Abstract
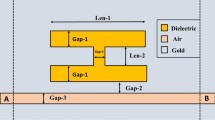
A metal–insulator–metal (MIM) waveguide coupled with two unequal vertical rectangular cavities optimized for high sensitivity is proposed in this study. Due to the interaction of the continuum and the discrete state in the waveguide mode, a Fano like profile is obtained in the transmission spectra, the shift of which is utilized to identify the material under sensing. In order to guarantee the maximum device performance, an optimization technique is imposed on the structural parameters, resulting in a maximum sensitivity of 2625.87 nm/RIU and figure of merit (FOM) of 26.04. The sensor has been exploited to determine the human blood group by using the refractive index model proposed for different blood groups A, B, and O. Furthermore, this structure can also be used as a temperature sensor with the temperature sensitivity of \(-1.04 \, \hbox {nm}/^\circ \hbox {C}\). The excellent performance along with the blood sensing and temperature sensing capabilities of the device paves the way toward refractive index sensors that have not only been utilized in microchip processors but also a wide range of biomedical applications.















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424(6950):824–830
Butt MA, Khonina SN, Kazanskiy NL (2019) Plasmonic refractive index sensor based on M–I–M square ring resonator. In: 2018 international conference on computing, electronic and electrical engineering, ICE Cube 2018, January, pp 1–4
Danaie M, Shahzadi A (2019) Design of a high-resolution metal–insulator-metal plasmonic refractive index sensor based on a ring-shaped Si resonator. Plasmonics 14(6):1453–1465
Fano U (1961) Effects of configuration interaction on intensities and phase shifts. Phys Rev 124(6):1866–1878
Hassan MF, Hasan MM, Ahmed MI, Sagor RH (2020a) Numerical investigation of a plasmonic refractive index sensor based on rectangular MIM topology. In: Proceedings—2020 international seminar on intelligent technology and its application: humanification of reliable intelligent systems, ISITIA, 2020, pp 77–82
Hassan MF, Sagor RH, Tathfif I, Rashid KS, Radoan M (2020b) An optimized dielectric–metal–dielectric refractive index nanosensor. IEEE Sens J XX(XX):1
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constant of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6(12):4370–4379
Jung WK, Byun KM (2011) Fabrication of nanoscale plasmonic structures and their applications to photonic devices and biosensors. Biomed Eng Lett 1(3):153–162
Khani S, Danaie M, Rezaei P (2018) Realization of single-mode plasmonic bandpass filters using improved nanodisk resonators. Opt Commun 420(March):147–156
Li H, Lin L, Xie S (2000) Refractive index of human whole blood with different types in the visible and near-infrared ranges. Laser Tissue Interact XI Photochem Phototherm Photomech 3914:517
Lin X-S, Huang X-G (2008) Tooth-shaped plasmonic waveguide filters with nanometeric sizes. Opt Lett 33(23):2874
Liu Y, Zhou F, Yao B, Cao J, Mao Q (2013) High-extinction-ratio and low-insertion-loss plasmonic filter with coherent coupled nano-cavity array in a MIM waveguide. Plasmonics 8(2):1035–1041
Liu Z, Wei Y, Zhang Y, Zhu Z, Zhao E, Zhang Y, Yang J, Liu C, Yuan L (2016) Reflective-distributed SPR sensor based on twin-core fiber. Opt Commun 366:107–111
Lu H, Liu X, Wang L, Gong Y, Mao D (2011) Ultrafast all-optical switching in nanoplasmonic waveguide with Kerr nonlinear resonator. Opt Express 19(4):2910
Luk’Yanchuk B, Zheludev NI, Maier SA, Halas NJ, Nordlander P, Giessen H, Chong CT (2010) The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat Mater 9(9):707–715
Luo S, Li B, Xiong D, Zuo D, Wang X (2017) A high performance plasmonic sensor based on metal–insulator-metal waveguide coupled with a double-cavity structure. Plasmonics 12(2):223–227
Mohammad D, Behnam K (2018) Design of a label-free photonic crystal refractive index sensor for biomedical applications. Photon Nanostruct Fundam Appl 31(June):89–98
Nasirifar R, Danaie M, Dideban A (2019) Dual channel optical fiber refractive index sensor based on surface plasmon resonance. Optik 186(April):194–204
Pang S, Huo Y, Xie Y, Hao L (2016) Fano resonance in MIM waveguide structure with oblique rectangular cavity and its application in sensor. Opt Commun 381:409–413
Rahman-Zadeh F, Danaie M, Kaatuzian H (2019) Design of a highly sensitive photonic crystal refractive index sensor incorporating ring-shaped GaAs cavity. Opto Electron Rev 27(4):369–377
