Abstract
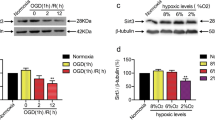
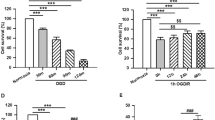
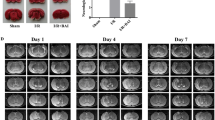
C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein-3 (CTRP3) had shown its angiogenesis and enhancement of mitochondrial biogenesis properties in the treatment of myocardial infarction, but its potential roles in cerebral ischemic stroke had not been fully understood. This study aimed to clarify the underlying mechanism of how CTRP3 regulated mitochondrial functions in hippocampal neuronal cells (HPPNCs) after oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD)/reoxygenation (R) treatment. Results showed that impeded CTRP3 expression and weakened viability were detected in OGD/R treated HPPNCs. CTRP3 showed its ability to enhance the viability and inhibited apoptosis of HPPNCs after OGD/R treatment and it could also promote the mitochondrial biogenesis and physiological functions. Silencing of PGC-1α partially abolished the protective function of CTRP3 on mitochondria and CTRP3 mediated the expression of PGC-1α via the AMPK/SIRT1-PGC-1α pathway. These findings provided information that CTRP3 prevented mitochondria from OGD/R injury through activating the AMPK/SIRT1-PGC-1α pathway. Our study suggested that CTRP3 might have the potential to become an emerging protective agent applied in the reperfusion treatment of ischemic stroke.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used during the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CTRP3:
-
C1q/tumour necrosis factor-related protein-3
- OGD/R:
-
Oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation
- HPPNCs:
-
Hippocampal neuronal cells
- PGC-1α:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- rtPA:
-
Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator
- NRF:
-
Nuclear respiratory factors
- TFAM:
-
Gene encoding transcription factor A
- SIRT1:
-
Sirtuin 1
- AMPK:
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- CTRP3:
-
C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein 3
References
Feigin VL, Krishnamurthi RV, Parmar P, Norrving B, Mensah GA, Bennett DA, Barker-Collo S, Moran AE, Sacco RL, Truelsen T, Davis S, Pandian JD, Naghavi M, Forouzanfar MH, Nguyen G, Johnson CO, Vos T, Meretoja A, Murray CJ, Roth GA (2015) Update on the global burden of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in 1990–2013: tthe GBD 2013 study. Neuroepidemiology 45(3):161–176. https://doi.org/10.1159/000441085
Shi L, Rocha M, Leak RK, Zhao J, Bhatia TN, Mu H, Wei Z, Yu F, Weiner SL, Ma F (2018) A new era for stroke therapy: integrating neurovascular protection with optimal reperfusion. 38(12):2073–2091. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678x18798162
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH, Iadecola C (2010) The science of stroke: mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 67(2):181–198. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2010.07.002
Becker BF (1993) Towards the physiological function of uric acid. Free Radic Biol Med 14(6):615–631. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0891-5849(93)90143-i
Shekhar S, Cunningham MW, Pabbidi MR, Wang S, Booz GW, Fan F (2018) Targeting vascular inflammation in ischemic stroke: recent developments on novel immunomodulatory approaches. Eur J Pharmacol 833:531–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.06.028
Zou Y, Hu J, Huang W, Ye S, Han F, Du J, Shao M, Guo R, Lin J, Zhao Y, Xiong Y, Wang X (2020) Non-mitogenic fibroblast growth factor 1 enhanced angiogenesis following ischemic stroke by regulating the sphingosine-1-phosphate 1 pathway. Front Pharmacol 11:59. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00059
Yang JL, Mukda S, Chen SD (2018) Diverse roles of mitochondria in ischemic stroke. Redox Biol 16:263–275. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.03.002
Niizuma K, Yoshioka H, Chen H, Kim GS, Jung JE, Katsu M, Okami N, Chan PH (2010) Mitochondrial and apoptotic neuronal death signaling pathways in cerebral ischemia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802(1):92–99. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.09.002
Ham PB 3, Raju R (2017) Mitochondrial function in hypoxic ischemic injury and influence of aging. Progress Neurobiol 157:92–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.06.006
Russell LK, Mansfield CM, Lehman JJ, Kovacs A, Courtois M, Saffitz JE, Medeiros DM, Valencik ML, McDonald JA, Kelly DP (2004) Cardiac-specific induction of the transcriptional coactivator peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and reversible cardiomyopathy in a developmental stage-dependent manner. Circ Res 94(4):525–533. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.res.0000117088.36577.eb
