Abstract
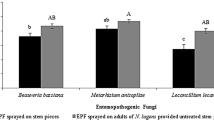
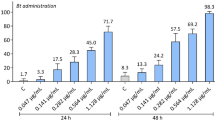
The whitebacked planthopper, Sogatella furcifera Horváth (Homoptera: Delphacidae), is a serious pest of rice crop in Pakistan. In the current study the efficacy of entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana, Metarhizium anisopliae and Akanthomyces lecanii was evaluated against whitebacked planthopper (WBPH) under laboratory and field conditions. There were two concentrations of entomopathogenic fungi (EPF, 1 × 109 CFU/mL and 1 × 108 CFU/mL) used in the bioassays. Combination of EPF with the insecticide buprofezin at low dose rates (0.001 mg/mL and 0.006 mg/mL) was also evaluated. Results showed that mortality of the pest ranged from 50–80% when EPF was used alone. Mortality of WBPH was 53–90% when buprofezin was combined with EPF. B. bassiana and M. anisopliae were more effective than A. Lecanii. In field trials, EPF were applied at the rate of 2.5 × 1012 CFU/ha and buprofezin at the rate of 78 g/ha. Relative efficacies of EPF ranged from 40.54–59.17% when only using EPF after 21 days of the first application. Relative efficacy climbed to 71.62% and 70.20% when buprofezin was combined with B. bassiana and M. anisopliae, respectively, after 14 days of the first spray. The results revealed that EPF has the potential to control the population of WBPH. Additionally, their efficacy can be further enhanced by combining them with buprofezin even at low dose rates.
Zusammenfassung
Die Weißrückenzikade, Sogatella furcifera Horváth (Homoptera: Delphacidae), ist ein ernster Schädling der Reisernte in Pakistan. In der aktuellen Studie wurde die Wirksamkeit der entomopathogenen Pilze Beauveria bassiana, Metarhizium anisopliae und Akanthomyces lecanii gegen die Weißrückenzikade unter Labor- und Feldbedingungen untersucht. Es wurden zwei Konzentrationen entomopathogener Pilze (EPF, 1 × 109 KBE/mL und 1 × 108 KBE/mL) in den Bioassays verwendet. Die Kombination der EPF mit dem Insektizid Buprofezin bei niedrigen Dosisraten (0,001 mg/mL und 0,006 mg/mL) wurde ebenfalls untersucht. Die Ergebnisse zeigten, dass die Mortalität des Schädlings bei alleiniger Anwendung der EPF zwischen 50 und 80 % lag. Die Mortalität der Zikade betrug 53–90 %, wenn Buprofezin mit EPF kombiniert wurde. B. bassiana und M. anisopliae waren wirksamer als A. Lecanii. In Feldversuchen wurden EPF in einer Menge von 2,5 × 1012 KBE/ha und Buprofezin in einer Menge von 78 g/ha eingesetzt. Die relativen Wirksamkeiten der EPF reichten von 40,54–59,17 % (21 Tage nach der ersten Anwendung), wenn die EPF allein angewendet wurden. Die relative Wirksamkeit kletterte auf 71,62 % und 70,20 %, wenn Buprofezin mit B. bassiana und M. anisopliae kombiniert wurde (14 Tage nach der ersten Anwendung). Die Ergebnisse zeigten, dass EPF das Potenzial haben, die Population der Weißrückenzikade zu kontrollieren. Darüber hinaus kann ihre Wirksamkeit durch die Kombination mit Buprofezin auch bei niedrigen Dosisraten weiter verbessert werden.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amjad M, Bashir MH, Afzal M, Sabri MA, Javed N (2012) Effects of commercial pesticides used against cotton whitefly (Bemisia tabaci Genn.) and mites (Tetranychus urticae Koch) on growth and conidial germination of two species of entomopathogenic fungi. Pak J Life Soc Sci 10:22–24
Asi MR, Bashir MH, Afzal M, Ashfaq M, Sahi ST (2010) Compatibility of entomopathogenic fungi, Metarhizium anisopliae and Paecilomyces fumosoroseus with selective insecticides. Pak J Bot 42:4207–4214
