Abstract
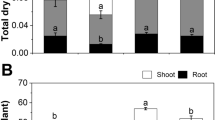
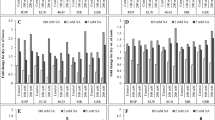
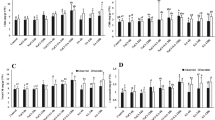
At present plants continuously exposed to salinity stress due to the challenging environment that has reduced the crop growth and productivity worldwide. Application of phytohormones by using seed priming method emerges as one of the most reliable and cost effective to alleviate the toxic effect of salinity stress. In this study, we evaluate the effect of seed-primed salicylic acid (SA) to reduce the adverse effect of different salt concentrations (0, 100, 200, and 300 mM NaCl) in pea (Pisum sativum L.) seedlings. After seedling emergence, percent seed germination was calculated; however, after 60 days; plants were sampled for studying the growth and photosynthetic traits, lipid peroxidation level, antioxidant activities, ions accumulation, and its sequestration. The results depicted that salinity treatments hampered overall growth performance and induced oxidative stress in a dose-dependent manner. Salinity also has negatively influence on ion accumulation as Na+ ion increased while K+ ion decreased. On the other hand, seed priming with SA significantly reduced the salinity-induced effects on the overall performance of plants, including growth and photosynthetic attributes. SA alleviated the adverse effect of salinity even at higher salinity level by inducing enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant systems, soluble sugars, and proline accumulation, and regulating ion homeostasis along with up-regulation of Na+/H+ antiporters (SOS1 and NHX1). Thus, seed priming with SA shows a comprehensive role in mitigation of salinity stress and can be used as a model for promising salinity tolerant cultivation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo-Doma A, Edrees S, Abdel-Aziz SH (2016) The effect of mycorrhiza growth and expression of some genes in barley. Egypt J Genet Cytol 40:301–313. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejgc.2011.10794
Achard P, Cheng H, De Grauwe L, Decat J, Schoutteten H, Moritz T, Van Der Straeten D, Peng J, Harberd NP (2006) Integration of plant responses to environmentally activated phytohormonal signal. Science 311:91–94
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Afzal I, Basra S, Iqbal A (2005) The effect of seed soaking with plant growth regulators on seedling vigor of wheat under salinity stress. J Stress Physiol Biochem 1:6–14
Ahanger MA, Agarwal RM (2017) Salinity stress induced alterations in antioxidant metabolism and nitrogen assimilation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) as influenced by potassium supplementation. Plant Physiol Biochem 115:449–460
Ahanger MA, Aziz U, Alsahli AA, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2019) Influence of exogenous salicylic acid and nitric oxide on growth, photosynthesis, and ascorbate-glutathione cycle in salt stressed Vigna angularis. Biomolecules 10:42. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010042
Albaladejo I, Meco V, Plasencia F, Flores FB, Bolarin MC, Egea I (2017) Unravelling the strategies used by the wild tomato species Solanum pennellii to confront salt stress: from leaf anatomical adaptations to molecular responses. Environ Exp Bot 135:1–12
Anjum NA, Sofo A, Scopa A, Roychoudhury A, Gill SS, Iqbal M et al (2015) Lipids and proteins—major targets of oxidative modifications in abiotic stressed plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:4099–4121
Arias C, Serrat X, Moysset L, Perissé P, Nogués S (2018) Morphophysiological responses of alamo switchgrass during germination and early seedling stage under salinity or water stress conditions. Bioenergy Res 11:677–688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-018-9930-3
Ayaz FA, Kadioglu A, Turgut R (2000) Water stress effects on the content of low molecular weight carbohydrates and phenolic acids in Ctenanthe setosa (Rose.) Eichler. Can J Plant Sci 80:373–378
Bates LS, Wadern RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid estimation of free proline for water stress determination. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Blois MS (1958) Antioxidant determinations by the use of a stable free radical. Nature 181:1199–1200
Boukraâ D, Benabdelli K, Belabid L, Bennabi F (2013) Effect of salinity on chickpea seed germination pre-treated with salicylic acid. Sci J Biol Sci 2:86–93
Cabot C, Sibole JV, Barceló J, Poschenrieder C (2014) Lessons from crop plants struggling with salinity. Plant Sci 226:2–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.04.013