Scarpulla RC (2008) Transcriptional paradigms in mammalian mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Physiol Rev 88(2):611–638. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00025.2007
Chuang YC, Chen SD (2019) Sirtuin 1 regulates mitochondrial biogenesis and provides an endogenous neuroprotective mechanism against seizure-induced neuronal cell death in the hippocampus following status epilepticus. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143588
Huang B, Cheng X, Wang D, Peng M, Xue Z, Da Y, Zhang N, Yao Z, Li M, Xu A, Zhang R (2014) Adiponectin promotes pancreatic cancer progression by inhibiting apoptosis via the activation of AMPK/Sirt1/PGC-1α signaling. Oncotarget 5(13):4732–4745. doi:https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.1963
Lin JY, Kuo WW, Baskaran R, Kuo CH, Chen YA, Chen WS, Ho TJ, Day CH, Mahalakshmi B, Huang CY (2020) Swimming exercise stimulates IGF1/PI3K/Akt and AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1α survival signaling to suppress apoptosis and inflammation in aging hippocampus. Aging 12(8):6852–6864. doi:https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103046
Huang J, Liu W, Doycheva DM, Gamdzyk M, Lu W, Tang J, Zhang JH (2019) Ghrelin attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis via GHSR-1α/AMPK/Sirt1/PGC-1α/UCP2 pathway in a rat model of neonatal HIE. Free Radic Biol Med 141:322–337. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.07.001
Li Y, Wright GL, Peterson JM (2017) C1q/TNF-related protein 3 (CTRP3) function and regulation. Compr Physiol 7(3):863–878. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c160044
Yi W, Sun Y, Yuan Y, Lau WB, Zheng Q, Wang X, Wang Y, Shang X, Gao E, Koch WJ, Ma XL (2012) C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein-3, a newly identified adipokine, is a novel antiapoptotic, proangiogenic, and cardioprotective molecule in the ischemic mouse heart. Circulation 125(25):3159–3169. doi:https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.112.099937
Sun B, Ding Y, Jin X, Xu S, Zhang H (2019) Long non-coding RNA H19 promotes corneal neovascularization by targeting microRNA-29c. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20182394
Wang S, Zhou Y, Yang B, Li L, Yu S, Chen Y, Zhu J, Zhao Y (2016) C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein-3 attenuates brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage via AMPK-dependent pathway in rat. Front Cell Neurosci 10:237. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2016.00237
Yang LH, Xu YC, Zhang W (2020) Neuroprotective effect of CTRP3 overexpression against sevoflurane anesthesia-induced cognitive dysfunction in aged rats through activating AMPK/SIRT1 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(9):5091–5100. doi:https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202005_21202
Meng J, Wang DM, Luo LL (2019) CTRP3 acts as a novel regulator in depressive-like behavior associated inflammation and apoptosis by meditating p38 and JNK MAPK signaling. Biomed Pharmacother [Biomedecine pharmacotherapie] 120:109489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109489
Zhang CL, Feng H, Li L, Wang JY, Wu D, Hao YT, Wang Z, Zhang Y (1861) Wu LL (2017) globular CTRP3 promotes mitochondrial biogenesis in cardiomyocytes through AMPK/PGC-1α pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1:3085–3094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.10.022
Krämer CE, Wiechert W, Kohlheyer D (2016) Time-resolved, single-cell analysis of induced and programmed cell death via non-invasive propidium iodide and counterstain perfusion. Sci Rep 6:32104. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32104
Venegas V, Halberg MC (2012) Measurement of mitochondrial DNA copy number. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton, NJ) 837:327–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-504-6_22
Gill T, Levine AD (2013) Mitochondria-derived hydrogen peroxide selectively enhances T cell receptor-initiated signal transduction. J Biol Chem 288(36):26246–26255. doi:https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.476895
Dickinson BC, Chang CJ (2008) A targetable fluorescent probe for imaging hydrogen peroxide in the mitochondria of living cells. J Am Chem Soc 130(30):9638–9639. doi:https://doi.org/10.1021/ja802355u
Dirnagl U, Iadecola C, Moskowitz MA (1999) Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci 22(9):391–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-2236(99)01401-0
