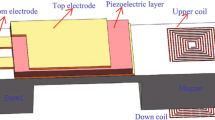
Abstract
The multiple forms of vibration exist in an ambient environment diffusely and already become a considerable object for energy harvesting. However, how to effectively extract low-level, low-frequency, and multi-directional vibration from the ambient environment is becoming a key issue in the field of energy harvesting. To solve this issue, a tower-shaped piezoelectric vibration energy harvester (TS-PVEH) is reported. Finite element simulation indicates that TS-PVEH works in two fundamental modes, i.e., its in-plane and out-of-plane vibration modes. Meanwhile, simulation results show that the natural frequency of TS-PVEH is 3.39 Hz, 3.40 Hz, and 11.50 Hz, respectively; and the experiments also verified that. By virtue of the tower structure of TS-PVEH, the device is pretty sensitive to three-dimensional vibration. At a low level of acceleration 1 m/s2, the maximum load power of TS-PVEH is 65.8 µW in out-of-plane mode and 17.2 µW in in-plane mode, respectively. Furthermore, the effects of the PVDF connection mode on the output performance of TS-PVEH were studied in detail, and comparative experimental results show that a reasonable connection of PVDF can improve energy harvesting efficiency. The proposed TS-PVEH is expected to be used to scavenge energy from multi-dimensional, low-level, and low-frequency vibrations that present in an ambient environment.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zou, H. X., Zhao, L. C., Gao, Q. H., Zuo, L., Liu, F. R., Tan, T., et al. (2019). Mechanical modulations for enhancing energy harvesting: Principles, methods and applications. Applied Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113871
Dong, L., Closso, A. B., Jin, C., Tras, I., Chen, Z., & Zhang, J. X. (2019). Vibration-energy-harvesting system: transduction mechanisms, frequency tuning techniques, and biomechanical applications. Advanced Materials Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.201900177
Khalid, S., Raouf, I., Khan, A., Kim, N., & Kim, H. S. (2019). A review of human-powered energy harvesting for smart electronics: recent progress and challenges. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 6(4), 821–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-019-00144-y
Oh, Y., Kwon, D.-S., Eun, Y., Kim, W., Kim, M.-O., Ko, H.-J., et al. (2019). Flexible energy harvester with piezoelectric and thermoelectric hybrid mechanisms for sustainable harvesting. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 6(4), 691–698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-019-00132-2
Hwang, W., Kim, K.-B., Cho, J. Y., Yang, C. H., Kim, J. H., Song, G. J., et al. (2019). Watts-level road-compatible piezoelectric energy harvester for a self-powered temperature monitoring system on an actual roadway. Applied Energy, 243, 313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.03.122
Nguyen, M. S., Yoon, Y.-J., & Kim, P. (2019). Enhanced broadband performance of magnetically coupled 2-DOF bistable energy harvester with secondary intrawell resonances. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 6(3), 521–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-019-00048-x
Zhong, Y., Zhao, H., Guo, Y., Rui, P., Shi, S., Zhang, W., et al. (2019). An easily assembled electromagnetic-triboelectric hybrid nanogenerator driven by magnetic coupling for fluid energy harvesting and self-powered flow monitoring in a smart home/city. Advanced Materials Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.201900741
Wang, P. H., Liu, R. Y., Ding, W. B., Zhang, P., Pan, L., Dai, G. Z., et al. (2018). Complementary electromagnetic-triboelectric active sensor for detecting multiple mechanical triggering. Advanced Functional Materials. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201705808
Kim, J. E., Lee, S., & Kim, Y. Y. (2019). Mathematical model development, experimental validation and design parameter study of a folded two-degree-of-freedom piezoelectric vibration energy harvester. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 6(5), 893–906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-019-00149-7
Wang, P. H., Du, H. J., Shen, S. N., Zhang, M. S., & Liu, B. (2012). Preparation and characterization of ZnO microcantilever for nanoactuation. Nanoscale Research Letters, 7, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276x-7-176
Zhao, L. C., Zou, H. X., Yan, G., Liu, F. R., Tan, T., Wei, K. X., et al. (2019). Magnetic coupling and flextensional amplification mechanisms for high-robustness ambient wind energy harvesting. Energy Conversion and Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.112166
Yang, Z. B., & Zu, J. (2016). Toward harvesting vibration energy from multiple directions by a nonlinear compressive-mode piezoelectric transducer. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 21(3), 1787–1791. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmech.2015.2459014
Zhao, H. B., Wei, X. X., Zhong, Y. M., & Wang, P. H. (2019). A direction self-tuning two-dimensional piezoelectric vibration energy harvester. Sensors. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010077
Liu, H., Hou, C., Lin, J., Li, Y., Shi, Q., Chen, T., et al. (2018). A non-resonant rotational electromagnetic energy harvester for low-frequency and irregular human motion. Applied Physics Letters. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5053945
Fan, K. Q., Cai, M. L., Liu, H. Y., & Zhang, Y. W. (2019). Capturing energy from ultra-low frequency vibrations and human motion through a monostable electromagnetic energy harvester. Energy, 169, 356–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.12.053
Wang, P. H., Tanaka, K., Sugiyama, S., Dai, X. H., Zhao, X. L., & Liu, J. Q. (2009). A micro electromagnetic low level vibration energy harvester based on MEMS technology. Microsystem Technologies, 15(6), 941–951. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-009-0827-0
Chen, J., & Wang, Y. (2019). A dual electromagnetic array with intrinsic frequency up-conversion for broadband vibrational energy harvesting. Applied Physics Letters. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5083910
Tao, K., Lye, S. W., Miao, J., Tang, L., & Hu, X. (2015). Out-of-plane electret-based MEMS energy harvester with the combined nonlinear effect from electrostatic force and a mechanical elastic stopper. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering. https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/25/10/104014