Ayala-Zermeňo MA, Gallou A, Am BP, Serna-Dominguez MG, Arredondo-Bernal HC, Montesinos-Matias R (2015) Characterization of entomopathogenic fungi used in biological control programme of Diaphorina citri in Mexico. Biocontrol Sci Tech 25:1192–1207
Chang X, Yuan Y, Zhang T, Wang D, Du X, Wu X, Chen H, Chen Y, Jiao Y, Teng H (2015) The toxicity and detoxifying mechanism of cycloxaprid and buprofezin in controlling Sogatella furcifera (Homoptera: Delphacidae). J Insect Sci 15:1–5
Cheng JA (2015) Rice planthoppers in the past half century in China. In: Heong KL, Cheng JA, Escalada MM (eds) Rice planthoppers, ecology, management, Socio economics and policy. Zhejiang University & Springer, Hangzhou, pp 1–32
Cheng XN, Wu JC, Ma F (2003) Research and prevention of the brown planthopper. Chinese Agric Press, Beijing, pp 52–55
Cuthbertson AGS, Blackburn LF, Eyre DP, Cannon RJC, Miller J, Northing P (2011) Bemisia tabaci: the current situation in the UK and the prospect of developing strategies for eradication using entomopathogens. Insect Sci 18:1–10
Feng MG, Pu XY (2005) Time–concentration–mortality modeling of the synergistic interaction of Beauveria bassiana and imidacloprid against Nilaparvata lugens. Pest Manag Sci 61:363–370
Geng BW, Zhang RJ (2004) Pathogenicity of metarhizium anisopliae var. Acridum to the deveolpmental stages of brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens stal and Sogatella furcifera (Horvath). Entomol Sinica 11(2):89–97
Ghauri MSK (1979) Whitebacked planthopper attacks before introduction of new rice varieties in Pakistan. Int Rice Res Newsl 4:11–11
Guo R, Lu JP, Xiao WX, Li JH, Wang SM (2013) Investigation on rice virus disease transmitted by rice plant hoppers in low and hot valley of Yunnan Province in winter and suggestion on virus disease management. Plant Prot 39:131–135
Heinrichs EA, Medrano FG, Rapusas HR (1985) Genetic evaluation for insect resistance in rice. Int Rice Res Inst (IRRI), Philippines, p 356
Henderson CF, Tilton EW (1955) Tests with acaricides against the brown wheat mite. J Econ Entomol 48:157–161
Hu G, Lu F, Zhai BP, Lu MH, Liu WC, Zhu F, Wu XW, Chen GH, Zhang XX (2014) Outbreaks of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) in the Yangtze River Delta: immigration or local reproduction. Plos One 9:e88973
Hu SJ, Fu DY, Han ZL, Hui Y (2015) Density, demography, and influential environmental factors on overwintering populations of Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) in southern Yunnan, China. J Insect Sci 15(1):58
Jin SF, Feng MG, Ying SH, Mu WJ, Chen JQ (2010) Evaluation of alternative rice planthopper control by the combined action of oil-formulated Metarhizium anisopliae and low-rate buprofezin. Pest Manag Sci 67:36–43
Kalmath B, Yeligar R, Kapasi M (2016) Evaluation of different formulations of Metarhizium anisopliae against plant hoppers in rice ecosystem. Biopest Intl 12(2):173–181
Kepler RM, Luangsa-ard JJ, Hywel-Jones NL, Quandt CA, Sung G‑H, Rehner SA et al (2017) A phylogenetically-based nomenclature for Cordycipitaceae (Hypocreales). IMA Fungus 8(2):335–353
Kiran R, Veeranna R (2012) Evaluation of bio-pesticide Metarhizium anisopliae against brown plant hopper (Nilaparvatha lugens) and its efficiency on the improvement of the productivity of paddy. Int J Plant Prot 5:81–83
Kumar S, Ram L, Kumar A, Yadav SS, Singh B, Kalkal D (2015) Biology of whitebacked plant hopper Sogatella furcifera on basmati rice under agro climatic condition of Haryana. Agric Sci Dig 35(2):142–145
