Abstract
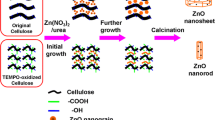
Phenol, considered as a stable and refractory organic pollutant, has posed an increasing threat to the environment and human health. Herein, the ZnO was regulated with nano-biochar (CCNC) derived from cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs). The CCNC/ZnO photocatalysts were fabricated via in situ precipitation and carbonization, in which CNCs served as both the templates and carbon source. Meanwhile, Zn2+ ions deposited on the surface of rod-like CNCs by electrostatic interaction. Subsequently, homogeneous dispersed ZnO nanoparticles were anchored onto the surface of CNCs, decreasing the ZnO nanoparticles size. As the CNCs transformed into CCNC, the resultant CCNC/ZnO photocatalysts demonstrated excellent degradation efficiency to phenol, corresponding to 99.8% within 90 min. Additionally, the CCNC/ZnO photocatalysts also displayed a satisfactory stability for five cycles without significant performance being decreased. The calculating and experimental results demonstrated that the conjugated graphitic structures of CCNC effectively reduced the band gap of ZnO from 3.26 to 2.96 eV. Besides, the CCNC remarkably promoted photogenerated electron-hole pairs separation and transfer, thereby improving the photodegradation efficiency for phenol. Furthermore, the efficiency for phenol photodegradation was comprehensively influenced by a combination of the ratio of photocatalyst, initial phenol concentration and catalyst dose, and pH value. This study broadened the application of CNCs in the field of photocatalysis, which provided a new perspective for the preparation of highly efficient photocatalysts using CNCs derived nano-biochar as a template and charge-transport pathway.
Graphic abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang AF, Ashaari Z, Lee SH, Tahir PM, Halis R (2019) Lignin-based copolymer adhesives for composite wood panels: a review. Int J Adhes Adhes 95:102408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2019.102408
Cai XX, Li J, Liu YG, Yan ZL, Tan XF, Liu SB, Zeng GM, Gu YL, Hu XJ, Jiang LH (2018) Titanium dioxide-coated biochar composites as adsorptive and photocatalytic degradation materials for the removal of aqueous organic pollutants. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 93:783–791. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5428
Cao SW, Low JX, Yu JG, Jaroniec M (2015) Polymeric photocatalysts based on graphitic carbon nitride. Adv Mater 27:2150–2176. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201500033
Chen DY, Zhu HG, Yang S, Li NJ, Xu QF, Li H, He JH, Lu JM (2016) Micro-nanocomposites in environmental management. Adv Mater 28:10443–10458. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201601486
Chen MX, Bao CZ, Hu DW, Jin X, Huang Q (2019) Facile and low-cost fabrication of ZnO/biochar nanocomposites from jute fibers for efficient and stable photodegradation of methylene blue dye. J Anal Appl Pyrol 139:319–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2019.03.009
Cheng S, Chen Q, Xia HY, Zhang LB, Peng JH, Lin G, Liao XF, Jiang X, Zhang Q (2018) Microwave one-pot production of ZnO/Fe3O4/activated carbon composite for organic dye removal and the pyrolysis exhaust recycle. J Clean Prod 188:900–910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.308
Comparelli R, Fanizza E, Curri ML, Cozzoli PD, Mascolo G, Agostiano A (2005) UV-induced photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes by organic-capped ZnO nanocrystals immobilized onto substrates. Appl Catal B Environ 60:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2004.07.011
Ding CX, Cai CY, Yin LX, Wu QL, Pan MZ, Mei CT (2019) Mechanically adaptive nanocomposites with cellulose nanocrystals: strainfield mapping with digital image correlation. Carbohyd Polym 211:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.098
Du MX, Du Y, Feng YB, Yang K, Lv XJ, Jiang N, Liu Y (2018) Facile preparation of BiOBr/cellulose composites by in situ synthesis and its enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible-light. Carbohyd Polym 195:393–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.04.092
Emad S, Elmolla MC (2010) Degradation of amoxicillin, ampicillin and cloxacillin antibiotics in aqueous solution by the UV/ZnO photocatalytic process. J Hazard Mater 173:445–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.07.035
Feng C, Chen ZY, Jiang JP, Hou J (2020) The photocatalytic phenol degradation mechanism of Ag-modified ZnO nanorods. J Mater Chem C 8:3000. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TC05010H
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Gao S, Cen WL, Li Q, Li JY, Lu YF, Wang HQ, Wu ZB (2018) A mild one-step method for enhancing optical absorption of amine-functionalized metal-organic frameworks. Appl Catal B Environ 227:190–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.01.007