Chawla S, Jain S, Jain V (2013) Salinity induced oxidative stress and antioxidant system in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive cultivars of rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 22:27–34
Chen C, Wang C, Liu Z, Liu X, Zou L, Shi J, Chen S, Chen J, Tan M (2018) Variations in physiology and multiple bioactive constituents under salt stress provide insight into the quality evaluation of Apocyni Veneti Folium. Int J Mol Sci 19:3042
Coskun D, Britto DT, Jean YK, Kabir I, Tolay I, Torun AA et al (2013) K+ efflux and retention in response to NaCl stress do not predict salt tolerance in contrasting genotypes of rice (Oryza sativa L.). PLoS ONE 8:e57767. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057767
Dantas BF, De Sá RL, Aragão CA (2007) Germination; initial growth and cotyledon protein content of bean cultivars under salinity stress. Rev Bras Sementes 29:106–110
Deinlein U, Stephan AB, Horie T, Luo W, Xu GH, Schroeder JI (2014) Plant salt-tolerance mechanisms. Trends Plant Sci 19:371–379
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L (2010) MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 15:573–581
El-Tayeb MA (2005) Response of barley grains to the interactive effect of salinity and salicylic acid. Plant Growth Regul 45:215–224
Farhangi-Abriz S, Ghassemi-Golezani K (2018) How can salicylic acid and jasmonic acid mitigate salt toxicity in soybean plants? Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:1010–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.070
Forghani AH, Almodares A, Ehsanpour AA (2020) The role of gibberellic acid and paclobutrazol on oxidative stress responses induced by in vitro salt stress in sweet sorghum. Russ J Plant Physiol 67:555–563
Foti C, Khah EM, Pavli OI (2019) Germination profiling of lentil genotypes subjected to salinity stress. Plant Biol 21:481–486. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.12714
Foyer CH, Halliwell B (1976) The presence of glutathione and glutathione reductase in chloroplasts: a proposed role in ascorbic acid metabolism. Planta 133:21–25
Garg N, Bharti A (2018) Salicylic acid improves arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis, and chickpea growth and yield by modulating carbohydrate metabolism under salt stress. Mycorrhiza 28:727–746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-018-0856-6
Ghassemi-Golezani K, Nikpour-Rashidabad N (2017) Seed pretreatment and salt tolerance of dill: osmolyte accumulation, antioxidant enzymes activities and essence production. Biocat Agric biotechnol 12:30–35
Giannopotitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutase in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Gunes A, Anal A, Alpaslan M, Eraslan F, Bagci EG, Cick N (2007) Salicylic acid induced changes on some physiological parameters symptomatic for oxidative stress and mineral nutrition in maize (Zea mays L.) grown under salinity. J Plant Physiol 164:728–736
Gupta B, Huang B (2014) Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants: physiological, biochemical, and molecular characterization. Int J Genom. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/701596
Hamid M, Ashraf MY, Rehman KU, Arshad M (2008) Influence of salicylic acid seed priming on growth and some biochemical attributes on wheat growth under saline conditions. Pak J Bot 40:361–367
Hao JH, Dong CJ, Zhang ZG, Wang XL, Shang QM (2012) Insights into salicylic acid responses in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) cotyledons based on a comparative proteomic analysis. Plant Sci 187:69–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.01.001
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Fujita M (2013) Plant response to salt stress and role of exogenous protectants to mitigate salt-induced damages. In: Ahmad P, Azooz MM, Prasad MNV (eds) Ecophysiology and responses of plants under salt stress. Springer, New York, pp 25–87
Homme PM, Gonalez B, Billard J (1992) Carbohydrate content, fructan and sucrose enzyme activities in roots, stubble and leaves of rye grass (Lolium perenne L.) as affected by source and sink modification after cutting. J Plant Physiol 140:282–291
Husen A, Iqbal M, Sohrab SS et al (2018) Salicylic acid alleviates salinity-caused damage to foliar functions, plant growth and antioxidant system in Ethiopian mustard (Brassica carinata A. Br.). Agric Food Secur 7:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40066-018-0194-0