Gao, C., Gao, S., Liu, H., Jin, L., Lu, J., & Li, P. (2017). Optimization for output power and band width in out-of-plane vibration energy harvesters employing electrets theoretically, numerically and experimentally. Microsystem Technologies, 23(12), 5759–5769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3408-7
Xu, M., Zhao, T., Wang, C., Zhang, S. L., Li, Z., Pan, X., et al. (2019). High power density tower-like triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting arbitrary directional water wave energy. ACS Nano, 13(2), 1932–1939. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b08274
Wang, P. H., Pan, L., Wang, J. Y., Xu, M. Y., Dai, G. Z., Zou, H. Y., et al. (2018). An ultra-low-friction triboelectric-electromagnetic hybrid nanogenerator for rotation energy harvesting and self-powered wind speed sensor. ACS Nano, 12(9), 9433–9440. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b04654
Xu, M. Y., Wang, P. H., Wang, Y. C., Zhang, S. L., Wang, A. C., Zhang, C. L., et al. (2018). A soft and robust spring based triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting arbitrary directional vibration energy and self-powered vibration sensing. Advanced Energy Materials. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201702432
Zou, H. Y., Zhang, Y., Guo, L. T., Wang, P. H., He, X., Dai, G. Z., et al. (2019). Quantifying the triboelectric series. Nature Communications. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09461-x
Fan, F. R., Tian, Z. Q., & Wang, Z. L. (2012). Flexible triboelectric generator! Nano Energy, 1(2), 328–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2012.01.004
Wang, Z. L., & Wang, A. C. (2019). On the origin of contact-electrification. Materials Today, 30, 34–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2019.05.016
Chen, R., Ren, L., Xia, H., Yuan, X., & Liu, X. (2015). Energy harvesting performance of a dandelion-like multi-directional piezoelectric vibration energy harvester. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 230, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2015.03.038
Fan, K., Chang, J., Pedrycz, W., Liu, Z., & Zhu, Y. (2015). A nonlinear piezoelectric energy harvester for various mechanical motions. Applied Physics Letters. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4922212
Deng, H., Du, Y., Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Ma, M., & Zhong, X. (2018). A multimodal and multidirectional vibrational energy harvester using a double-branched beam. Applied Physics Letters. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5024567
Wang, D., Lu, H., Deng, L., & Zhang, D. (2019). An H-shaped two-dimensional piezoelectric vibration energy harvester. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics. https://doi.org/10.7567/1347-4065/ab4074
Yang, Y. W., Wu, H., & Soh, C. K. (2015). Experiment and modeling of a two-dimensional piezoelectric energy harvester. Smart Materials and Structures. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/24/12/125011
Zhao, N., Yang, J., Yu, Q., Zhao, J., Liu, J., Wen, Y., et al. (2016). Three-dimensional piezoelectric vibration energy harvester using spiral-shaped beam with triple operating frequencies. Review of Scientific Instruments, 87(1), 015003. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4940417
Zhang, H., Jiang, S., & He, X. (2017). Impact-based piezoelectric energy harvester for multidimensional, low-level, broadband, and low-frequency vibrations. Applied Physics Letters. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4984895
Wang, P., Liu, X., Zhao, H., Zhang, W., Zhang, X., Zhong, Y., et al. (2019). A two-dimensional energy harvester with radially distributed piezoelectric array for vibration with arbitrary in-plane directions. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 30(7), 1094–1104. https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389x19828820
Mei, J., & Li, L. (2015). Double-wall piezoelectric cylindrical energy harvester. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 233, 405–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2015.07.022
Gratuze, M., Alameh, A. H., & Nabki, F. (2019). Design of the squared daisy: a multi-mode energy harvester, with reduced variability and a non-linear frequency response. Sensors (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/s19153247
Zhu, Y., Zu, J., & Su, W. (2013). Broadband energy harvesting through a piezoelectric beam subjected to dynamic compressive loading. Smart Materials and Structures. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/22/4/045007
Wang, P., & Du, H. (2015). ZnO thin film piezoelectric MEMS vibration energy harvesters with two piezoelectric elements for higher output performance. Review of Scientific Instruments, 86(7), 075002. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4923456
Liu, H., Tay, C. J., Quan, C., Kobayashi, T., & Lee, C. (2011). Piezoelectric MEMS energy harvester for low-frequency vibrations with wideband operation range and steadily increased output power. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 20(5), 1131–1142. https://doi.org/10.1109/jmems.2011.2162488
Chen, Y., & Yan, Z. (2020). Nonlinear analysis of axially loaded piezoelectric energy harvesters with flexoelectricity. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105473
Lin, Z. M., Chen, J., Li, X. S., Li, J., Liu, J., Awais, Q., et al. (2016). Broadband and three-dimensional vibration energy harvesting by a non-linear magnetoelectric generator. Applied Physics Letters. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4972188
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61671017), Excellent Youth Talent Support Program in Colleges and Universities of Anhui Province in China (gxyqZD2018004), Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Higher Education Institution of China (KJ2019A0016, KJ2016A787), Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (1908085MF198, 1508085ME72), Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Pulsed Power Laser Technology (No. SKL2018KF04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, X., Zhao, H., Yu, J. et al. A Tower-Shaped Three-Dimensional Piezoelectric Energy Harvester for Low-Level and Low-Frequency Vibration. Int. J. of Precis. Eng. and Manuf.-Green Tech. 8, 1537–1550 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00281-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00281-9