Rahmatiyar M, Afsahi M, Danaie M (2020a) Design of a refractive index plasmonic sensor based on a ring resonator coupled to a MIM waveguide containing tapered defects. Plasmonics 15(6):2169–2176
Rahmatiyar M, Danaie M, Afsahi M (2020b) Employment of cascaded coupled resonators for resolution enhancement in plasmonic refractive index sensors. Opt Quantum Electron 52(3):1–19
Rakibul Islam M, Moinul Islam Khan M, Mehjabin F, Alam Chowdhury J, Isla M (2020) Design of a fabrication friendly and highly sensitive surface plasmon resonance-based photonic crystal fiber biosensor. Results Phys 19:103501
Sharma AK, Jha R, Pattanaik HS, Mohr GJ (2009) Design considerations for surface plasmon resonance-based fiber-optic detection of human blood group. J Biomed Opt 14(6):064041
Wang L, Zeng YP, Wang ZY, Xia XP, Liang QQ (2018) A refractive index sensor based on an analogy T shaped metal–insulator–metal waveguide. Optik 172(June):1199–1204
Wen K, Yan L, Hu Y, Chen L, Lei L (2014a) A plasmonic wavelength-selected intersection structure. Plasmonics 9(3):685–690
Wen K, Yan L, Pan W, Luo B, Guo Z, Guo Y, Luo X (2014b) Electromagnetically induced transparency-like transmission in a compact side-coupled t-shaped resonator. J Lightwave Technol 32(9):1701–1707
Wu T, Liu Y, Yu Z, Peng Y, Shu C, Ye H (2014) The sensing characteristics of plasmonic waveguide with a ring resonator. Opt Express 22(7):7669
Xiao S, Liu L, Qiu M (2006) Resonator channel drop filters in a plasmon-polaritons metal. Opt Express 14(7):2932
Yahya M, Saghir MZ (2016) Empirical modelling to predict the refractive index of human blood. Phys Med Biol 61(4):1405–1415
Yan SB, Luo L, Xue CY, Zhang ZD (2015) A refractive index sensor based on a metal–insulator–metal waveguide-coupled ring resonator. Sensors (Switzerland) 15(11):29183–29191
Yang Q, Liu X, Guo F, Bai H, Zhang B, Li X, Tan Y, Zhang Z (2020) Multiple Fano resonance in MIM waveguide system with cross-shaped cavity. Optik 220:165163
Ye Y, Xu J, Huang B, Wu X, Zhang W, Wang X, Nikdast M, Wang Z, Liu W, Wang Z (2013a) 3-D mesh-based optical network-on-chip for multiprocessor system-on-chip. IEEE Trans Comput Aided Design Integr Circuits Syst 32(4):584–596
Ye Y, Xu J, Wu X, Zhang W, Wang X, Nikdast M, Wang Z, Liu W (2013b) System-level modeling and analysis of thermal effects in optical networks-on-chip. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr (VLSI) Syst 21(2):292–305
Yeh YL (2008) Real-time measurement of glucose concentration and average refractive index using a laser interferometer. Opt Lasers Eng 46(9):666–670
Yin Y, Qiu T, Li J, Chu PK (2012) Plasmonic nano-lasers. Nano Energy 1(1):25–41
Yue W, Wang Z, Yang Y, Chen L, Syed A, Wong K, Wang X (2012) Electron-beam lithography of gold nanostructures for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J Micromech Microeng 22(12):125007
Zafar R, Salim M (2015) Achievement of large normalized delay bandwidth product by exciting electromagnetic-induced transparency in plasmonic waveguide. IEEE J Quantum Electron 51(10):1–6
Zayats AV, Smolyaninov II, Maradudin AA (2005) Nano-optics of surface plasmon polaritons. Phys Rep 408(3–4):131–314
Zhan S, Peng Y, He Z, Li B, Chen Z, Xu H, Li H (2016) Tunable nanoplasmonic sensor based on the asymmetric degree of fano resonance in MDM waveguide. Nature Publishing Group, Berlin, pp 1–8
Zhang Z, Wang H, Zhang Z (2013) Fano resonance in a gear-shaped nanocavity of the metal–insulator–metal waveguide. Plasmonics 8:797–801
Zhang Y, Li S, Zhang X, Chen Y, Wang L, Zhang Y, Yu L (2016a) Evolution of Fano resonance based on symmetric/asymmetric plasmonic waveguide system and its application in nanosensor. Opt Commun 370:203–208
Zhang Z, Luo L, Xue C, Zhang W, Yan S (2016b) Fano resonance based on metal–insulator–metal waveguide-coupled double rectangular cavities for plasmonic nanosensors. Sensors (Switzerland) 16(5):22–24
Zhou J, Chen H, Zhang Z, Tang J, Cui J, Xue C, Yan S (2017) Transmission and refractive index sensing based on Fano resonance in MIM waveguide-coupled trapezoid cavity. AIP Adv 7(1):015020
Zou S, Wang F, Liang R, Xiao L, Hu M (2015) A nanoscale refractive index sensor based on asymmetric plasmonic waveguide with a ring resonator: a review. IEEE Sens J 15(2):646–650
Funding
No funding was received for this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sagor, R.H., Hassan, M.F., Yaseer, A.A. et al. Highly sensitive refractive index sensor optimized for blood group sensing utilizing the Fano resonance. Appl Nanosci 11, 521–534 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01622-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01622-5