Li M, Lin H, Li S, Chen P, Jin L, Yang J (2012) Virulence of entomopathogenic fungi to adults and eggs of Nilaparvata lugens Stal (Homopera: Delphacidae). Afr J Agric Res 7:2183–2190
Mahar MM, Bhatti IM, Hakro MR (1978) Whitebacked planthopper appears on rice in Sind Pakistan. Int Rice Res Newsl 3:11–11
Majid A, Makdoomi MA, Dar IA (1979) Occurrence and control of the white-backed planthopper in the Punjab of Pakistan. Int Rice Res Newsl 4(l):17
Michalaki MP, Athanassiou CG, Kavallieratos NG, Batta YA, Balotis GN (2006) Effectiveness of Metarhizium anisopliae (Metshinkoff) Sorokin applied alone or in combination with diatomaceous earth against Tribolium confusum Du Val Larvae: influence of temperature, relative humidity and type of commodity. Crop Prot 25:418–425
Mochida O, Perfect TJ, Dyck VA, Mahar MM (1982) The whitebacked planthopper Sogatella furcifera (Horvath) (Hom. Delphacidae) its pest status and ecology. In: Proceedings of the international rice research conference on rice cropping systems 19–23. April International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, p 72
Mohan C, Sridhar RP, Nakkeeran S (2016) Studies on efficacy of entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium anisopliae (Metchnikoff) Sorokin against Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Int J Agric Sci Res 6:227–234
Neves PMOJ, Hirose E, Tchujo PT, Moino AJ (2001) Compatibility of entomopathogenic fungi with neonicotinoid Insecticides. Neotrop Entomol 30:263–268
Oliveira CN, Neves PMOJ, Kawazoe LS (2003) Compatibility between the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana and insecticides used in coffee plantations. Sci Agric 60:663–667
Ouedraogo A, Fargues J, Goettel MS, Lomer CJ (1997) Effect of temperature on vegetative growth among isolates of Metarhizium anisopliae and M. flavoviride. Mycopathol 137:37–43
Palumbo JC (2009) Spray timing of spiromesifen and buprofezin for managing Bemisia whiteflies in cantaloupes. Plant Health Prog. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHP-2009-0407-01-RS
Patel MG, Jhala RC, Vaghela NM, Chauhan NR (2010) Bioefficacy of buprofezin against mealybug, Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) an invasive pest of cotton. Karnataka J Agric Sci 23:14–18
Pu XY, Feng MG, Shi CH (2005) Impact of three application methods on the field efficacy of a Beauveria bassiana-based mycoinsecticide against the false-eye leafhopper, Empoasca vitis (Homoptera: Cicadellidae), in tea canopy. Crop Prot 24:167–175
Rasdi Z, Salmah M, Hassan A, Hamady D, Hamaseh A, Ismail F (2012) Field evaluation of some insecticides on whitefly (Trialeurodes vaporariorum) and predator (Macrolophus caliginosus) on brinjal and tomato plants. Asian J Rural Dev 2:302–311
Reddy AV, Devi RS, Dhurua S, Reddy DVV (2013) Study on the efficacy of some entomogenous fungi against brown plant hopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stal in irrigated rice. J Biopest 6(2):139–143
Rehman A, lnayatullah C, Ashraf M (1986) Whitebacked plant-hopper: a major pest of paddy. Prog Farm 6:65–67
Riasat T, Wakil W, Ashfaq M, Sahi ST (2011) Effect of Beauveria bassiana mixed with diatomaceous earth on mortality, mycosis and sporulation of Rhyzopertha dominica on stored wheat. Phytoparasitica 39:325–331
Roberts DW, Leger StRJ (2004) Metarhizium spp., cosmopolitan insect pathogenic fungi: mycological aspects. Adv Appl Microbiol 54:1–70