Geng AB, Meng L, Han JQ, Zhong Q, Li MR, Han SG, Mei CT, Xu LJ, Tan L, Gan L (2018) Highly efficient visible-light photocatalyst based on cellulose derived carbon nanofiber/BiOBr composites. Cellulose 25:4133–4144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1851-y
Gu WT, Sevilla M, Magasinski A, Fuertes AB, Yushin G (2013) Sulfur-containing activated carbons with greatly reduced content of bottle neck pores for double-layer capacitors: a case study for pseudocapacitance detection. Energ Environ Sci 6:2465–2476. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ee41182f
Guido B, Silvia B, Carlo R, Laura A (2008) Technologies for the removal of phenol from fluid streams: a short review of recent developments. J Hazard Mater 160:265–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.03.045
Han J, Qiu W, Gao W (2010) Potential dissolution and photo-dissolution of ZnO thin films. J Hazard Mater 178:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.050
Jaramillo-Páeza C, Sánchez-Cid P, Navío JA, Hidalgo MC (2018) A comparative assessment of the UV-photocatalytic activities of ZnO synthesized by different routes. J Environ Chem Eng 6:7161–7171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.11.004
Kalantari E, Khalilzadeh MA, Zareyee D, Shokouhimehr M (2020) Catalytic degradation of organic dyes using green synthesized Fe3O4-cellulose-copper nanocomposites. J Mol Struct 1218:128488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128488
Kansal SK, Singh M, Sud D (2007) Studies on photodegradation of two commercial dyes in aqueous phase using different photocatalysts. J Hazard Mater 141:581–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.07.035
Katarzyna P, Agata B, Paulina B, Jerzy Z (2015) Phenol degradation in heterogeneous system generating singlet oxygen employing light activated electropolymerized phenothiazines. Appl Surf Sci 359:426–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.10.103
Ke Q, Zhang YG, Wu XL, Su XM, Wang YY, Lin HJ, Mei RW, Zhang Y, Hashmi MZ, Chen CJ (2018) Sustainable biodegradation of phenol by immobilized Bacillus sp. SAS19 with porous carbonaceous gels as carriers. J Environ Manage 222:185–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.05.061
Khalilzadeh MA, Tajik S, Beitollahi H, Venditti RA (2020) Green synthesis of magnetic nanocomposite with iron oxide deposited on cellulose nanocrystals with copper (Fe3O4@CNC/Cu): investigation of catalytic activity for the development of a venlafaxine electrochemical sensor. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:4219–4228. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b06214
Kuglaur SR, Anitha S, Brabu B, Tamer U (2017) Nano grained surface shell wall controlled ZnO–ZnS core–shell nanofibers and their shell wall thickness dependent visible photocatalytic properties. Catal Sci Technol 7:1167–1180. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CY02556K
Laszlo K, Podkoscielny P, Dabrowski A (2003) Heterogeneity of polymer-based active carbons in the adsorption of aqueous solutions of phenol and 2,3,4-trichlorophenol. Langmuir 19:5287–5294. https://doi.org/10.1021/la026761s
Lee H, Kannan P, Shoaibi AA, Srinivasakannan C (2019) Phenol degradation catalyzed by metal oxide supported porous carbon matrix under UV irradiation. J Water Process Eng 31:100869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100869
Li HQ, Hu JT, Zhou X, Li X, Wang XJ (2018) An investigation of the biochar-based visible-light photocatalyst via a self-assembly strategy. J Environ Manag 217:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.03.083
Li MR, Song C, Wu Y, Wang M, Pan ZP, Sun Y, Meng L, Han SG, Xu LJ, Gan L (2019) Novel Z-scheme visible-light photocatalyst based on CoFe2O4/BiOBr/Graphene composites for organic dye degradation and Cr(VI) reduction. Appl Surf Sci 478:744–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.017
Li CY, Ma YY, Zheng SZ, Hu CY, Qin F, Wei L, Zhang CQ, Duo SW, Hu QH (2020) One-pot synthesis of Bi2O3/Bi2O4 p-n heterojunction for highly efficient photocatalytic removal of organic pollutants under visible light irradiation. J Phys Chem Solids 140:109376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109376
Liang XZ, Wang P, Gao YG, Huang HN, Tong FX, Zhang QQ, Wang ZY, Liu YY, Zheng ZK, Dai Y, Huang BB (2020) Design and synthesis of porous M-ZnO/CeO2 microspheres as efficient plasmonic photocatalysts for nonpolar gaseous molecules oxidation: insight into the role of oxygen vacancy defects and M = Ag, Au nanoparticles. Appl Catal B Environ 260:118151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118151
