Abstract
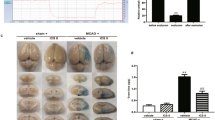
The current study aimed to determine the protective effect of AY9944 related to Caveolin-1 and Claudin-5 role in lipid raft, which can rescue the blood–brain barrier from enhanced permeability. Therefore, in vivo analyses were performed following ischemia in normal, ischemic, and AY9944-treated animal groups. The results revealed that AY9944 reduced the infarct size, edema, and brain water content. The extravasation of Alb-Alexa 594 and biocytin-TMR was minimum in the AY9944-treated animals. The results showed a significant decrease in the expression level of Caveolin-1 over 8 h and 48 h and a remarkable increase in the level of Claudin-5 over 48 h following ischemia in AY9944-treated animals. Molecular docking simulation demonstrated that AY9944 exerts a possible protective role via attenuating the interaction of the Caveolin-1 and cholesterol in lipid raft. These findings point out that AY9944 plays a protective role in stroke by means of blood–brain barrier preservation.
Graphic Abstract
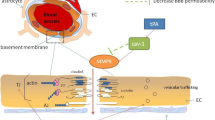
Proper neural function essentially needs a constant homeostatic brain environment which is provided by the blood-brain barrier. Rescuing blood-brain barrier from enhanced permeability via inducing the protective effect of AY9944 related to caveolin-1 and claudin-5 role in lipid raft was the aim of the current study.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Research data are not shared.
References
Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE, Yusof SR, Begley DJ (2010) Structure and function of the blood–brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis 37(1):13–25
Anderson JM, Van Itallie CM (2009) Physiology and function of the tight junction. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol 1(2):a002584
Andreone BJ, Chow BW, Tata A, Lacoste B, Ben-Zvi A, Bullock K et al (2017) Blood-brain barrier permeability is regulated by lipid transport-dependent suppression of caveolae-mediated transcytosis. Neuron 94(3):581–594
Arbuzova A, Wang L, Wang J, Hangyás-Mihályné G, Murray D, Honig B, McLaughlin S (2000) Membrane binding of peptides containing both basic and aromatic residues. Experimental studies with peptides corresponding to the scaffolding region of caveolin and the effector region of MARCKS. Biochemistry 39(33):10330–10339
Beziaud T, Chen XR, El Shafey N, Frechou M, Teng F, Palmier B et al (2011) Simvastatin in traumatic brain injury: effect on brain edema mechanisms. Crit Care Med 39(10):2300–2307
Boyd NL, Park H, Yi H, Boo YC, Sorescu GP, Sykes M, Jo H (2003) Chronic shear induces caveolae formation and alters ERK and Akt responses in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285(3):H1113–H1122
Breen MR, Camps M, Carvalho-Simoes F, Zorzano A, Pilch PF (2012) Cholesterol depletion in adipocytes causes caveolae collapse concomitant with proteosomal degradation of cavin-2 in a switch-like fashion. PLoS ONE 7(4):e34516
Chang W-J, Rothberg KG, Kamen BA, Anderson R (1992) Lowering the cholesterol content of MA104 cells inhibits receptor-mediated transport of folate. J Cell Biol 118(1):63–69
Collins TR (2017) Neurologic diseases found to be the largest cause of disability worldwide. Neurol Today 17(22):1–32
Coskun A, Serteser M, Unsal I (2013) Inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis in hypercholesterolemia—is it the right choice?/Inhibicija Biosinteze Holesterola u Hiperholesterolemiji—Da Li Je Pravi Izbor? J Med Biochem 32(1):16–19
Cummins TR, Longa E, Weinstein SP, Carlson CS (1988) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
DeLano WL (2002) The PyMOL molecular graphics system. Delano Scientific, San Carlos
D’Onofrio PM, Thayapararajah M, Lysko MD, Magharious M, Spratt SK, Lee G et al (2011) Gene therapy for traumatic central nervous system injury and stroke using an engineered zinc finger protein that upregulates VEGF-A. J Neurotrauma 28(9):1863–1879
Engel O, Kolodziej S, Dirnagl U, Prinz V (2011) Modeling stroke in mice-middle cerebral artery occlusion with the filament model. J Vis Exp JoVE 47:2423
Fielding CJ, Bist A, Fielding PE (1997) Caveolin mRNA levels are up-regulated by free cholesterol and down-regulated by oxysterols in fibroblast monolayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci 94(8):3753–3758
Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1990) Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature 343(6257):425
Harder T, Simons K (1997) Caveolae, DIGs, and the dynamics of sphingolipid—cholesterol microdomains. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9(4):534–542
Hoop CL, Sivanandam V, Kodali R, Srnec MN, van der Wel PC (2011) Structural characterization of the caveolin scaffolding domain in association with cholesterol-rich membranes. Biochemistry 51(1):90–99
