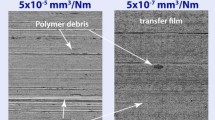
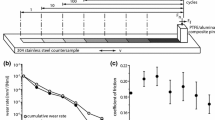
Abstract
The addition of 0.2–5% nanoscale (40–80 nm) α-phase or microscale (40 μm) γ-phase Al2O3 particles in PTFE effectively reduce the matrix wear rate by 99.99%, whereas microscale (> 0.5 μm) α-Al2O3 or nanoscale (40–80 nm) γ-Al2O3 only reduce PTFE wear by ~ 90% under identical loading, dispersion and testing conditions. This paradoxical material system best illustrates the complexity of tribology and the importance of filler–matrix interactions at small scales. We studied the independent effect of the Al2O3/PTFE interface area and alumina structure by systematically varying the particle size over two orders of magnitude for both α- and γ-Al2O3/PTFE composites. Detailed characterizations of filler size, surface area and tribofilm’s chemical composition were conducted. The results found: (1) DLS median particle sizes conformed reasonably to vendor reported values and percentages of microscale filler aggregates correlated weakly with wear rates, (2) electron microscopy of the as-worn composite surface suggested a strong relation between the characteristic size of ‘unreinforced’ polymer domain and composite wear rate, (3) third bodies (i.e., transfer films, debris) played an important role in counterface abrasion, (4) wear rate correlated strongly with filler’s specific surface area and ultralow wear was only maintained ~ 0.3–10 m2/g nominal specific filler–matrix area values, (5) ultralow wear coincided with perfluorinated carboxylic salt rich tribofilms which supported a previously proposed wear reduction mechanism that mechanochemically degraded PTFE chelate with alumina and cause crosslinked and wear-resistant tribofilms, (6) tribofilm Al-F bond signal increased with filler surface area and high wear coincided with excessive tribofilm Al-F signal for γ-Al2O3/PTFE systems. Based on these results and literature hypothesis, we proposed that (1) the 1 μm α-Al2O3 provided the least filler–matrix interface and largest unreinforced polymer domain in PTFE, which lead to the least crosslinked and compartmentalized tribofilms; (2) in γ-alumina filled composites, Al-F bond forms as a product of mechanochemically degraded PTFE but also blocks chelation between the degraded PTFE and alumina fillers, (3) the 20 nm γ-Al2O3 provided the most filler–matrix interface which leads to excessive aluminum fluoride that blocked the filler–matrix chelation, prevented the tribofilm crosslinking and lead to high wear rates. This hypothesis was additionally supported by small molecule experiments in this study. However, this study provides no direct insight into how sensitive the filler–matrix tribochemical interaction is to filler phase or aggregate strength (strong, weak or fully dense).
Graphic Abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Interestingly, our results suggested the measured oxygen content on unworn composite surface contains surface absorbed hydroxyl groups from environmental moisture which could also be altered due to wear in some cases.
References
Myshkin, N., Kovalev, A.: Adhesion and surface forces in polymer tribology—a review. Friction 6, 143–155 (2018)
Scharf, T.W., Prasad, S.V.: Solid lubricants: a review. J. Mater. Sci. 48, 511–531 (2012)
Schadler, L., Brinson, L.C., Sawyer, W.: Polymer nanocomposites: a small part of the story. Jom 59, 53–60 (2007)
Burris, D.L., Zhao, S., Duncan, R., Lowitz, J., Perry, S.S., Schadler, L.S., et al.: A route to wear resistant PTFE via trace loadings of functionalized nanofillers. Wear 267, 653–660 (2009)
Anthony, K.: Interface effects and the work of fracture of a fibrous composite. Proc. R. Soc. London A 319, 95–116 (1970)
Cotterell, B., Chia, J.Y.H., Hbaieb, K.: Fracture mechanisms and fracture toughness in semicrystalline polymer nanocomposites. Eng. Fract. Mech. 74, 1054–1078 (2007)
Reynaud, E., Jouen, T., Gauthier, C., Vigier, G., Varlet, J.: Nanofillers in polymeric matrix: a study on silica reinforced PA6. Polymer 42, 8759–8768 (2001)
Singh, R.P., Zhang, M., Chan, D.: Toughening of a brittle thermosetting polymer: effects of reinforcement particle size and volume fraction. J. Mater. Sci. 37, 781–788 (2002)
Wichmann, M.H.G., Schulte, K., Wagner, H.D.: On nanocomposite toughness. Compos. Sci. Technol. 68, 329–331 (2008)
Michler, G.H., Adhikari, R., Henning, S.: Toughness enhancement of nanostructured amorphous and semicrystalline polymers. Macromol. Symp. 214, 47–72 (2004)
Marega, C., Marigo, A., Causin, V., Kapeliouchko, V., Di Nicolò, E., Sanguineti, A.: Relationship between the size of the latex beads and the solid−solid phase transitions in emulsion polymerized poly (tetrafluoroethylene). Macromolecules 37, 5630–5637 (2004)
Xiao, Z., Li, Y., Ma, D., Schadler, L.S., Akpalu, Y.A.: Probing the use of small-angle light scattering for characterizing structure of titanium dioxide/low-density polyethylene nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. B 44, 1084–1095 (2006)
Dasari, A., Yu, Z.-Z., Mai, Y.-W.: Fundamental aspects and recent progress on wear/scratch damage in polymer nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 63, 31–80 (2009)
Qian, D., Dickey, E.C., Andrews, R., Rantell, T.: Load transfer and deformation mechanisms in carbon nanotube-polystyrene composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 2868–2870 (2000)
Thostenson, E.T., Ren, Z., Chou, T.-W.: Advances in the science and technology of carbon nanotubes and their composites: a review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 61, 1899–1912 (2001)
Thostenson, E.T., Li, C., Chou, T.-W.: Nanocomposites in context. Compos. Sci. Technol. 65, 491–516 (2005)
Burris, D.L., Boesl, B., Bourne, G.R., Sawyer, W.G.: Polymeric nanocomposites for tribological applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 292, 387–402 (2007)
Gersappe, D.: Molecular mechanisms of failure in polymer nanocomposites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 058301 (2002)
Jordan, J., Jacob, K.I., Tannenbaum, R., Sharaf, M.A., Jasiuk, I.: Experimental trends in polymer nanocomposites—a review. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 393, 1–11 (2005)
Tanaka, K., Kawakami, S.: Effect of various fillers on the friction and wear of polytetrafluoroethylene-based composites. Wear 79, 221–234 (1982)
Makowiec, M.E., Blanchet, T.A.: Improved wear resistance of nanotube- and other carbon-filled PTFE composites. Wear 374–375, 77–85 (2017)
Lancaster, J.K.: Polymer-based bearing materials—the role of fillers and fibre reinforcement in wear. Wear 22, 412 (1972)
Burris, D.L., Sawyer, W.G.: Improved wear resistance in alumina-PTFE nanocomposites with irregular shaped nanoparticles. Wear 260, 915–918 (2006)
Krick, B.A., Pitenis, A.A., Harris, K.L., Junk, C.P., Sawyer, W.G., Brown, S.C., et al.: Ultralow wear fluoropolymer composites: Nanoscale functionality from microscale fillers. Tribol. Int. 95, 245–255 (2016)
Bahadur, S., Gong, D.: The action of fillers in the modification of the tribological behavior of polymers. Wear 158, 41–59 (1992)
Conte, M., Pinedo, B., Igartua, A.: Role of crystallinity on wear behavior of PTFE composites. Wear 307, 81–86 (2013)
Burris, D.L., Sawyer, W.G.: Tribological sensitivity of PTFE/alumina nanocomposites to a range of traditional surface finishes. Tribol. Trans. 48, 147–153 (2005)
Campbell, K.L., Sidebottom, M.A., Atkinson, C.C., Babuska, T.F., Kolanovic, C.A., Boulden, B.J., et al.: Ultralow wear PTFE-based polymer composites—the role of water and tribochemistry. Macromolecules 52, 5268–5277 (2019)
Harris, K.L., Pitenis, A.A., Sawyer, W.G., Krick, B.A., Blackman, G.S., Kasprzak, D.J., et al.: PTFE tribology and the role of mechanochemistry in the development of protective surface films. Macromolecules 48, 3739–3745 (2015)
Krick, B.A., Ewin, J.J., Blackman, G.S., Junk, C.P., Gregory Sawyer, W.: Environmental dependence of ultra-low wear behavior of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and alumina composites suggests tribochemical mechanisms. Tribol. Int. 51, 42–46 (2012)
Krick, B.A., Ewin, J.J., McCumiskey, E.J.: Tribofilm formation and run-in behavior in ultra-low-wearing polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and alumina nanocomposites. Tribol. Trans. 57, 1058–1065 (2014)
Pitenis, A.A., Ewin, J.J., Harris, K.L., Sawyer, W.G., Krick, B.A.: In vacuo tribological behavior of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and alumina nanocomposites: the importance of water for ultralow wear. Tribol. Lett. 53, 189–197 (2013)
