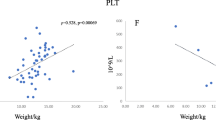
Abstract
Hematological and serum biochemical reference values for 33 free-ranging sambar deer following immobilization with medetomidine (70–100 μgkg−1) and ketamine (1–2 mgkg−1) in Sariska Tiger Reserve in India were established and the differences across sex and age group were compared. Hematological and biochemical variables across different age-classes for red blood cell count, eosinophils, mean corpuscular hemoglobin, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, triglycerides, and blood glucose varied significantly though the hematological values did not vary between sexes. Blood urea nitrogen and creatinine levels were significantly influenced by sex in the present study. Interpretation of the result, however, needs to be made with caution due to the low number of sub-adult compared to adults in the present study. The study highlights the need for understanding the source of individual variation for meaningful interpretation. This paper provides the first report of baseline hematologic and serum biochemistry values for free-ranging sambar deer that can form basis for assessing the state of health and nutritional condition of the animal.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Andheria AP, Karanth KU, Kumar NS (2007) Diet and prey profiles of three sympatric large carnivores in Bandipur Tiger Reserve, India. J Zool 273(2):169–175
Arnemo JM, Ranheim B (1999) Effects of medetomidine and atipamezole on serum glucose and cortisol levels in captive reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus). Rangifer 19:85–89
Arnemo JM, Negard T, Søli NE (1994) Chemical capture of free-ranging red deer (Cervus elaphus) with medetomidine-ketamine. Rangifer 14(3):123–127
Barić Rafaj R, Tončić J, Vicković I, Šoštarić B (2011) Haematological and biochemical values of farmed red deer (Cervus elaphus). Veterinarski Arhiv 81(4):513–523
Broom DM (2000) Welfare assessment and problem areas during handling and transport. In: Grandin T (ed) Livestock, handling and transport, 2nd edn. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 43–61
Camargo C, Duarte J, Fagliari JJ, Santana AM, Simplício KM, Santana AE (2013) Effect of sex and seasons of the year on hematologic and serum biochemical variables of captive brown brocket deer (Mazama gouazoubira). Pesqui Vet Bras 33(11):1364–1370
Casas-Díaz E, López-Olvera JR, Marco I, Mentaberre G, Lavín S (2008) Hematologic and biochemical values for Spanish ibex (Capra pyrenaica) captured via drive-net and box-trap. J Wildl Dis 44(4):965–972
Chapple RS, English AW, Mulley RC, Lepherd EE (1991) Hematology and serum biochemistry of captive unsedated chital deer (Axis axis) in Australia. J Wildl Dis 27(3):396–406
Cross JP, Mackintosh CG, Griffin JF (1988) Effect of physical restraint and xylazine sedation on haematological values in red deer (Cervus elaphus). Res Vet Sci 45(3):281–286
Da Luz Mathias M, Mira A (1992) Serum proteins and hematological values in the fallow deer (Dama dama L.) (Cervidae, Artiodactyla). Mammalia (Paris) 56(3):485–488
DelGiudice GD, Mech LD, Kunkel KE, Gese EM, Seal US (1992) Seasonal patterns of weight, hematology, and serum characteristics of free-ranging female white-tailed deer in Minnesota. Can J Zool 70(5):974–983
Flesness N (1986) Normal physiological values. Apple Valley, Minnesota, International Species Inventory System (ISIS)
Gill J (1990) Seasonal cyclicity in carbohydrate metabolism parameters in the European bison, Bison bonasus L. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol 96(3):435–439
Gupta AR, Patra RC, Saini M, Swarup D (2007) Haematology and serum biochemistry of chital (Axis axis) and barking deer (Muntiacus muntjak) reared in semi-captivity. Vet Res Commun 31(7):801–808
