Abstract
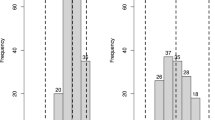
Knowledge on the genetics of maydis leaf blight (MLB) is crucial to breed the resistant maize cultivars to combat disease epidemics as a sustainable and cost-effective approach. The present investigation was framed to understand the genetics of MLB resistance in subtropical maize. Two contrasting genotypes CM119 (susceptible) and SC-7-2-1-2-6-1 (resistant) were used to generate six genetic populations, namely P1, P2, F1, F2, BC1P1 and BC1P2, and evaluated in three target environments for MLB resistance under artificial epiphytotic condition. The CM119 and SC-7-2-1-2-6-1 showed susceptible and resistant reactions with mean disease reaction of 3.89–3.98 and 1.88–2.00, respectively. The derived generations, namely F1, F2, BC1P1 and BC1P2 showed mean disease reaction of 2.15–2.28, 2.44–2.51, 2.19–2.24 and 2.22–2.28, respectively in the test locations. The segregating generations (F2: 0.35–0.37; BC1P1: 0.24–0.29 and BC1P2: 0.17–0.20) showed variation for MLB disease resistance over the parental and first filial generations (P1: 0.11–0.17; P2: 0.08–0.13 and F1: 0.12–0.14). The genetic analysis of MLB resistance revealed the nonallelic interactions of duplicate epistasis type across the test locations. Among the gene interactions, dominance × dominance [l] effect was predominant over additive × additive [i] and additive × dominance [j] effects. The segregation analysis and the prediction of the number of major loci revealed at least two major genes associated with MLB tolerance in subtropical maize. Our investigation paved the foundation for the improvement of subtropical maize germplasm of MLB resistance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal P. K., Mallikarjuna M. G. and Gupta H. S. 2018 Genetics and applied genomics of quality protein maize for food and nutritional security. In Biotechnologies of crop improvement, vol. 3, pp. 151–178. Springer, Cham.
Akbar W., Aslam M., Maqbool M. A., Ali M. and Arshad M. 2018 Inheritance pattern of mungbean yellow mosaic disease resistance and gene action for different traits in mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek) under protected and unprotected field conditions. Plant Breed. 137, 763–772.
Balint-Kurti P. J. and Carson M. L. 2006 Analysis of quantitative trait loci for resistance to southern leaf blight in juvenile maize. Phytopathology 96, 221–225.
Balint-Kurti P. J., Krakowsky M. D., Jines M. P., Robertson L. A., Molnár T. L., Goodman M. M. and Holland J. B. 2006 Identification of quantitative trait loci for resistance to southern leaf blight and days to anthesis in a maize recombinant inbred line population. Phytopathology 96, 1067–1071.
Balint-Kurti P. J., Zwonitzer J. C., Wisser R. J., Carson M. L., Oropeza-Rosas M. A., Holland J. B. and Szalma S. J. 2007 Precise mapping of quantitative trait loci for resistance to southern leaf blight, caused by Cochliobolus heterostrophus race O, and flowering time using advanced intercross maize lines. Genetics 176, 645–657.
Belcher A. R., Zwonitzer J. C., Cruz J. S., Krakowsky M. D., Chung C. L., Nelson R. et al. 2012 Analysis of quantitative disease resistance to southern leaf blight and multiple disease resistance in maize, using near-isogenic lines. Theor. Appl. Genet. 124, 433–445.
Burnette D. C. and White D. G. 1985 Inheritance of resistance to Bipolaris maydis race O in crosses derived from nine resistant inbred lines of maize. Phytopathology 75, 1195–1200.
Cai H. W., Gao Z. S., Yuyama N. and Ogawa N. 2003 Identification of AFLP markers closely linked to the rhm gene for resistance to Southern corn leaf bight in maize by using bulked segregant analysis. Mol. Genet. Genomics 269, 299–303.