Lin XP, Xing JC, Wang WD, Shan ZC, Xu FF, Huang FQ (2007) Photocatalytic activities of heterojunction semiconductors Bi2O3/BaTiO3: a strategy for the design of efficient combined photocatalysts. J Phys Chem C 111:18288–18293. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp073955d
Lin Y, Wu X, Han Y, Yang CP, Ma Y, Du C, Teng Q, Liu HY, Zhong YY (2019) Spatial separation of photogenerated carriers and enhanced photocatalytic performance on Ag3PO4 catalysts via coupling with PPy and MWCNTs. Appl Catal B Environ 258:117969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117969
Liu Y (2017) Industrial pollution resulting in mass incidents: Urban residents’ behavior and conflict mitigation. J Clean Prod 166:1253–1264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.08.125
Liu S, Yao K, Wang B, Ma MG (2017) Microwaveassisted hydrothermal synthesis of cellulose/ZnO composites and its thermal transformation to ZnO/carbon composites. Iran Polym J 26:681–691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-017-0553-x
Liu J, Wang PL, Qu WQ, Li HR, Shi LY, Zhang DS (2019) Nanodiamond-decorated ZnO catalysts with enhanced photocorrosion resistance for photocatalytic degradation of gaseous toluene. Appl Catal B Environ 257:117880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117880
Luo W, Schardt J, Bommier C, Wang B, Razink J, Simonsen J, Ji XL (2013) Carbon nanofibers derived from cellulose nanofibers as a long-life anode material for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 1:10662. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta12389h
Ma SS, Xue JJ, Zhou YM, Zhang ZW, Wu X (2014) A facile route for the preparation of ZnO/C composites with high photocatalytic activity and adsorption capacity. CrystEngComm 16:4478. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ce00110a
Mayara GG, Paulo ASV, Mayara RF, Patricio PZ, Antonio SM, Siara S (2020) Relationship of the physicochemical properties of novel ZnO/biochar composites to their efficiencies in the degradation of sulfamethoxazole and methyl orange. Sci Total Environ 748:141381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141381
Mohamed MM, Ghanem MA, Khairy M, Naguib E, Alotaibi NH (2019) Zinc oxide incorporated carbon nanotubes or graphene oxide nanohybrids for enhanced sonophotocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. Appl Surf Sci 487:539–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.135
Özbay G, Ayrilmis N (2015) Bonding performance of wood bonded with adhesive mixtures composed of phenol-formaldehyde and bio-oil. Ind Crop Prod 66:68–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.12.028
Ren T, Jin ZH, Yang J, Hu RS, Zhao F, Gao XJ, Zhao CX (2019) Highly efficient and stable p-LaFeO3/n-ZnO heterojunction photocatalyst for phenol degradation under visible light irradiation. J Hazard Mater 377:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.05.070
Seyednejhad S, Khalilzadeh MA, Zareyee D, Sadeghifar H, Venditti R (2019) Cellulose nanocrystal supported palladium as a novel recyclable catalyst for Ullmann coupling reactions. Cellulose 26:5015–5031. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02436-7
Seyednejhad S, Khalilzadeh MA, Sadeghifar H, Zareyee D (2020) Cellulose nanocrystals -palladium, a novel recyclable catalyst for coupling reaction. Eurasian Chem Commun 2:349–361. https://doi.org/10.33945/SAMI/ECC.2020.3.6
Shen ZF, Zhang QL, Yin CC, Kang SF, Jia HY, Li X, Li X, Wang YG, Cui LF (2019) Facile synthesis of 3D flower-like mesoporous Ce-ZnO at room temperature for the sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradations of RhB and phenol. J Colloid Interf Sci 556:726–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.08.111
Shin YS, Exarhos GG (2007) Template synthesis of porous titania using cellulose nanocrystals. Mater Lett 61:2594–2597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.10.005
Shuang W, Kong LJ, Zhong M, Wang DH, Liu J, Bu XH (2018) Rational design of Co embedded N,S-codoped carbon nanoplates as anode materials for high performance lithium-ion batteries. Dalton T 47:12385. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8DT02082E
Sin JC, Lam SM, Lee KT, Rahman MA (2015) Preparation of flower-like ZnO hierarchical structures for photodegradation of phenol under UV irradiation. Res Chem Intermediat 41:2489–2502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-013-1363-1
Song JL, Fu GS, Cheng Q (2013) Bimodal mesoporous silica nanotubes fabricated bydual templates of CTAB and bare nanocrystalline cellulose. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:708–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/10.1021/ie4036803
Su R, Tiruvalam R, He Q, Dimitratos N, Kesavan L, Hammond C, Lopez-Sanchez JA, Bechstein R, Kiely CJ, Hutchings GJ, Besenbacher F (2012) Promotion of phenol photodecomposition over TiO2 using Au, Pd, and Au-Pd nanoparticles. ACS Nano 6:6284–6292. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn301718v
