Abstract
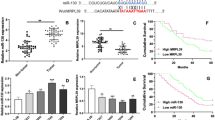
Circular RNA carboxypeptidase A4 (circCPA4) has been shown to involve in the tumorigenesis of glioma. However, the function and the molecular mechanism of circCPA4 in glioma remain inadequate. Levels of circCPA4 and microRNA (miR)-760 were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion were analyzed using MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide), colony formation, flow cytometry, and transwell assays, respectively. Western blot was used to detect the protein levels of matrix metallopeptidase 2 (MMP2), MMP9 and myocyte enhancer factor 2D (MEF2D). The interaction between miR-760 and circCPA4 or MEF2D was analyzed by the dual-luciferase reporter assay or RNA pull-down assay. In vivo experiments were conducted using murine xenograft models. We found circCPA4 was highly expressed in glioma, and circCPA4 knockdown suppressed tumor cell proliferative, migratory and invasive behaviors, but enhanced cell apoptosis and radiosensitivity in glioma. CircCPA4 directly bound to miR-760 to suppress its expression, and miR-760 inhibition reversed circCPA4 knockdown-mediated inhibition of cell malignant phenotypes in glioma. MEF2D was a target of miR-760, and miR-760 performed anti-tumor effects by targeting MEF2D in glioma cells. Meanwhile, we found circCPA4 could indirectly regulate MEF2D by sponging miR-760. Importantly, xenograft analysis suggested that circCPA4 knockdown impeded tumor growth in vivo via regulating miR-760 and MEF2D. In conclusion, circCPA4 knockdown suppressed cell malignant phenotypes in glioma via miR-760/MEF2D axis to impede the progression of glioma, suggesting potential therapeutic targets for glioma treatment.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
20 November 2020
The article titled "CircCPA4 Promotes the Malignant Phenotypes in Glioma via miR-760/MEF2D Axis", written by Yunjuan Zhang, Zengyan Cai, Jin Liang, Erqing Chai, Anqing Lu, Yinwu Shang was originally published electronically on the publisher's internet portal (currently SpringerLink) on 17 October 2020 with open access.
References
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Liao P, Vecchione-Koval T, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C et al (2017) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2010–2014. Neuro Oncol 19:v1–v88
Chen TC, Da Fonseca CO, Schönthal AH (2018) Intranasal perillyl alcohol for glioma therapy: molecular mechanisms and clinical development. Int J Mol Sci 19:3905
Holland EC (2000) Glioblastoma multiforme: the terminator. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6242–6244
Stupp R, Mason WP, Van Den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Eng J Med 352:987–996
Wang B, Wu Z-s, Wu Q (2017) CMIP promotes proliferation and metastasis in human glioma. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5340160
Rybak-Wolf A, Stottmeister C, Glazar P, Jens M, Pino N, Giusti S et al (2015) Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant, conserved, and dynamically expressed. Mol Cell 58:870–885
Ebbesen KK, Kjems J, Hansen TB (2016) Circular RNAs: identification, biogenesis and function. Biochim Biophys Acta 1859:163–168
Meng S, Zhou H, Feng Z, Xu Z, Tang Y, Li P et al (2017) CircRNA: functions and properties of a novel potential biomarker for cancer. Mol Cancer 16:94
Li J, Yang J, Zhou P, Le Y, Zhou C, Wang S et al (2015) Circular RNAs in cancer: novel insights into origins, properties, functions and implications. Am J Cancer Res 5:472
Cao S, Chen G, Yan L, Li L, Huang X (2018) Contribution of dysregulated circRNA_100876 to proliferation and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget Ther 11:7385
Xie H, Ren X, Xin S, Lan X, Lu G, Lin Y et al (2016) Emerging roles of circRNA_001569 targeting miR-145 in the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 7:26680
Shuai M, Hong J, Huang D, Zhang X, Tian Y (2018) Upregulation of circRNA_0000285 serves as a prognostic biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma and is involved in radiosensitivity. Oncol Lett 16:6495–6501
Jin P, Huang Y, Zhu P, Zou Y, Shao T, Wang O (2018) CircRNA circHIPK3 serves as a prognostic marker to promote glioma progression by regulating miR-654/IGF2BP3 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503:1570–1574
Shi F, Shi Z, Zhao Y, Tian J (2019) CircRNA hsa-circ-0014359 promotes glioma progression by regulating miR-153/PI3K signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 510:614–620
