Abstract
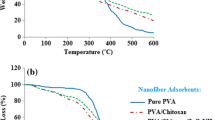
The rapid growth of human population and global industrialization has resulted in the generation of larger amounts of wastewater containing various pollutants, among which toxic heavy metals. Adsorption is efficient for this purpose, but its application is limited by the high cost of adsorbent materials. Chitosan (CS) and phosphorylated microcellulose (PMC) have a high potential as low-cost and effective adsorbents for water remediation. Nonwoven CS/PMC nanocomposite fiber mats were produced by electrospinning with up to 50% by weight of PMC. The thermal, chemical, and morphological properties of the mats were studied. Batch adsorption trials were carried out using Cd2+ ions. Kinetics and isotherm models were tested against experimental results and the thermodynamic properties were calculated. Results showed that the pseudo-second order model best fitted experimental data and suggested chemisorption as the mechanism for Cd2+ removal. Langmuir isotherm best described equilibrium data reaching the maximum adsorption capacity of 283 mg/g at 60 °C. This high value was attributed mainly to the large amount of phosphate groups, which require less energy to capture the metal cations. Thermodynamic evaluation suggested that the adsorption is a spontaneous endothermic reaction. These results confirm that CS/PMC mats are easy to produce, and provide high adsorption capacity in simulated wastewater containing Cd2+. These laboratory-based adsorption experiments will assist in selecting/ranking of potential candidate matrices, and scale-up development of technologies for complex wastewater applications.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdolali, A., Ngo, H. H., Guo, H. S., Lee, D. J., Tung, K. L., & Wang, X. C. (2014). Development and evaluation of a new multi-metal binding biosorbent. Bioresource Technology, 160, 98–106.
Adeleye, A. S., Conway, J. R., Garner, K., Huang, Y., Su, Y., & Keller, A. A. (2016). Engineered nanomaterials for water treatment and remediation: Costs, benefits, and applicability. Chemical Engineering Journal, 286, 640–662.
Aliabadi, M., Irani, M., Ismaeili, J., Piri, H., & Parnian, M. J. (2013). Electrospun nanofiber membrane of PEO/chitosan for the adsorption of nickel, cadmium, lead and copper ions from aqueous solution. The Chemical Engineering Journal, 220, 237–243.
Bergeron, C., Perrier, E., Potier, A., & Delmas, G. (2012). A study of the deformation, network, and aging of polyethylene oxide films by infrared spectroscopy and calorimetric measurements. International Journal of Spectroscopy, 2012, 1–13.
Bilal, M., Shah, J. A., Ashfak, T., Gardazi, S. M. H., Tahir, A. A., Pervez, A., & Mahmood, Q. (2013). Waste biomass adsorbents for copper removal from industrial wastewater - a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 263, 322–333.
Brandes, R., Belosinschi, D., Brouillette, F., & Chabot, B. (2019). A new electrospun chitosan/phosphorylated nanocellulose biosorbent for the removal of cadmium ions from aqueous solutions. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7(6), 103477.
Carpenter, A. W., Lannoy, C., & Wiesner, M. R. (2015). Cellulose nanomaterials in water treatment technologies. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(9), 5277–5287.
Chen, X., He, H., & Chen, G. (2020). Effects of biochar and crop straws on the bioavailability of cadmium in contaminated soil. Scientific Reports, 10, 9528.
Chowdhary, P., Raj, A., & Bharagava, R. N. (2018). Environmental pollution and health hazards from distillery wastewater and treatment approaches to combat the environmental threats: A review. Chemosphere, 194, 229–246.
Deng, L., Su, Y., Su, H., Wang, X., & Zhu, X. (2007). Sorption and desorption of lead (II) from wastewater by green algae Cladophora fascicularis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 143, 220–225.
Erdoğan, S., Önal, Y., Akmil-Başar, C., Bilmez-Erdemoğlu, S., Sarıcı-Özdemir, Ç., Köseoğlu, E., & İçduygu, G. (2005). Optimization of nickel adsorption from aqueous solution by using activated carbon prepared from waste apricot by chemical activation. Applied Surface Science, 252(5), 1324–1331.
George, J., & Sabapathi, S. N. (2015). Cellulose nanocrystals: Synthesis, functional properties, and applications. Nanotechnology, Science and Applications, 8, 45–54.
Guo, Q., Ma, Q., Xue, Z., Gao, X., & Chen, H. (2018). Studies on the binding characteristics of three polysaccharides with different molecular weight and flavonoids from corn silk (Maydis stigma). Carbohydrate Polymers, 198, 581–588.