Hussein M, Nadia EL, Gereadly HM, EL-Desuki M (2006) Role of puterscine in resistance to salinity of pea plants (Pisum sativum L.). J Appl Sci Res 2:598–604
Isayenkov SV, Maathuis FJ (2019) Plant salinity stress: many unanswered questions remain. Front Plant Sci 10:80
Jayakannan M, Bose J, Babourina O, Rengel Z, Shabala S (2013) Salicylic acid improves salinity tolerance in Arabidopsis by restoring membrane potential and preventing salt-induced K(+) loss via a GORK channel. J Exp Bot 64:2255–2268. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert085
Jini D, Joseph B (2017) Physiological mechanism of salicylic acid for alleviation of salt stress in rice. Rice Sci 24:97–108
Kang HM, Saltveit ME (2002) Antioxidant enzymes and DPPH-radical scavenging activity in chilled and heat shocked rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings radicles. J Agric Food Chem 50:513–518
Katschnig D, Bliek T, Rozema J, Schat H (2015) Constitutive high-level SOS1 expression and absence of HKT1; 1 expression in the salt-accumulating halophyte Salicornia dolichostachya. Plant Sci 234:144–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.02.011
Khan MI, Asgher M, Khan NA (2014) Alleviation of salt-induced photosynthesis and growth inhibition by salicylic acid involves glycinebetaine and ethylene in mungbean (Vigna radiata L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 80:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.03.026
Khodary SEA (2004) Effect of salicylic acid on the growth, photosynthesis and carbohydrate metabolism in salt stressed maize plants. Int J Agric Biol 6:5–8
Kirk JTO, Allen RL (1965) Dependence of chloroplast pigments synthesis on protein synthetic effects on actilione. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 27:523–530
Kováčik J, Grúz J, Bačkor M, Strnad M, Repčák M (2009) Salicylic acid-induced changes to growth and phenolic metabolism in Matricaria chamomilla plants. Plant Cell Rep 28:135–143
Li T, Hu Y, Du X, Tang H, Shen C, Wu J (2014) Salicylic acid alleviates the adverse effects of salt stress in Torreya grandis cv. Merrillii seedlings by activating photosynthesis and enhancing antioxidant systems. PLoS ONE 9:109492
Lin J, Wang Y, Sun S, Mu C, Yan X (2017) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth, photosynthesis and photosynthetic pigments of Leymus chinensis seedlings under salt alkali stress and nitrogen deposition. Sci Total Environ 576:234–241
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) The original method. J Biol Chem 193:265
Machado RMA, Serralheiro RP (2017) Soil salinity: effect on vegetable crop growth, management practices to prevent and mitigate soil salinization. Horticulturae 3:30
Maehly A, Chance B (1954) The assay of catalases and peroxidases. In: Methods of biochemical analysis, pp 357–424
Magome H, Yamaguchi S, Hanada A, Kamiya Y, Oda K (2008) The DDF1 transcriptional activator upregulates expression of a gibberellin-deactivating gene, GA2ox7, under high-salinity stress in Arabidopsis. Plant J 56:613–626
Matthews JSA, Vialet-Chabrand SRM, Lawson T (2017) Diurnal variation in gas exchange: the balance between carbon fixation and water loss. Plant Physiol 174:614–623
McDonald S, Prenzler PD, Autolovich M, Robards K (2001) Phenolic content and antioxidant activity of olive extracts. Food Chem 73:73–84
Mimouni H, Wasti S, Manaa A, Gharbi E, Chalh A, Vandoorne B, Lutts S, Ahmed HB (2016) Does salicylic acid (SA) improve tolerance to salt stress in plants? A study of SA effects on tomato plant growth, water dynamics, photosynthesis, and biochemical parameters. OMICS 20:180–190. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2015.0161
Misra N, Misra R, Mariam A, Yusuf K, Yusuf L (2014) Salicylic acid alters antioxidant and phenolics metabolism in Catharanthus roseus grown under salinity stress. Afr J Tradit Compl Altern Med 11:118–125. https://doi.org/10.4314/ajtcam.v11i5.19
Miura K, Okamoto H, Okuma E, Shiba H, Kamada H, Hasegawa PM, Murata Y (2013) SIZ1 deficiency causes reduced stomatal aperture and enhanced drought tolerance via controlling salicylic acid induced accumulation of reactive oxygen species in Arabidopsis. Plant J 73:91–104
Mukerji KG (2004) Fruit and vegetable diseases. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Hingham, p 145
Munns R, James RA, Xu B, Athman A, Conn SJ, Jordans C et al (2012) Wheat grain yield on saline soils is improved by an ancestral Na+ transporter gene. Nat Biotechnol 30:360–364
Mutlu S, Atici Ö, Nalbantoglu B (2009) Effects of salicylic acid and salinity on apoplastic antioxidant enzymes in two wheat cultivars differing in salt tolerance. Biol Plant 53:334–338