Rodriguez M, Gerding M, France A, Ceballos R (2009) Evaluation of Metarhizium anisopliae var. anisopliae Qu-M845 isolate to control Varroa destructor (Acari: Varroidae) in laboratory and field trials. Chil J Agric Res 69:541–547
Sabir AM, Shah ZU, Sabar M, Rizwan M, Atta B, Qadir A, Asghar M (2019) Rice planthoppers: potential threat to the sustainable rice production in the Punjab, Pakistan. In: 39 th Pakistan Congress of Zoology. Department of Zoology, Islamia College University, Peshawar, p 229
Shan LT, Feng MG (2010) Evaluation of the biocontrol potential of various Metarhizium isolates against green peach aphid Myzus persicae (Homoptera: Aphididae). Pest Manag Sci 66:669–675
Skrobek A (2001) Investigations on the effect of entomopathogenic fungi on whiteflies. Dissertation. Institut für Pflanzenkrankheiten der Rheinischen Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn, Bonn
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1995) Biometry, 3rd edn. W. H. Freeman, New York
Sumikarsih E, Herlinda S, Pujiastuti Y (2019) Conidial density and viability of Beauveria bassiana isolates from Java and Sumatra and their virulence against Nilaparvata lugens at different temperatures. Agrivita J Agri Sci 41(2):335–350
Sun J, Fuxa JR, Henderson G (2003) Effects of virulence, sporulation and temperature on Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana laboratory transmission in Coptotermes formosanus. J Invertebr Pathol 48:38–46
Tefera T, Pringle KL (2003) Effect of exposure method to Beauveria bassiana and conodia concentration on mortality, mycosis, and sporulation in cadavers of Chilo partellus (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J Invertebr Pathol 84:90–95
Tian L, Feng MG (2006) Evaluation of the time–concentration–mortality responses of Plutella xylostella larvae to the interaction of Beauveria bassiana with a nereistoxin analogue insecticide. Pest Manag Sci 62:69–76
Vega FE (2008) Insect pathology and fungal endophytes. J Invertebr Pathol 98(3):277–279
Wang B, Shahzad MF, Zhang Z, Sun H, Han P, Li F, Han Z (2014) Genome-wide analysis reveals the expansion of cytochrome P450 genes associated with xenobiotic metabolism in rice striped stem borer, Chilo suppressalis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443:756–760
Ye SD, Dun YH, Feng MG (2005) Time and concentration dependent interactions of Beauveria bassiana with sublethal rates of imidacloprid against the aphid pests Macrosiphoniella sanborni and Myzus persicae. Ann Appl Biol 146:459–468
Zhang HM, Yang J, Chen JP, Adams MJ (2008) A black-streaked dwarf disease on rice in China is caused by a noval fijivirus. Arch Virol 153:1893–1898
Zhou GH, Wen JJ, Cai DJ, Li P, Xu DL, Zhang SG (2008) Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus: a new proposed Fijivirus species in the family Reoviridae. Chin Sci Bull 53:3677–3685
Funding
The authors thank AgriLife SOM Phytopharma (India) Limited (www.agrilife.in) for providing entomopathogenic fungi free of cost for experimental use.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
I. Haider, M. Sufyan, M. Akhtar, M.J. Arif and S.T. Sahi declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haider, I., Sufyan, M., Akhtar, M. et al. Efficacy of Entomopathogenic Fungi Alone and in Combination with Buprofezin Against Sogatella Furcifera (Horváth) on Rice. Gesunde Pflanzen 73, 85–94 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-020-00531-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-020-00531-5
Keywords
- Beauveria bassiana
- Metarhizium anisopliae
- Akanthomyces lecanii
- Sogatella furcifera
- Buprofezin
- Rice crop