Carson M. L., Stuber C. W. and Senior M. L. 2004 Identification and mapping of quantitative trait loci conditioning resistance to southern leaf blight of maize caused by Cochliobolus heterostrophus race O. Phytopathology 94, 862–867.
Castle W. E. 1921 An improved method of estimating the number of genetic factors concerned in cases of blending inheritance. Science 54, 223.
Cavalli L. L. 1952 A joint-scale test. In An analysis of linkage in quantitative inheritance (ed. E. C. R. Rieve and C. H. Waddington), pp. 135–144. HMSO, London.
Chang R. Y. and Peterson P. A. 1995 Genetic control of resistance to Bipolaris maydis: One gene or two genes? J. Hered. 86, 94–97.
Craig J. and Fajemisin J. M. 1969 Inheritance of chlorotic lesion resistance to Helminthosporium maydis in maize. Plant Dis. Rep. 53, 742–743.
Falconer D. and Mackay T. F. C. 1996 Introduction to quantitative genetics. Pearson Education, India.
Faluyi J. O. and Olorode O. 1984 Inheritance of resistance to Helminthosporium maydis blight in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 67, 341–344 .
Hayman B. I. 1958 The separation of epistatic from additive and dominance variation in generation means. Heredity 12, 371–390.
Hayman B. I. and Mather K. 1955 The description of genic interactions in continuous variation. Biometrics 11, 69–82.
Hettiarachchi K., Prasanna B. M., Rajan A., Singh O. N., Gowda K. T. P., Pant S. K. and Kumar S. 2009 Generation mean analysis of Turcicum leaf blight resistance in maize. Indian J. Genet. 69, 102–108.
Hooker A. L. 1972 Southern leaf blight of corn—Present status and future prospects. J. Environ. Qual. 1, 244–249.
Hooker A. L., Smith D. R., Lim S. M. and Beckett J. B. 1970 Reaction of corn seedlings with male-sterile cytoplasm to Helminthosporium maydis. Plant Dis. Report. 54, 708–712.
Jinks J. L. and Jones R. M. 1958 Estimation of the components of heterosis. Genetics 43, 223–234.
Kumar B., Hooda K. S., Gogoi R., Kumar V., Kumar S., Abhishek A. et al. 2016 Inheritance study and stable sources of maydis leaf blight (Cochliobolus heterostrophus) resistance in tropical maize germplasm. Cereal Res. Commun. 44, 424–434.
Kump K. L., Bradbury P. J., Wisser R. J., Buckler E. S., Belcher A. R., Oropeza-Rosas M. A. et al. 2011 Genome-wide association study of quantitative resistance to southern leaf blight in the maize nested association mapping population. Nat. Genet. 43, 163–168.
Lyimo H. J. F., Pratt R. C. and Mnyuku R. S. O. W. 2011 Heritability and gene effect estimates for components of partial resistance to grey leaf spot of maize by generation mean analysis. Plant Breed. 130, 633–639.
Mallikarjuna M. G., Nepolean T., Hossain F., Manjaiah K. M., Singh A. M. and Gupta H. S. 2014 Genetic variability and correlation of kernel micronutrients among exotic quality protein maize inbreds and their utility in breeding programme. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 74, 166–173.
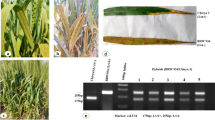
Manjunatha C., Gogoi R., Singh B., Jeevan B., Rai S. N. and Singh P. K. 2019 Phenotypic and physiological characterization of maize inbred lines resistant and susceptible to maydis leaf blight. Indian Phytopathol. 72, 217–224.
Mather K. and Jinks J. L. 1982 Introduction to biometrical genetics, 3rd edition. Chapman and Hall, London.
Misra A. P. 1979 Variability, physiological specialization and genetics of pathogenicity in grarninicolous Helminthosporia affecting cereal crops. Indian Phytopathol. 32, 1–22.