NakanoY AK (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Nazar R, Umar S, Khan NA, Sareer O (2015) Salicylic acid supplementation improves photosynthesis and growth in mustard through changes in proline accumulation and ethylene formation under drought stress. S Afr J Bot 98:84–94
Nimir NEA, Lu S, Zhou G, Ma BL, Guo W, Wang Y (2014) Exogenous hormones alleviated salinity and temperature stresses on germination and early seedling growth of sweet sorghum. Agron J 106:2305–2315. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj13.0594
Noreen S, Ashraf M, Akram NA (2011) Does exogenous application of salicylic acid improve growth and some key physiological attributes in sunflower plants subjected to salt stress? J Appl Bot Food Qual 84:169–177
Oh DH, Leidi E, Zhang Q, Hwang SM, Li Y, Quintero FJ et al (2009) Loss of halophytism by interference with SOS1 expression. Plant Physiol 151:210–222
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay of lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Oukarroum A, Bussotti F, Goltsev V, Kalaji MH (2015) Correlation between reactive oxygen species production and photochemistry of photosystems I and II in Lemna gibba L. plants under salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 109:80–88
Panuccio MR, Jacobsen SE, Akhtar SS, Muscolo A (2014) Effect of saline water on seed germination and early seedling growth of the halophyte quinoa. AoB Plants 6:plu047. https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/plu047
Pérez-Labrada F, López-Vargas ER, Ortega-Ortiz H, Cadenas-Pliego G, Benavides-Mendoza A, Juárez-Maldonado A (2019) Responses of tomato plants under saline stress to foliar application of copper nanoparticles. Plants 8:151. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8060151
Pokorny J, Yanishieva N, Gordon MH (2001) Antioxidants. In: Food: Practical applications. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge, pp 16–18
Raskin I (1992) Role of salicylic acid in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 43:439–463
Romero-Aranda R, Soria T, Cuartero J (2001) Tomato plant water uptake and plant-water relationships under saline growth conditions. Plant Sci 160:65–72
Ryu H, Cho YG (2015) Plant hormones in salt stress tolerance. J Plant Biol 58:147–155
Sairam RK, Tyagi A (2004) Physiology and molecular biology of salinity stress tolerance in plants. Curr Sci 86:407–421
Shaki F, Maboud H, Ebrahimzadeh NV (2019) Effects of salicylic acid on hormonal cross talk, fatty acids profile, and ions homeostasis from salt-stressed safflower. J Plant Interact 14:340–346. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2019.1635660
Shakirova FM, Sakhabutdinova AR, Bezrukova MV, Fatkhutdinova RA, Fatkhutdinova DR (2003) Changes in the hormonal status of wheat seedlings induced by salicylic acid and salinity. Plant Sci 164:317–322
Shams M, Ekinci M, Ors S, Turan M, Agar G, Kul R, Yildirim E (2019) Nitric oxide mitigates salt stress effects of pepper seedlings by altering nutrient uptake, enzyme activity and osmolyte accumulation. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 25:1149–1161
Sharma A, Shahzad B, Rehman A, Bhardwaj R, Landi M, Zheng B (2019) Response of phenylpropanoid pathway and the role of polyphenols in plants under abiotic stress. Molecules 24:2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132452
Sharma A, Sidhu G, Araniti F, Bali AS, Shahzad B, Tripathi DK, Brestic M, Skalicky M, Landi M (2020) The role of salicylic acid in plants exposed to heavy metals. Molecules 25:540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030540
Shi Q, Bao Z, Zhu Z, Ying Q, Qian Q (2006) Effects of different treatments of salicylic acid on heat tolerance, chlorophyll fluorescence, and antioxidant enzyme activity in seedlings of Cucumis sativa L. Plant Grow Regul 48:127–135
Song SY, Chen Y, Chen J, Dai XY, Zhang WH (2011) Physiological mechanisms underlying OsNAC5-dependent tolerance of rice plants to abiotic stress. Planta 234:331–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1403-2
Stepien P, Klobus G (2006) Water relations and photosynthesis in Cucumis sativus L. leaves under salt stress. Biol Planta 50:610–616
Stevens J, Senaratna T, Sivasithamparam K (2006) Salicylic acid induces salinity tolerance in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum cv. Roma): associated changes in gas exchange, water relations and membrane stabilisation. Plant Growth Regul 49:77–83