Pitenis, A.A., Harris, K.L., Junk, C.P., Blackman, G.S., Sawyer, W.G., Krick, B.A.: Ultralow wear PTFE and alumina composites: it is all about tribochemistry. Tribol. Lett. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0445-6
Bhargava, S., Blanchet, T.A.: Unusually effective nanofiller a contradiction of microfiller-specific mechanisms of PTFE composite wear resistance? J. Tribol. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4032818
McElwain, S.E., Blanchet, T.A., Schadler, L.S., Sawyer, W.G.: Effect of particle size on the wear resistance of alumina-filled PTFE micro- and nanocomposites. Tribol. Trans. 51, 247–253 (2008)
Onodera, T., Kawasaki, K., Nakakawaji, T., Higuchi, Y., Ozawa, N., Kurihara, K., et al.: Effect of tribochemical reaction on transfer-film formation by poly(tetrafluoroethylene). J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 11820–11826 (2014a)
Takeichi, Y., Wibowo, A., Kawamura, M., Uemura, M.: Effect of morphology of carbon black fillers on the tribological properties of fibrillated PTFE. Wear 264, 308–315 (2008)
Kandanur, S.S., Rafiee, M.A., Yavari, F., Schrameyer, M., Yu, Z.-Z., Blanchet, T.A., et al.: Suppression of wear in graphene polymer composites. Carbon 50, 3178–3183 (2012)
Blanchet, T.A., Kandanur, S.S., Schadler, L.S.: coupled effect of filler content and countersurface roughness on PTFE nanocomposite wear resistance. Tribol. Lett. 40, 11–21 (2010)
Onodera, T., Kawasaki, K., Nakakawaji, T., Higuchi, Y., Ozawa, N., Kurihara, K., et al.: Tribocatalytic reaction of polytetrafluoroethylene sliding on an aluminum surface. J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 15954–15962 (2015)
Alam, K.I., Dorazio, A., Burris, D.L.: Polymers tribology exposed: eliminating transfer film effects to clarify ultralow wear of PTFE. Tribol. Lett. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-020-01306-9
Ye, J., Zhang, H., Liu, X., Liu, K.: Low wear steel counterface texture design: a case study using micro-pits texture and alumina–PTFE nanocomposite. Tribol. Lett. 65, 165 (2017)
Burris, D.L., Sawyer, W.G.: Measurement uncertainties in wear rates. Tribol. Lett. 36, 81–87 (2009)
Ye, J., Burris, D.L., Xie, T.: A review of transfer films and their role in ultra-low-wear sliding of polymers. Lubricants 4, 4 (2016)
Sawyer, W.G., Argibay, N., Burris, D.L., Krick, B.A.: Mechanistic studies in friction and wear of bulk materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 44, 395–427 (2014)
Khare, H.S., Moore, A.C., Haidar, D.R., Gong, L., Ye, J., Rabolt, J.F., et al.: Interrelated effects of temperature and environment on wear and tribochemistry of an ultralow wear PTFE composite. J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 16518–16527 (2015)
Trueba, M., Trasatti, S.P.: γ-alumina as a support for catalysts: a review of fundamental aspects. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 3393–3403 (2005)
Paglia, G., Rohl, A.L., Buckley, C.E., Gale, J.D.: Determination of the structure ofγ-alumina from interatomic potential and first-principles calculations: the requirement of significant numbers of nonspinel positions to achieve an accurate structural model. Phys. Rev. B (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.71.224115
Sun, W., Liu, X., Liu, K., Wang, W., Ye, J.: Ultralow wear PTFE composites filled with beryllia and germania particles. Wear 450–451, 203270 (2020)
Padmaja, P., Pillai, P.K., Warrier, K.G.K., Padmanabhan, M.: Adsorption isotherm and pore characteristics of nano alumina derived from sol-gel boehmite. J. Porous Mater. 11, 147–155 (2004)
Liang, C.Y., Krimm, S.: Infrared spectra of high polymers. III. Polytetrafluoroethylene and polychlorotrifluoroethylene. J. Chem. Phys. 25, 563–571 (1956)
Wang, Y., Du, X., Guo, L., Liu, H.: Chain orientation and headgroup structure in Langmuir monolayers of stearic acid and metal stearate (Ag Co, Zn, and Pb) studied by infrared reflection-absorption spectroscopy. J. Chem. Phys. 124, 134706 (2006)
Przedlacki, M., Kajdas, C.: Tribochemistry of fluorinated fluids hydroxyl groups on steel and aluminum surfaces. Tribol. Trans. 49, 202–214 (2006)
Kajdas, C.K.: Importance of the triboemission process for tribochemical reaction. Tribol. Int. 38, 337–353 (2005)
Vanni, H., Rabolt, J.F.: Fourier transform infrared investigation of the effects of irradiation on the 19 and 30°C phase transitions in polytetrafluoroethylene. J. Polym. Sci 18, 587–596 (1980)
Lenk, T.J., Hallmark, V.M., Hoffmann, C.L., Rabolt, J.F., Castner, D.G., Erdelen, C., et al.: Structural investigation of molecular organization in self-assembled monolayers of a semifluorinated amidethiol. Langmuir 10, 4610–4617 (1994)
Haidar, D.R., Alam, K.I., Burris, D.L.: Tribological insensitivity of an ultralow-wear poly(etheretherketone)–polytetrafluoroethylene polymer blend to changes in environmental moisture. J. Phys. Chem. C 122, 5518–5524 (2018)
Danchevskaya, M., Ivakin, Y.D., Martynova, L., Zuy, A., Muravieva, G., Lazarev, V.: Investigation of thermal transformations in aluminium hydroxides subjected to mechanical treatment. J. Therm. Anal. 46, 1215–1222 (1996)
Onodera, T., Kawasaki, K., Nakakawaji, T., Higuchi, Y., Ozawa, N., Kurihara, K., et al.: Chemical reaction mechanism of polytetrafluoroethylene on aluminum surface under friction condition. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 5390–5396 (2014b)
Morales, W.: The decomposition of a commercial perfluoropolyalkylether on alpha and gamma catalytic aluminas. Tribol. Trans. 39, 148–156 (1996)
Limcharoen, A., Pakpum, C., Limsuwan, P.: An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy investigation of redeposition from fluorine-based plasma etch on magnetic recording slider head substrate. Proced. Eng. 32, 1043–1049 (2012)
Baggetto, L., Dudney, N.J., Veith, G.M.: Surface chemistry of metal oxide coated lithium manganese nickel oxide thin film cathodes studied by XPS. Electrochim. Acta 90, 135–147 (2013)
Ye, J., Khare, H.S., Burris, D.L.: Quantitative characterization of solid lubricant transfer film quality. Wear 316, 133–143 (2014)
Khare, H.S., Burris, D.L.: A quantitative method for measuring nanocomposite dispersion. Polymer 51, 719–729 (2010)
Haidar, D.R., Ye, J., Moore, A.C., Burris, D.L.: Assessing quantitative metrics of transfer film quality as indicators of polymer wear performance. Wear 380–381, 78–85 (2017)
Blanchet, T.A.: A model for polymer composite wear behavior including preferential load support and surface accumulation of filler particulates. Tribol. Trans. 38, 821–828 (1995)
Briscoe, B.: Wear of polymers: an essay on fundamental aspects. Tribol. Int. 14, 231–243 (1981)
Ye, J., Khare, H.S., Burris, D.L.: Transfer film evolution and its role in promoting ultra-low wear of a PTFE nanocomposite. Wear 297, 1095–1102 (2013)
Ye, J., Moore, A.C., Burris, D.L.: Transfer film tenacity: a case study using ultra-low-wear alumina–PTFE. Tribol. Lett. 59, 50 (2015)
Deli, G., Qunji, X., Hongli, W.: ESCA study on tribochemical characteristics of filled PTFE. Wear 148, 161–169 (1991)
Gao, X., Chorover, J.: Adsorption of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid to iron oxide surfaces as studied by flow-through ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Environ. Chem. 9, 148 (2012)
Doan, V., Köppe, R., Kasai, P.H.: Dimerization of carboxylic acids and salts: an IR study in perfluoropolyether media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119, 9810–9815 (1997)
Crist, B.V.: XPS in industry—problems with binding energies in journals and binding energy databases. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 231, 75–87 (2019)
McHale, J., Auroux, A., Perrotta, A., Navrotsky, A.: Surface energies and thermodynamic phase stability in nanocrystalline aluminas. Science 277, 788–791 (1997)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully thank the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers 51875153 and 51875152, 51975174), Postdoctoral Research Foundation of China and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JZ2020HGTB0054). The authors also gratefully thank Yu Ning, Gang Qian, Tianci Zhang (Hefei University of Technology) for their help in spectroscopy analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W., Liu, X., Liu, K. et al. Paradoxical Filler Size Effect on Composite Wear: Filler–Matrix Interaction and Its Tribochemical Consequences. Tribol Lett 68, 131 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-020-01375-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-020-01375-w