Yang P, Qiu Z, Jiang Y, Dong L, Yang W, Gu C et al (2016) Silencing of cZNF292 circular RNA suppresses human glioma tube formation via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget 7:63449
Peng H, Qin C, Zhang C, Su J, Xiao Q, Xiao Y et al (2019) CircCPA4 acts as a prognostic factor and regulates the proliferation and metastasis of glioma. J Cell Mol Med 23(10):6658–6665
Salzman J, Chen RE, Olsen MN, Wang PL, Brown PO (2013) Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet 9:e1003777
Peng Z, Liu C, Wu M (2018) New insights into long noncoding RNAs and their roles in glioma. Mol cancer 17:61
Jiang L-h, Sun D-w, Hou J-c, Ji Z-l (2018) CircRNA: a novel type of biomarker for cancer. Breast cancer 25:1–7
Chen J, Chen T, Zhu Y, Li Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y et al (2019) CircPTN sponges miR-145-5p/miR-330-5p to promote proliferation and stemness in glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:398
He Z, Ruan X, Liu X, Zheng J, Liu Y, Liu L et al (2019) FUS/circ_002136/miR-138-5p/SOX13 feedback loop regulates angiogenesis in Glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:65
Hao Z, Hu S, Liu Z, Song W, Zhao Y, Li M (2019) Circular RNAs: functions and prospects in Glioma. J Mol Neurosci 67:72–81
Li J, Sun D, Pu W, Wang J, Peng Y (2020) Circular RNAs in cancer: biogenesis, function, and clinical significance. Trends Cancer 6:319–336
Monk D, Mackay DJG, Eggermann T, Maher ER, Riccio A (2019) Genomic imprinting disorders: lessons on how genome, epigenome and environment interact. Nat Rev Genet 20:235–248
Xiong DD, Dang YW, Lin P, Wen DY, He RQ, Luo DZ et al (2018) A circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network identification for exploring underlying pathogenesis and therapy strategy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med 16:220
Zhou B, Yu JW (2017) A novel identified circular RNA, circRNA_010567, promotes myocardial fibrosis via suppressing miR-141 by targeting TGF-beta1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 487:769–775
Han ML, Wang F, Gu YT, Pei XH, Ge X, Guo GC et al (2016) MicroR-760 suppresses cancer stem cell subpopulation and breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis: by down-regulating NANOG. Biomed Pharmacother 80:304–310
Hu SH, Wang CH, Huang ZJ, Liu F, Xu CW, Li XL et al (2016) miR-760 mediates chemoresistance through inhibition of epithelial mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20:5002–5008
Tian T, Fu X, Lu J, Ruan Z, Nan K, Yao Y et al (2018) MicroRNA-760 inhibits doxorubicin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating Notch1/Hes1-PTEN/Akt signaling pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 32:e22167
Zhu L, Xue F, Cui Y, Liu S, Li G, Li J et al (2019) miR-155-5p and miR-760 mediate radiation therapy suppressed malignancy of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Biofactors 45:393–400
Li Q, Lu J, Xia J, Wen M, Wang C (2019) Long non-coding RNA LOC730100 enhances proliferation and invasion of glioma cells through competitively sponging miR-760 from FOXA1 mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 512:558–563
McKinsey TA, Zhang CL, Olson EN (2002) MEF2: a calcium-dependent regulator of cell division, differentiation and death. Trends Biochem Sci 27:40–47
Song Z, Feng C, Lu Y, Gao Y, Lin Y, Dong C (2017) Overexpression and biological function of MEF2D in human pancreatic cancer. Am J Transl Res 9:4836–4847
Xu K, Zhao YC (2016) MEF2D/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway regulates the proliferation of gastric cancer cells and is regulated by microRNA-19. Tumour Biol 37:9059–9069
Yu H, Sun H, Bai Y, Han J, Liu G, Liu Y et al (2015) MEF2D overexpression contributes to the progression of osteosarcoma. Gene 563:130–135
Feng L, He M, Rao M, Diao J, Zhu Y (2019) Long noncoding RNA DLEU1 aggravates glioma progression via the miR-421/MEF2D axis. Onco Targets Ther 12:5405–5414
Liu L, Cui S, Zhang R, Shi Y, Luo L (2017) MiR-421 inhibits the malignant phenotype in glioma by directly targeting MEF2D. Am J Cancer Res 7:857
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised: The article was originally published in SpringerLink with open access. With the author(s)’ decision to step back from Open Choice, the copyright of the article changed on 7th November 2020 to © Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Cai, Z., Liang, J. et al. CircCPA4 Promotes the Malignant Phenotypes in Glioma via miR-760/MEF2D Axis. Neurochem Res 45, 2903–2913 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03139-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03139-3