Su F, Jacquard C, Villaume S, Michel J, Rabenoelina F, Clement C, Barka EA, Dhondt-Cordelier S, Vaillant-Gaveau N (2016) Burkholderia phytofirmans PsJN reduces impact of freezing temperatures on photosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 6:810
Sui N, Yang Z, Liu M, Wang B (2015) Identification and transcriptomic profiling of genes involved in increasing sugar content during salt stress in sweet sorghum leaves. BMC Genomics 16:534. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00007
Szalai G, Páldi E, Janda T (2005) Effect of salt stress on the endogenous salicylic acid content in maize (Zea mays L.) plants. Acta Biol Szeged 49:47–48
Taylor LP, Grotewold E (2005) Flavonoids as developmental regulators. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:317–323
Upchurch RG (2008) Fatty acid unsaturation, mobilization, and regulation in the response of plants to stress. Biotechnol Lett 30:967–977
Valifard M, Mohsenzadeh S, Kholdebarin B, Rowshan V (2014) Effects of salt stress on volatile compounds, total phenolic content and antioxidant activities of Salvia mirzayanii. S Afr J Bot 93:92–97
Wani SH, Kumar V, Shriram V, Sah SK (2016) Phytohormones and their metabolic engineering for abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Crop J 4:162–176
West G, Inzé D, Beemster GTS (2004) Cell cycle modulation in the response of the primary root of Arabidopsis to salt stress. Plant Physiol 135:1050–1058. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.040022
Whistler RL, Wolform ML, BeMiller JN (1962) Anthrone colorimetric method. In: Methods in carbohydrate chemistry 1. Academic Press, London, p 384
Wiciarz M, Niewiadomska E, Kruk J (2017) Effects of salt stress on low molecular antioxidants and redox state of plastoquinone and P700 in Arabidopsis thaliana (glycophyte) and Eutrema salsugineum (halophyte). Photosynthetica 56:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-017-0733-0
Yang L, Li B, Zheng X, Li J, Yang M, Dong X, He G, An C, Deng XW (2015) Salicylic acid biosynthesis is enhanced and contributes to increased biotrophic pathogen resistance in Arabidopsis hybrids. Nat Commun 6:7309
Yu L, Nie J, Cao C, Jin Y, Yan M, Wang F et al (2010) Phosphatidic acid mediates salt stress response by regulation of MPK6 in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 188:762–773. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03422.x
Yücel NC, Heybet EH (2016) Salicylic acid and calcium treatments improves wheat vigor, lipids and phenolics under high salinity. Acta Chim Slov 63:738–746. https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2016.2449
Zahra S, Amin B, Ali VSM, Ali Y, Mehdi Y (2010) The salicylic acid effect on the tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum Mill.) sugar, protein and proline contents under salinity stress (NaCl). J Biophys Struct Biol 2:35–41
Zhang YM, Zhang HM, Liu ZH, Li HC, Guo XL, Li GL (2015) The wheat NHX antiporter gene TaNHX2 confers salt tolerance in transgenic alfalfa by increasing the retention capacity of intracellular potassium. Plant Mol Biol 87:317–327
Zhou Y, Tang N, Huang L, Zhao Y, Tang X, Wang K (2018) Effects of salt stress on plant growth, antioxidant capacity, glandular trichome density, and volatile exudates of Schizonepeta tenuifolia Briq. Int J Mol Sci 19:252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010252
Zou YN, Wu QS, Huang YM, Ni QD, He XH (2013) Mycorrhizal mediated lower proline accumulation in Poncirus trifoliata under water deficit derives from the integration of inhibition of proline synthesis with increase of proline degradation. PLoS ONE 8:e80568. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080568
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Researchers Supporting Project (RSP-2020/194), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The authors are grateful to the research division of the Integral University, Lucknow, for allotting manuscript number (MCN : IU/R&D/2020-MCN000947).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FA, AK, AS, and FA are involved in methodology, data curation, formal analysis, and investigation. AK, FA, MHS and SA contributed to conceptualization, validation, and formal analysis, and wrote and edited original draft and review.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, F., Kamal, A., Singh, A. et al. Salicylic Acid Modulates Antioxidant System, Defense Metabolites, and Expression of Salt Transporter Genes in Pisum sativum Under Salinity Stress. J Plant Growth Regul 41, 1905–1918 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10271-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10271-5