Habiba, U., AfifiA, A. M., Salleh, A., & Ang, B. C. (2017). Chitosan/(polyvinyl alcohol)/zeolite electrospun composite nanofibrous membrane for adsorption of Cr6+, Fe3+ and Ni2+. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 322(Part A), 182–194.
Ho, Y. S. (2006). Isotherms for the sorption of lead onto peat: Comparison of linear and non-linear methods. Polish Journal of Environmental, 15(1), 81–86.
Ho, Y. S., & Mckay, G. (1999). A kinetic study of dye sorption by biosorbent waste product pith. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 25, 171–193.
Ho, Y. S., Porter, J. F., & Mckay, G. (2002). Equilibrium isotherm studies for the sorption of divalent metal ions onto peat: Copper, nickel and lead single component systems. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 141(1–33).
Jamshidifard, S., Koushkbaghi, S., Hosseini, S., Rezaei, S., Karamipour, A., Rad, A. J., & Irani, M. (2019). Incorporation of UiO-66-NH2 MOF into the PAN/chitosan nanofibers for adsorption and membrane filtration of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 368, 10–20.
Jang, W., Yun, J., Jeon, K., & Byun, H. (2015). PVdF/graphene oxide hybrid membranes via electrospinning for water treatment applications. RSC Advances, 5(58), 46711–46717.
Kokol, V., Božič, M., Vogrinčič, R., & Mathew, A. P. (2015). Characterisation and properties of homo- and heterogenously phosphorylated nanocellulose. Carbohydrate Polymers, 125, 301–313.
Kumar, R., Chawla, J., & Kaur, I. (2015). Removal of cadmium ions from wastewater by carbon-based nanosorbents: A review. Journal of Water and Health, 13(1), 18–33.
Lakhdhar, I., Belosinschi, D., Mangin, P., & Chabot, B. (2016). Development of a bio-based sorbent media for the removal of nickel ions from aqueous solutions. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 4(3), 3159–3169.
Lemma, S. M., Bossard, F., & Rinaudo, M. (2016). Preparation of pure and stable chitosan nanofibers by electrospinning in the presence of poly(ethylene oxide). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(11), 1774–1790.
Li, L., Li, Y., Cao, L., & Yang, C. (2015a). Enhanced chromium (VI) adsorption using nanosized chitosan fibers tailored by electrospinning. Carbohydrate Polymers, 125, 206–213.
Li, M., Wu, Q., Song, K., Lee, S., Qing, Y., & Wu, Y. (2015b). Cellulose nanoparticles: Structure–morphology–rheology relationships. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 3(5), 821–832.
Liu, P., Borrell, P. F., Božič, M., Kokol, V., Oksman, K., & Mathew, A. P. (2015). Nanocelluloses and their phosphorylated derivatives for selective adsorption of Ag+, Cu2+ and Fe3+ from industrial effluents. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 294, 177–185.
Luo, X., Yuan, J., Liu, Y., Liu, C., Zhu, X., Dai, X., Ma, Z., & Wang, F. (2017). Improved solid-phase synthesis of phosphorylated cellulose microsphere adsorbents for highly effective Pb2+ removal from water: Batch and fixed-bed column performance and adsorption mechanism. ACS Sustainable Chemical & Engineering, 5(6), 5108–5117.
Martins, B. L., Cruz, C. V., Luna, A. S., & Henriques, C. A. (2006). Sorption and desorption of Pb2+ ions by dead Sargassum sp. biomass. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 27, 310–314.
Mautner, A., Maples, H. A., Kobkeatthawin, T., Kokol, V., Karim, Z., Li, K., & Bismarck, A. (2016). Phosphorylated nanocellulose papers for copper adsorption from aqueous solutions. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 13(8), 1861–1872.
Montoya, V. H., Goncalves, A. C., Strey, L., Rubio, F., Schwantes, D., & Casarin, J. (2013). Biosorption and removal of chromium from water by using moringa seed cake (Moringa oleifera Lam.). Quimica Nova, 36(8), 1104–1110.
Moreira, S. A., Sousa, F. W., & Oliveira, A. G. (2009). Remoção de metais de solução aquosa usando bagaço de caju. Química nova, 32(7), 1717–1722.
Naderi, A., Lindström, T., Flodberg, G., Sundström, J., Junel, K., Runebjörk, A. M., Weise, C. F., & Erlandsson, J. (2016). Phosphorylated nanofibrillated cellulose: Production and properties. Nordic Pulp & Paper Research Journal, 31(1), 20–29.
