Abstract
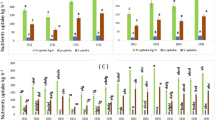
In this study, an experiment was conducted to describe the effects of using microwaves and chemical fertilization (isolated and combined) on the number of bacteria and fungi in the soil and on the growth of cowpea plants Vigna unguiculata L. Several times of exposure to microwave radiation (0, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45 s) and several concentrations of chemical fertilizer NPK (0, 0.9, 1.8 g 3 kg−1 soil) were carried out. After individual and combined treatments, experiments were carried out to quantify microorganisms (bacteria and fungi). In addition, 45 days after planting, analyzes were made of the cowpea plants for their development under different experimental conditions. The experiment was conducted in plastic pots to find out some characteristics of plant growth. The results indicated that the microwave sterilization resulted in the complete killing of bacteria and fungi and the fertilizer additive (NPK) to the soil had a critical role in increasing the values significantly for the number of root nodes and the remaining plant growth characteristics measured in this study.
Zusammenfassung
In dieser Studie wurde ein Experiment durchgeführt, um die Auswirkungen von Mikrowellen und chemischer Düngung (isoliert und kombiniert) auf die Anzahl von Bakterien und Pilzen im Boden und auf das Wachstum der Augenbohnen-Pflanzen Vigna unguiculata L. zu bestimmen. Es wurden mehrere Expositionen mit Mikrowellenstrahlung (0, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45 s) und mehrere Konzentrationen des chemischen Düngers NPK (0, 0,9, 1,8 g 3 kg−1 Boden) getestet. Nach individuellen und kombinierten Behandlungen wurden Experimente zur Quantifizierung von Mikroorganismen (Bakterien und Pilze) durchgeführt. Darüber hinaus wurden 45 Tage nach der Pflanzung Analysen der Augenbohnen-Pflanzen bezüglich ihrer Entwicklung unter verschiedenen Versuchsbedingungen durchgeführt. Das Experiment wurde in Plastiktöpfen durchgeführt, um einige Merkmale des Pflanzenwachstums zu untersuchen. Die Ergebnisse deuteten darauf hin, dass die Mikrowellensterilisation zur vollständigen Abtötung von Bakterien und Pilzen führte und dass der Düngerzusatz (NPK) zum Boden eine entscheidende Rolle bei der signifikanten Erhöhung der in dieser Studie gemessenen Werte für die Anzahl der Wurzelknoten und die übrigen Pflanzenwachstumsmerkmale spielte.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abayomi YA, Ajibade TV, Sammuel OF, Saadudeen BF (2008) Growth and yield responses of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp) genotypes to nitrogen fertilizer (NPK) application in the Southern Guinea Savanna zone of Nigeria. Asian J Plant Sci 7(2):170–176
Adam T (1990) Diseases affecting cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walpers) in Niger. AMBIO 1:358–360
AL-Samarrai FH, AL-Bahadli AH, AL-Rawi FA (1988) Compression between effect of soil disinfestation methods on some pathogens of cucumber. Arab J PIant Prot 6(2):106
Almeida MT, Mouga T, Barracosa P (1994) The weathering ability of higher plants. The case of Ailanthus altissima (Miller) Swingle. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 33(4):333–343
Astuti D, Suhartanto B, Umami N, Irawan A (2020) Effect of density between intercropped sorghum and stylosanthes on biomass production and quality under varying NPK fertilizer application rates. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 23:197–205
Blacksmith N, Willford JC, Behrend TS (2016) Technology in the employment interview: a meta-analysis and future research agenda. Pers Assess Decis 2(1):2
Brodie G, Grixti M, Hollins E, Cooper A, Li T, Cole M (2015) Assessing the impact of microwave treatment on soil microbial populations. Glob J Agric Innov Res Dev 2(1):25–32
Brodie G, Hamilton S, Woodworth J (2007) An assessment of microwave soil pasteurization for killing seeds and weeds. Plant Prot Q 22(4):143
Cawse PA, Crawford DV (1967) Accumulation of nitrite in fresh soils after gamma irradiation. Nature 216(5120):1142–1143
Chen YP (2006) Microwave treatment of eight seconds protects cells of lsafis indigofica from enhanced UV‑8 radiation lesions. Photochem Photobiol 82(2):503–507
Cooper A, Brodie G (2009) The effect of microwave radiation and soil depth on soil pH, N, P, K, SO {4} and bacterial colonies. Plant Prot Q 24(2):67
Diprose MF (2001) Some considerations when using a microwave oven as a laboratory research tool. Plant Soil 229(2):271–280
Erabi A, Ali SA (2014) Effect of sterilization methods and replication in the microbial community and the growth of the soybean plant Glycine max L. in the gypsum soil. Anbar J Agric Sci 12(2):43–49
Ferriss RS (1984) Effects of microwave oven treatment on microorganisms in soil. Phytopathology 74(1):121–126
Gibson F, Fox FM, Deacon JW (1988) Effects of microwave treatment of soil on growth of birch (Betula pendula) seedlings and infection of them by ectomycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 108(2):189–204
Halmagyi A, Surducan E, Surducan V (2017) The effect of low-and high-power microwave irradiation on in vitro grown Sequoia plants and their recovery after cryostorage. J Biol Phys 43(3):367–379
Haruna IM, Aliyu L (2011) Yield and economic returns of sesame (Sesamum indicum .L.) as influenced by poultry manure, nitrogen and phosphorus at Samaru, Nigeria. Elixir Agric 39:4884–4887
Hendricks CW, Pascoe N (1988) Soil mcirobial biomass estimates using 2450 MHz microwave irradiation. Plant Soil 110(1):39–47