Itallie CMV, Anderson JM (2012) Caveolin binds independently to claudin-2 and occludin. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1257(1):103–107
Kang E-J, Major S, Jorks D, Reiffurth C, Offenhauser N, Friedman A, Dreier J (2013) Blood–brain barrier opening to large molecules does not imply blood–brain barrier opening to small ions. Neurobiol Dis 52:204–218
Keep RF, Hua Y, Xi G (2012) Brain water content: a misunderstood measurement? Transl Stroke Res 3(2):263–265
Knowland D, Arac A, Sekiguchi KJ, Hsu M, Lutz SE, Perrino J et al (2014) Stepwise recruitment of transcellular and paracellular pathways underlies blood-brain barrier breakdown in stroke. Neuron 82(3):603–617
Krieger E, Koraimann G, Vriend G (2002) Increasing the precision of comparative models with yasara nova—a self-parameterizing force field. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinform 47(3):393–402
Kurzepa J, Szczepanska-Szerej A, Stryjecka-Zimmer M, Malecka-Massalska T, Stelmasiak Z (2006) Simvastatin could prevent increase of the serum MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio in acute ischaemic stroke. Folia Biol Praha 52(6):181
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM (1993) PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Crystallogr 26(2):283–291
Li D-D, Song J-N, Huang H, Guo X-Y, An J-Y, Zhang M et al (2013) The roles of MMP-9/TIMP-1 in cerebral edema following experimental acute cerebral infarction in rats. Neurosci Lett 550:168–172
Liu J, Jin X, Liu KJ, Liu W (2012) Matrix metalloproteinase-2-mediated occludin degradation and caveolin-1-mediated claudin-5 redistribution contribute to blood–brain barrier damage in early ischemic stroke stage. J Neurosci 32(9):3044–3057
Maltese WA, Aprille J (1985) Relation of mevalonate synthesis to mitochondrial ubiquinone content and respiratory function in cultured neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 260(21):11524–11529
Michinaga S, Koyama Y (2015) Pathogenesis of brain edema and investigation into anti-edema drugs. Int J Mol Sci 16(5):9949–9975
Mortensen SA, Rosenfeldt F, Kumar A, Dolliner P, Filipiak KJ, Pella D et al (2014) The effect of coenzyme Q10 on morbidity and mortality in chronic heart failure: results from Q-SYMBIO: a randomized double-blind trial. JACC Heart Failure 2(6):641–649
Nag S (2003) Morphology and molecular properties of cellular components of normal cerebral vessels. In: Nag S (ed) The blood-brain barrier. Springer, New York, pp 3–36
Nag S, Venugopalan R, Stewart DJ (2007) Increased caveolin-1 expression precedes decreased expression of occludin and claudin-5 during blood–brain barrier breakdown. Acta Neuropathol 114(5):459–469
Nagai N, De Mol M, Van Hoef B, Verstreken M, Collen D (2001) Depletion of circulating α2-antiplasmin by intravenous plasmin or immunoneutralization reduces focal cerebral ischemic injury in the absence of arterial recanalization. Blood 97(10):3086–3092
Nategh M, Shaveisi K, Shabanzadeh AP, Sadr SS, Parviz M, Ghabaei M (2010) Systemic Hyperthermia Masks the Neuroprotective Effects of MK-801, but not Rosiglitazone in Brain Ischaemia. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 107(3):724–729
Nitta T, Hata M, Gotoh S, Seo Y, Sasaki H, Hashimoto N et al (2003) Size-selective loosening of the blood-brain barrier in claudin-5-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 161(3):653–660
Nusrat A, Parkos C, Verkade P, Foley C, Liang T, Innis-Whitehouse W et al (2000) Tight junctions are membrane microdomains. J Cell Sci 113(10):1771–1781
Ohkura Y, Akanuma S-I, Tachikawa M, Hosoya K-I (2010) Blood-to-retina transport of biotin via Na+-dependent multivitamin transporter (SMVT) at the inner blood-retinal barrier. Exp Eye Res 91(3):387–392
Owolabi MO, Arulogun O, Melikam S, Adeoye AM, Akarolo-Anthony S, Akinyemi R et al (2015) The burden of stroke in Africa: a glance at the present and a glimpse into the future. Cardiovasc J Afr 26(2):S27
Panahpour H, Farhoudi M, Omidi Y, Mahmoudi J (2018) An in vivo assessment of blood-brain barrier disruption in a rat model of ischemic stroke. JoVE J Vis Exp 133:e57156
Pol A, Martin S, Fernández MA, Ingelmo-Torres M, Ferguson C, Enrich C, Parton RG (2005) Cholesterol and fatty acids regulate dynamic caveolin trafficking through the Golgi complex and between the cell surface and lipid bodies. Mol Biol Cell 16(4):2091–2105
Ponce J, de la Ossa NP, Hurtado O, Millan M, Arenillas JF, Dávalos A, Gasull T (2008) Simvastatin reduces the association of NMDA receptors to lipid rafts: a cholesterol-mediated effect in neuroprotection. Stroke 39(4):1269–1275
Racine RJ (1972) Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation: II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 32(3):281–294
Rothberg KG, Ying Y-S, