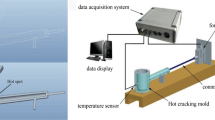
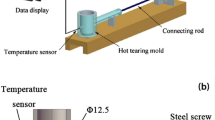
Abstract
Gd has higher solid solubility than Y in Mg, which has a greater influence on the mechanical properties of the alloy, but there is little research on its hot tearing. In this paper, the coupling behavior of solidification and hot tearing of Mg–xZn–2xGd (x = 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2 at.%) alloy was studied, and its micro-mechanism was revealed. It is found that the microstructure of Mg–2xGd–xZn alloy is composed of α-Mg, LPSO and W phase. With the increase of x, α-Mg grain is refined, the second phase content is increased, and the hot tearing susceptibility is decreased. Under the same composition, Gd has a better effect on reducing the hot tearing tendency than Y. Further studies show that with the increase of x, the relative content of residual liquid phase between α-Mg grains increases after crystallization, and its feeding ability to local shrinkage of solid phase is enhanced. In addition, the morphology of LPSO precipitated along the grain boundary is wedged into both sides of α-Mg matrix, which is considered to be helpful to prevent the propagation of hot cracking along the grain boundary, which is another important reason to reduce the hot cracking sensitivity of the alloy.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Zhou, Y.D. Huang, P.L. Mao, Influence of composition on hot tearing in binary Mg–Zn alloys. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 24(3–4), 170–176 (2011)
Z.Q. Wei, Y. Wang, Z. Liu, Effects of Zn and Y on hot-tearing susceptibility of Mg–xZn–2xY alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34(16), 1–7 (2018)
J.F. Song, F.S. Pan, B. Jiang, A review on hot tearing of magnesium alloys. J. Magnes. Alloys 8(3), 151–172 (2016)
Z.P. Luo, S.Q. Zhang, High-resolution electron microscopy on the X-Mg12ZnY phase in a high strength Mg–Zn–Zr–Y magnesium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 19(9), 813–815 (2000)
X. Shi, Y. Long, H. Zhang et al., Role of LPSO phase in crack propagation behavior of an as-cast Mg–Y–Zn Alloy Subjected to dynamic loadings. J. Mater. 12(3), 498 (2019)
Y. Kawamura, M. Yamasaki, Formation and mechanical properties of Mg97Zn1RE2 alloys with long-period stacking ordered structure. J. Mater. Trans. 48(11), 2986 (2007)
S. Yoshimoto, M. Yamasaki, Y. Kawamura, Microstructure and mechanical properties of extruded Mg–Zn–Y alloys with 14H long period ordered structure. Mater. Trans. 47(4), 959 (2006)
B. Chen, D.L. Lin, X.Q. Zeng et al., Effects of yttrium and zinc addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Y–Zn alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 45(9), 2510–2517 (2010)
B. Chen, D.L. Lin, X.Q. Zeng et al., Microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine grained Mg97Y2Zn1 alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing. J. Alloys Compd. 440(1–2), 98 (2007)
Y.J. Wu, D.L. Lin, X.Q. Zeng et al., Formation of a lamellar 14H-type long period stacking ordered structure in an as-cast Mg–Gd–Zn–Zr alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 44(6), 1607–1612 (2009)
W.J. Ding, Y.J. Wu, L.M. Peng et al., Formation of 14H-type long period stacking orde red structure in the as-cast and solid-solution-treated Mg–Gd–Zn–Zr alloys. J. Mater. Res. 24(5), 1842–1854 (2009)
J. Li, Z. He, P. Fu et al., Heat treatment and mechanical properties of a high-strength cast Mg–Gd–Zn alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 651, 745–752 (2016)
Z. Liu, S.B. Zhang, P.L. Mao et al., Effects of Y on hot tearing formation mechanism of Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 30(10), 1214–1222 (2014)
Z. Wang, Y.Z. Li, F. Wang et al., Hot tearing susceptibility of Mg–xZn–2Y alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26, 3115–3122 (2016)
H. Liu, W.F. Xu, N.C. Wilson et al., Formation of and interaction between β’ and β1 phases in a Mg–Gd alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 712, 334–344 (2017)