Juurlink BH, Hertz L (1993) Ischemia-induced death of astrocytes and neurons in primary culture: pitfalls in quantifying neuronal cell death. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 71(2):239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-3806(93)90175-a
Wang G, Wang T, Hu Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Li F, Liu W, Sun Y, Yu B, Kou J (2020) NMMHC IIA triggers neuronal autophagic cell death by promoting F-actin-dependent ATG9A trafficking in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Cell death Dis 11(6):428. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2639-1
Zhou X, Wang HY, Wu B, Cheng CY, Xiao W, Wang ZZ, Yang YY, Li P, Yang H (2017) Ginkgolide K attenuates neuronal injury after ischemic stroke by inhibiting mitochondrial fission and GSK-3β-dependent increases in mitochondrial membrane permeability. Oncotarget 8(27):44682–44693. doi:https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17967
Wei WY, Ma ZG, Zhang N, Xu SC, Yuan YP, Zeng XF, Tang QZ (2018) Overexpression of CTRP3 protects against sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol 476:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2018.04.006
Hou M, Liu J, Liu F, Liu K, Yu B (2014) C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein-3 protects mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia- and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med 33(1):97–104. doi:https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2013.1550
Fricker M, Tolkovsky AM, Borutaite V, Coleman M, Brown GC (2018) Neuronal cell death. Physiol Rev 98(2):813–880. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00011.2017
Chan PH (2001) Reactive oxygen radicals in signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J Cerebral Blood Flow Metab 21(1):2–14. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004647-200101000-00002
Ye Q, Chen C, Si E, Cai Y, Wang J, Huang W, Li D, Wang Y, Chen X (2017) Mitochondrial effects of PGC-1alpha silencing in MPP(+) treated human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Front Mol Neurosci 10:164. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2017.00164
Koh JH, Hancock CR, Terada S, Higashida K, Holloszy JO, Han DH (2017) PPARβ is essential for maintaining normal levels of PGC-1α and mitochondria and for the increase in muscle mitochondria induced by exercise. Cell Metabol 25(5):1176-1185.e1175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2017.04.029
Feng H, Wang JY, Zheng M, Zhang CL, An YM, Li L, Wu LL (2016) CTRP3 promotes energy production by inducing mitochondrial ROS and up-expression of PGC-1α in vascular smooth muscle cells. Exp Cell Res 341(2):177–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.02.001
Herzig S, Shaw RJ (2018) AMPK: guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19(2):121–135. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.95
Quan N, Wang L, Chen X, Luckett C, Cates C, Rousselle T, Zheng Y, Li J (2018) Sestrin2 prevents age-related intolerance to post myocardial infarction via AMPK/PGC-1α pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol 115:170–178. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.01.005
Guo X, Jiang Q, Tuccitto A, Chan D, Alqawlaq S, Won GJ, Sivak JM (2018) The AMPK-PGC-1α signaling axis regulates the astrocyte glutathione system to protect against oxidative and metabolic injury. Neurobiol Dis 113:59–69. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2018.02.004
Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z, Meziane H, Lerin C, Daussin F, Messadeq N, Milne J, Lambert P, Elliott P, Geny B, Laakso M, Puigserver P, Auwerx J (2006) Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Cell 127(6):1109–1122. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.013
Chandrasekaran K, Anjaneyulu M, Choi J, Kumar P, Salimian M, Ho CY, Russell JW (2019) Role of mitochondria in diabetic peripheral neuropathy: influencing the NAD(+)-dependent SIRT1-PGC-1α-TFAM pathway. Int Rev Neurobiol 145:177–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.irn.2019.04.002
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.G. and T.Q. performed the experiments, analyzed data and wrote the paper. W.W. conceived and designed the experiments and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the research in ensuring that the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, J., Qian, T. & Wang, W. CTRP3 Activates the AMPK/SIRT1-PGC-1α Pathway to Protect Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Functions in Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Neurochem Res 45, 3045–3058 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03152-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03152-6