design. Pearson Education Inc, New Jersey
Mohanapriya D, Saravanakumar DN, BIT E (2016) A comparative analysis of different 32-bit adder topologies with multiplexer based full adder. Int J Eng Sci 1(1):4850–4854
Ostler PS, Caffrey MP, Gibelyou DS, Graham PS, Morgan KS, Pratt BH, Quinn HM, Wirthlin MJ (2009) Sram fpga reliability analysis for harsh radiation environments. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 56(6):3519–3526
Pratt B, Caffrey M, Graham P, Morgan K, Wirthlin M (2006) Improving fpga design robustness with partial tmr. In: Proc. 2006 IEEE international reliability physics symposium proceedings, pp 226–232
Qin X, Feng C, Zhang D, Miao B, Zhao L, Hao X, Liu S, An Q (2013) Development of a high resolution tdc for implementation in flash-based and anti-fuse fpgas for aerospace application. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear science 60(5):3550–3556
Radu M (2014) Reliability and fault tolerance analysis of fpga platforms. In: Proc. IEEE Long island systems, applications and technology (LISAT) conference 2014, pp 1–4
Ratter D (2004) Fpgas on mars. Xcell J 50:8–11
SaiKumar M, Punniakodi S (2013) Design and performance analysis of various adders using verilog. International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing 2(9):128–138
Salehi M, Azarpeyvand A, Aboutalebi AH (2018) Vulnerability analysis of adder architectures considering design and synthesis constraints. J Electron Test 34(1):7–14
Sari A, Psarakis M (2011) Scrubbing-based seu mitigation approach for systems-on-programmable-chips. In: Proc. 2011 international conference on field-programmable technology, pp 1–8
Vitoroulis K, Al-Khalili AJ (2007) Performance of parallel prefix adders implemented with fpga technology. In: Proc. 2007 IEEE northeast workshop on circuits and systems, pp 498–501
Wang J-J, Cronquist B, Sin B, Moriarta J, Katz R (1997) Antifuse fpga for space applications. In: Proc. fourth european conference on radiation and its effects on components and systems, pp 1–6
Xilinx Inc (2012) 7 series fpgas configuration user guide, ug470 (v. 1.3)
Xilinx Inc. (2013) Constraints guide, ug625 (v. 14.5)
Xilinx Inc. (2015) Soft error mitigation controller v4.1, logicore ip product guide
Xilinx Inc. (2015) Device reliability report
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) under grant number 116E095.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: A. Orailoglu
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gokalan, A., Tosun, S. & Dal, D. Library Characterization of Arithmetic Circuits for Reliability-Aware Designs in SRAM-Based FPGAs. J Electron Test 36, 743–756 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-020-05913-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-020-05913-1