Noguchi, Y., Homma, I., & Matsubara, Y. (2017). Complete nanofibrillation of cellulose prepared by phosphorylation. Cellulose, 24(3), 1295–1305.
Pan, H., Song, L., Ma, L., Pan, Y., Liew, K. M., & Hu, Y. (2014). Layer-by-layer assembled thin films based on fully biobased polysaccharides: Chitosan and phosphorylated cellulose for flame-retardant cotton fabric. Cellulose, 21, 2995–3006.
Pawlak, A., & Mucha, M. (2003). Thermogravimetric and FTIR studies of chitosan blends. Thermochimica Acta, 396, 153–166.
Qi, Y., Yang, M., Xu, W., He, S., & Men, Y. (2017). Natural polysaccharides-modified graphene oxide for adsorption of organic dyes from aqueous solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 486, 84–96.
Rahimzadeh, M. R., Rahimzadeh, M. R., Kazemi, S., & Moghadamnia, A. (2017). Cadmium toxicity and treatment: An update. Caspian Journal of Internal Medicine, 8(3), 135–145.
Ray, S. S., Chen, S., Li, C., Nguyenac, N. C., & Nguyenac, H. T. (2016). A comprehensive review: Electrospinning technique for fabrication and surface modification of membranes for water treatment application. RSC Advances, 6(88), 85495–85514.
Rodell, M., Famiglietti, J. S., Wiese, D. N., Reager, J. T., Beaudoing, H. K., Landerer, J. W., & Lo, M. H. (2018). Emerging trends in global freshwater availability. Nature, 557, 651–659.
Sangsanoh, P., & Supaphol, P. (2006). Stability improvement of electrospun chitosan nanofibrous membranes in neutral or weak basic aqueous solutions. Biomacromolecules, 7(10), 2710–2714.
Saxena, G., Chandra, R., & Bharagava, R. N. (2016). Environmental pollution, toxicity profile and treatment approaches for tannery wastewater and its chemical pollutants. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 240, 31–69.
Suflet, D., Popescu, I., & Pelin, I. (2017). Preparation and adsorption studies of phosphorylated cellulose microspheres. Cellulose Chemistry and Technology, 51(1–2), 23–34.
Tian, Y., Wu, M., Liu, R., Li, Y., Wang, D., Tan, J., Wu, R., & Huang, Y. (2011). Electrospun membrane of cellulose acetate for heavy metal ion adsorption in water treatment. Carbohydrate Polymers, 83(2), 743–748.
Ungureanu, G., Santos, S., Boaventura, R., & Botelho, C. (2015). Arsenic and antimony in water and wastewater: Overview of removal techniques with special reference to latest advances in adsorption. Journal of Environmental Management, 151, 326–342.
Van den Broek, L. A. M., Knoop, R. J. L., Kappen, F. H. J., & Boeriu, C. G. (2015). Chitosan films and blends for packaging material. Carbohydrate Polymers, 116, 237–242.
Xiao, P., Zhang, J., Feng, Y., Wu, J., He, J., & Zhang, J. (2014). Synthesis, characterization and properties of novel cellulose derivatives containing phosphorus: Cellulose diphenyl phosphate and its mixed esters. Cellulose, 21(4), 2369–2378.
Xu, X., Ding, N. S. H., & Hou, F. F. (2018). Environmental pollution and kidney diseases. Nature Reviews Nephrology, 14, 313–324.
Younes, I., & Rinaudo, M. (2015). Chitin and chitosan preparation from marine sources. Structure, properties and applications. Marine Drugs, 13(3), 1133–1174.
Zhang, L., Zeng, Y., & Cheng, C. (2016). Removal of heavy metal ions using chitosan and modified chitosan: A review. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 214, 175–191.
Zhou, D., Kim, D., & Ko, S. (2015). Heavy metal adsorption with biogenic manganese oxides generated by pseudomonas putida strain MnB1. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 24, 132–139.
Zilov, E. A. (2013). Water resources and the sustainable development of humankind: International cooperation in the rational use of freshwater-lake resources: Conclusions from materials of foreign studies. Water Resources, 40, 84–95.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brandes, R., Brouillette, F. & Chabot, B. Laboratory Adsorption Studies on Cadmium (II) by Nonwoven Chitosan/Phosphorylated Microcellulose Nanocomposite. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 566 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04936-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04936-w