Pate J. B. and Harvey P. H. 1954 Studies on the inheritance of resistance in corn to Helminthosporium maydis leaf spot 1. Agron. J. 46, 442–445.
Payak M. M. and Sharma R. 1983 Disease rating scales in maize in India. In Techniques of scoring for resistance to diseases of maize in India, pp. 1–4. All India Co-ordinated Maize Improvement Project, New Delhi.
Poole N. F. and Arnaudin M. E. 2014 The role of fungicides for effective disease management in cereal crops. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 36, 1–11.
Prakash R. N., Zunjare R. U., Muthusamy V., Chand G., Kamboj M. C., Bhat J. S. and Hossain F. 2019 Genetic analysis of prolificacy in ‘Sikkim Primitive’–a prolific maize (Zea mays) landrace of northeastern Himalaya. Plant Breed. 138, 781–789.
Rai D., Kumar A., Kumar M and Prasad R. 2010 Field screening of maize genotypes against maydis leaf blight caused by Helminthosporiun maydis Nisicado and Miyake. Int. J. Plant Prot. 2, 265–266.
Sharma P., Punia M. S., Kamboj M. C. and Mehra R. 2017 Generation mean analysis of maydis leaf blight resistance in maize. Indian Phytopathol. 70, 302–306.
Sharma R. and Rai S. N. 2000 Assessment and quantitative analysis of losses due to Dreschlera maydis in maize. In Proceedings of international conference on integrated plant disease management for sustainable agriculture, pp. 246–248. Indian Phytopathological Society, New Delhi.
Sharma R. and Rai S. N. 2005 Evaluation of maize inbred lines and hybrids for resistance to maydis leaf blight. Indian Phytopathol. 58, 339–340.
Sharma R. C., Rai S. N., Mukherjee B. K. and Gupta N. P. 2003 Assessing potential of resistance source for the enhancement of resistance to Maydis leaf blight (Bipolaris maydis) in maize (Zea mays L.). Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 63, 33–36.
Shashikumar K. T., Pitchaimuthu M. and Rawal R. D. 2010 Generation mean analysis of resistance to downy mildew in adult muskmelon plants. Euphytica 173, 121–127.
Smith D. R. 1975 Expression of monogenic chlorotic-lesion resistance to Helminthosporium maydis in corn. Phytopathology 65, 1160–1165.
Sullenberger M. T, Jia M., Gao S. and Foolad M. R. 2018 Genetic analysis of late blight resistance in Solanum pimpinellifolium accession PI 270441: Heritability and response to selection. Plant Breed. 137, 89–96.
Thompson D. L. and Bergquist R. R. 1984 Inheritance of mature plant resistance to Helminthosporium maydis Race O in Maize 1. Crop Sci. 24, 807–811.
Ullstrup A. J. 1972 The impacts of the Southern corn leaf blight epidemics of 1970–1971. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 10, 37–50.
Warner J. N. 1952 A method for estimating heritability. Agron. J. 44, 427–430.
Wei J.-K. 1988 Pathological and physiological identification of race C of Bipolaris maydis in China. Phytopathology 78, 550.
Wright S. 1952 The genetics of quantitative variability. In Quantitative genetics (ed. E. C. R. Reever and C. H. Waddington), pp. 4–41. H. M. Stat Office, London.
Zaitlin D., DeMars S. and Ma Y. 1993 Linkage of rhm, a recessive gene for resistance to southern corn leaf blight, to RFLP marker loci in maize (Zea mays) seedlings. Genome 36, 555–564.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi and Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), New Delhi for their financial support. The authors graciously thank Dr S. N. Rai, CTO for his assistance in field experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Manoj Prasad
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeevan, B., Gogoi, R., Sharma, D. et al. Genetic analysis of maydis leaf blight resistance in subtropical maize (Zea mays L.) germplasm. J Genet 99, 89 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-020-01245-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-020-01245-3