Hawkey CM (1975) Comparative mammalian haematology. Cellular Components and Blood Coagulation of Captive Animals. William Heinemann Medical Books Ltd, London
Hawkey CM, Hart MG (1985) Normal hematologic values of axis deer (Axis axis), Père David’s deer (Elaphus davidianus) and barasingha (Cervus duvauceli). Res Vet Sci 39(2):247–248
Jalanka HH (1988) Evaluation of medetomidine and ketamine induced immobilization in markhors (Capra falconeri megaceros) and its reversal by atipamezole. J Zoo Anim Med 19:95–105
Jalanka HH, Roeken BO (1990) The use of medetomidine, medetomidine-ketamine combinations, and atipamezole in nondomestic mammals: a review. J Zoo Wildl Med 21:259–282
Johns J, George Chandy JA, Sooryadas S, John KD, Martin M, Ajithkumar S (2018) Haematological observations in twenty saptive male sambar deer (Rusa unicolor). J Vet Anim Sci 49(1):22–24
Jones ML, Allison RW (2007) Evaluation of the ruminant complete blood cell count. Vet Clin N Am Food Anim Pract 23(3):377–402
Kaneko JJ (1997) Carbohydrate metabolism and its diseases. In: Kaneko JJ, Harvey JW, Bruss ML (eds) Clinical biochemistry of domestic animals, 5th edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 45–81
Karanth KU, Kumar NS (2005) Distribution and dynamics of tiger and prey populations in Maharashtra, India. https://www.nfwf.org/sites/default/files/finalreports1/16394_FinalReport2004_0103_007DDTP-Mreport[1].pdf. Accessed 22 Jan 2020
Karanth KU, Sunquist ME (1995) Prey selection by tiger, leopard and dhole in tropical forests. J Anim Ecol 64:439–450
Khatri-Chhetri R, Sun CM, Wu HY, Pei KJC (2015) Reference intervals for hematology, serum biochemistry, and basic clinical findings in free-ranging Chinese pangolin (Manis pentadactyla) from Taiwan. Vet Clin Pathol 44(3):380–390
Kirkpatrick RL, Buckland DE, Abler WA, Scanlon PF, Whelan JB, Burkhart HE (1975) Energy and protein influences on blood urea nitrogen of white-tailed deer fawns. J Wildl Manag 1:692–698
Kreeger TJ, Arnemo JM, Raath JP (2002) Handbook of wildlife chemical immobilization. International Edition. Wildlife Pharmaceutical, Inc., Fort Collins
Leslie DM Jr (2011) Rusa unicolor (Artiodactyla: Cervidae). Mamm Species 43(871):1–30
Linkie M, Martyr DJ, Holden J, Yanuar A, Hartana AT, Sugardjito J, Leader-Williams N (2003) Habitat destruction and poaching threaten the Sumatran tiger in Kerinci Seblat National Park, Sumatra. Oryx 37(1):41–48
Lumsden JH (1998) “Normal” or reference values. Vet Clin Pathol 27:102–107
Marco I, Lavín S (1999) Effect of the method of capture on the haematology and blood chemistry of red deer (Cervus elaphus). Res Vet Sci 66:81–84
Matsubayashi H, Lagan P, Sukor JRA, Kitayama K (2007) Seasonal and daily use of natural licks by sambar deer (Cervus unicolor) in a Bornean tropical rain forest. Tropics 17(1):81–86
Miller AL, Evans AL, Os Ø, Arnemo JM (2013) Biochemical and hematologic reference values for free-ranging, chemically immobilized wild Norwegian reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) during early winter. J Wildl Dis 49(2):221–228
Ngampongsai C (1987) Habitat use by the sambar (Cervus unicolor) in Thailand: a case study for Khao- Yai National Park. In: Wemme CM (ed) Biology & Management of the Cervidae. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington D.C 577pp
Nuvoli S, Burrai GP, Secci F, Columbano N, Careddu GM, Mandas L, Sanna MA, Pirino S, Antuofermo E (2014) Capture myopathy in a corsican red deer (Cervus elaphus corsicanus) (Ungulata: Cervidae). Ital J Zool 81(3):457–462. https://doi.org/10.1080/11250003.2014.942712
Padilla S, Bouda J, Quiroz-Rocha GF, Dávalos JL, Sánchez A (2000) Biochemical and haematological values in venous blood of captive red deer (Cervus elaphus) at high altitude. Acta Vet Brno 69:327–331