MCM Hess M, De Wilde M, Yavercovski N, Willm L, Mesléard F, Buisson E (2018) Microwave soil heating reduces seedling emergence of a wide range of species including invasives. Restor Ecol 26:S160–S169
Iqbal U, Mukhtar T (2020) Evaluation of Biocontrol Potenzial of seven indigenous Trichoderma species against charcoal rot causing fungus, Macrophomina phaseolina. Gesunde Pflanzen 1(72):195–202
Ishaq F, Khan A (2011) Isolation, identification and comparative study of fungal and bacterial strains found in organic and inorganic soils of different agricultural fields. Recent Res Sci Technol 3(11):30–36
Khan MJ, Brodie G, Gupta D (2016) Effect of microwave (2.45 GHz) treatment of soil on yield components of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Microw Power Electromagn Energy 50(3):191–200
Komarova AS, Likhacheva AA, Zvyagintsev DG (2008) Influence of microwave radiation on soil bacteria. Mosc Univ Soil Sci Bull 63(4):190–195
Krasilnikoff G, Gahoonia T, Erik-Nelson N (2003) Variation in phosphorus uptake by genotypes of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp) due to differences in root and root hair length and induced rhizosphere processes. Plant Soil 251:83–91
Kwon SJ, Kim HR, Roy SK, Kim HJ, Boo HO, Woo SH, Kim HH (2019) Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers on growth characteristics of two species of bellflower (Platycodon grandiflorum). J Crop Sci Biotechnol 22(5):481–487
Motaleb NA, Abd Elhady SA, Ghoname AA (2020) AMF, bacillus megaterium neutralize the harmful effects of salt stress on bean plants. Gesunde Pflanz 72(1):29–39
Ndakidemi PA, Dakora FD (2007) Yield components of nodulated cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp) and maize (Zea mays) plants grown with exogenous phosphorus in different cropping systems. Aust J Exp Agric 47:587–590
Nelson SO (1996) A review and assessment of microwave energy for soil treatment to control pests. Trans ASAE 39(1):281–289
Nkaa F, Nwokeocha OW, Ihuoma O (2014) Effect of phosphorus fertilizer on growth and yield of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). J Pharm Biol Sci 9(5):74–82
Nutter GM (1957) Soil sterilization practices in turf. USGA J Turf Manag, p 25–27
Nyoki D, Patrick A, Ndakidemi R (2013) Economic benefits of Bradyrhizobium japonicum inoculation and phosphorus supplementation in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp) grown in northern Tanzania. Am J Res Comm 1(11):173–189
O’neill PE, Jackson TJ (1990) Observed effects of soil organic matter content on the microwave emissivity of soils. Remote Sens Environ 31(3):175–182
Oza SR, Panigrahy S, Parihar JS (2008) Concurrent use of active and passive microwave remote sensing data for monitoring of rice crop. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinform 10(3):296–304
Pokluda R, Shehata SM, Kopta T (2018) Vegetative, chemical status and productivity of zucchini squash (Cucurbita pepo L.) plants in responses to foliar application of Pentakeep and Strigolactones under NPK rates. Gesunde Pflanz 70(1):21–29
Rahi GS, Rich JR (2008) Potenzial of microwaves to control plant-parasitic nematodes in soil. J Microw Power Electromagn Energy 42(1):5–42112
Sahin H (2014) Effects of microwaves on the germination of weed Seeds. J Biosyst Eng 39(4):304–309
Song ZX, Wang ZY, Wu LY, Fan YT, Hou HW (2012) Effect of microwave irradiation pretreatment of cow dung compost on bio-hydrogen process from corn stalk by dark fermentation. Int J Hydrogen Energy 37(8):6554–6561
Soriano-Martín ML, Porras-Piedra A, Porras-Soriano A (2006) Use of microwaves in the prevention of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. melonis infection during the commercial production of melon plantlets. Crop Prot 25(1):52–57
Tisserat B, Jones D, Galletta PD (1992) Microwave sterilization of plant tissue culture media. HortScience 27(4):358–361
Velázquez-Martí B, Gracia-López C, De La Puerta R (2008) Work conditions for microwave applicators designed to eliminate undesired vegetation in a field. Biosyst Eng 100(1):31–37
Wainwright M, Killham K, Diprose MF (1980) Effects of 2450 MHz microwave radiation on nitrification, respiration and S‑oxidation in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 12(5):489–493
De Wilde M, Buisson E, Yavercovski N, Willm L, Bieder L, Mesléard F (2017) Using microwave soil heating to inhibit invasive species seed germination. Invasive Plant Sci Manag 10(3):262–270
Zhang Y, Shen J (2006) Effect of temperature and iron concentration on the growth and hydrogen production of mixed bacteria. Int J Hydrogen Energy 31(4):441–446
Zieliński M, Zielińska M (2010) Impact of microwave radiation on nitrogen removal and quantity of nitrifiers in biofilm. Can J Civ Eng 37(4):661–666
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Department of Biology and Physics, College of Education, University of Samarra, Salah-AL-Din, Iraq to work in the laboratory and department facilities and would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their insightful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
W.M. Mahdi, K.S.L. Al-Badri and M.R.M. Alqaisi declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahdi, W.M., Al-Badri, K.S.L. & Alqaisi, M.R.M. Effect of Microwave Radiation on Bacteria, Fungi and Some Growth Characteristics of Cowpea Vigna unguiculata L.. Gesunde Pflanzen 73, 161–167 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-020-00534-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-020-00534-2