S.Q. Yin, Z.Q. Zhang, X. Liu et al., Effects of Zn/Gd ratio on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Gd–Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 695, 135–143 (2017)
Y.J. Wu, L.M. Peng, X.Q. Zeng et al., A high-strength extruded Mg–Gd–Zn–Zr alloy with superplasticity. J. Mater Res. 24(12), 3596–3602 (2009)
J.F. Song, Z. Wang, Y.D. Huang et al., Hot tearing susceptibility of Mg–Ca binary alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 46(12), 6003–6017 (2015)
G. Cao, I. Haygood, S. Kou, Onset of hot tearing in ternary Mg–Al–Sr alloy casting. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 41, 2139–2150 (2010)
Z.H. Huang, S.M. Liang, R.S. Chen et al., Solidification pathways and constituent phases of Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 468, 170–178 (2009)
D. Emadi, L.V. Whiting, S. Nafisi et al., Applications of thermal analysis in quality control of solidification processes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 81, 235–242 (2005)
H. Cruz, C. Gonzalez, A. Juárez et al., Quantification of the microconstituents formed during solidification by Newton thermal analysis method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 178, 128–134 (2006)
Z. Wang, Y. Li, F. Wang et al., Effect of Cu additions on microstructure, mechanical properties and hot-tearing susceptibility of Mg–6Zn–0.6Zr alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 25, 5530–5539 (2016)
L. Zhou, Z. Liu, Y.D. Huang et al., Prediction of hot tearing susceptibility for Mg–Zn–(Al) alloys. Adv. Mater. Res. 509, 138–146 (2012)
Z. Wang, Y.D. Huang, A. Srinivasan et al., Hot tearing susceptibility of binary Mg–Y alloy castings. Mater. Des. 47, 90–100 (2013)
X. Du, F. Wang, Z. Wang et al., Hot tearing susceptibility of AXJ530 alloy under low-frequency alternating magnetic field. Acta Metall. Sinica. 33, 1259–1270 (2020)
Z. Wei, S. Liu, Z. Liu et al., Effects of Zn content on hot tearing susceptibility of Mg–7Gd–5Y–0.5Zr alloy. Metals-Open Access Metall. J. 10, 414 (2020)
Z. Zhou, Z. Liu, Y. Wang et al., Investigations on the effect of grain size on hot tearing susceptibility of MgZn1Y2 alloy. J. Mater. Res. Express 5, 5 (2018)
Z. Wang, J. Song, Y.D. Huang et al., An investigation on hot tearing of Mg–4.5Zn–(0.5Zr) alloys with Y additions. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 46, 2108–2118 (2015)
H. Liu, J. Ju, X. Yang et al., A two-step dynamic recrystallization induced by LPSO phases and its impact on mechanical property of severe plastic deformation processed Mg97Y2Zn1 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 704, 509–517 (2017)
K. Hagihara, A. Kinoshita, Y. Sugino et al., Effect of long-period stacking ordered phase on mechanical properties of Mg97Zn1Y2 extruded alloy. Acta Mater. 58(19), 6282–6293 (2010)
H.Y. Qi, G.X. Huang, H. Bo et al., Experimental investigation and thermodynamic assessment of the Mg–Zn–Gd system focused on Mg-rich corner. J. Mater. Sci. 47(3), 1319–1330 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from High level innovation team of Liaoning Province (XLYC1908006), Innovation Talent Program in Science and Technology for Young and Middle-aged Scientists of Shenyang (No. RC.180111), Project of Liaoning Education Department (No. LQGD2019002 and LJGD2019004), Liaoning nature fund guidance plan (No. 2019-ZD-0210) and Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program (No. XLYC1807021 and 1907007), Joint Research Fund Liaoning-Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science (2019JH3/30100014), National Key Research and Development Programs (SQ2020YFC200162-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, X., Liu, S., Zhou, L. et al. Study on the Coupling Behavior and Micro-Mechanism of Solidification and Hot Tearing of Mg–xZn–2xGd Alloys. Inter Metalcast 15, 1175–1183 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00541-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00541-z