Peinado VI, Celdrán JF, Palomeque J (1999a) Basic hematological values in some wild ruminants in captivity. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 124(2):199–203
Peinado VI, Celdrán JF, Palomeque J (1999b) Blood biochemistry values in some wild ruminants in captivity. Comp Haematol Int 9(4):175–181
Rosef O, Nystøyl HL, Solenes T, Arnemo JM (2004) Haematological and serum biochemical reference values in free-ranging red deer (Cervus elaphus atlanticus). Rangifer 24(2):79–85
Sankar K, Acharya B (2004) Sambar (Cervus unicolor Kerr, 1792). ENVIS bulletin (wildlife Institute of India, Dehra Dun) 7:163–170
Schaller G (1967) The deer and the tiger. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Seal US, Bush M (1982) Capture and chemical immobilization of cervids. In: Wemmer CM (ed) Biology and management of the Cervidae. Smithsonian Institution press, Washington D.C, pp 480–450
Semiadi G, Wilson PR, Muir PD, Barry TN (1995) Haematological values for captive sambar deer (Cervus unicolor). Media Veteriner 2(1):41–44
Siti Norzubaidah AR, Rosnina Y, Hazilawati H (2010) Blood and biochemistry profiles of sambar deer (Cervus unicolor) under different adaptation periods. In: 5th Seminar on Veterinary Sciences, 5–8 Jan 2010, Serdang, Selangor
Stringer EM, Kennedy-Stoskopf S, Chitwood MC, Thompson JR, DePerno CS (2011) Hyperkalemia in free-ranging white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). J Wildl Dis 47:307–313
Thorn NEE (2000) Hematology of the deer. In: Feldman BF, Zinkl JG, Jain NC (eds) Schalm’s veterinary hematology, 5th edn. Lippincott Wiliams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 1179–1183
Timmins R, Kawanishi K, Giman B, Lynam A, Chan B, Steinmetz R, Sagar Baral H, Samba Kumar N (2015) Rusa unicolor. The IUCN red list of threatened species 2015: e. T41790A85628124
Topal A, Gul NY, Yanik K (2010) Effect of capture method on hematological and serum biochemical values of red deer (Cervus elaphus) in Turkey. J Anim Vet Adv 9(8):1227–1231
Tun Yin U (1967) Wild animals of Burma. Rangoon Gazette Limited, Rangoon 301pp
Walton RM (2001) Establishing reference intervals: health as a relative concept. In: Seminars in Avian and Exotic Pet Medicine, WB Saunders 10(2):66–71
Wołk E, Józefczak E (1984) Serum proteins of the free-ranging European bison. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol 79(4):597–600
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to officers and frontline staff of Rajasthan Forest Department for according necessary permissions to carry out the work and for extending support during fieldwork. The study was supported by Wildlife Institute of India (WII) through various programs and the support from the Director, WII and Dean, Faculty of Wildlife Sciences is duly acknowledged. The authors are grateful to Christian Gortazar for the valuable comments and suggestions on our manuscript. The efforts of field researchers, field assistants, laboratory technicians, and frontline staff were extensive, and their contributions are duly acknowledged.
Funding
The study was funded by Wildlife Institute of India, Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate change (MoEFCC), Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The work has approval of the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee of Wildlife Institute of India. All the authors agree to participate in the publication. The work is presented for publication in European Journal of Wildlife Research journal.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nigam, P., Talukdar, A., Habib, B. et al. Hematologic and serum biochemical reference values in chemically immobilized free-ranging sambar (Rusa unicolor). Eur J Wildl Res 66, 102 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-020-01441-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-020-01441-7