Vaianoa V, Matarangoloa M, Murciab JJ, Rojasb H, Navíoc JA, Hidalgo MC (2018) Enhanced photocatalytic removal of phenol from aqueous solutions using ZnO modified with Ag. Appl Catal B Environ 225:197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.11.075
Wang JL, Wang SZ (2019) Preparation, modification and environmental application of biochar: a review. J Clean Prod 227:1002–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.282
Wang J, Wang G, Wei X, Liu G, Li J (2018a) ZnO nanoparticles implanted in TiO2 macrochannels as an effective direct Z-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst for degradation of RhB. Appl Surf Sci 456:666–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.182
Wang S, Kuang PY, Cheng B, Yu JG, Jiang CJ (2018b) ZnO hierarchical microsphere for enhanced photocatalytic activity. J Alloy Compd 741:622–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.141
Wang YR, Zhao JJ, Xiong XQ, Liu SW, Xu YM (2019) Role of Ni2+ ions in TiO2 and Pt/TiO2 photocatalysis for phenol degradation in aqueous suspensions. Appl Catal B Environ 258:117903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117903
Xu TG, Zhang LW, Cheng HY, Zhu YF (2011) Significantly enhanced photocatalytic performance of ZnO via graphene hybridization and the mechanism study. Appl Catal B Environ 101:382–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.10.007
Yin T, Fu QG, Zhou L, Fu YW (2020) Carbon fiber @ silicone rubber core-sheath elastomer for enhancing wear-resisting performance of phenolic resin composites. Compos Part B-Eng 192:107991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.107991
Yu HY, Chen GY, Wang YB, Yao JM (2015) A facile one-pot route for preparing cellulose nanocrystal/zinc oxide nanohybrids with high antibacterial and photocatalytic activity. Cellulose 22:261–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0491-0
Zeng X, Yang ZH, Fan MK, Cui F, Meng JL, Chen HZ, Chen LL (2020) Shape-controlled growth of three-dimensional flower-like ZnO@Ag composite and its outstanding electrochemical performance for Ni-Zn secondary batteries. J Colloid Interf Sci 562:518–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.11.083
Zhang L, Adom PK, An Y (2018) Regulation-induced structural break and the long-run drivers of industrial pollution intensity in China. J Clean Prod 198:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.008
Zhang Y, Huang HL, Wei LY, Gan L, Pan MZ (2019) Preparation and adsorption-photocatalysis properties of biochar/ZnO composites. Acta Mater Compos Sin 36:2187–2195. https://doi.org/10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190109.004
Zhang Y, Duoerkun G, Shi Z, Cao W, Liu T, Liu JS, Zhang LS, Li MQ, Chen ZG (2020) Construction of TiO2/Ag3PO4 nanojunctions on carbon fiber cloth for photocatalytically removing various organic pollutants in static or flowing wastewater. J Colloid Interf Sci 571:213–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.049
Zhao DL, Sheng GD, Chen CL, Wang XK (2012) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue under visible irradiation on graphene@TiO2 dyade structure. Appl Catal B Environ 111–112:303–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.10.012
Zhao DL, Yang X, Chen CL, Wang XK (2013) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue on multiwalled carbon nanotubes-TiO2. J Colloid Interface Sci 398:234–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.02.017
Zhao GM, Ding CX, Pan MZ, Zhai SC (2018) Fabrication of NCC-SiO2 hybrid colloids and its application on waterborne poly(acrylic acid) coatings. Prog Org Coat 122:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2018.05.014
Zhu HL, Luo W, Ciesielski PN, Fang ZQ, Zhu JY, Henriksson G, Himmel ME, Hu LB (2016) Wood-derived materials for green electronics, biological devices, and energy applications. Chem Rev 116:9305–9374. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00225
Zhu HL, Shen F, Luo W, Zhu SZ, Zhao MH, Natarajan B, Dai JQ, Zhou LH, Ji XL, Yassar RS, Li T, Hu LB (2017) Low temperature carbonization of cellulose nanocrystals for high performance carbon anode of sodium-ion batteries. Nano Energy 33:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.01.021
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31670556), Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of Nanjing Forestry University (NLJQ2015-02), and the Qing Lan Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhao, G., Xuan, Y. et al. Enhanced photocatalytic performance for phenol degradation using ZnO modified with nano-biochar derived from cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 28, 991–1009 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03581-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03581-0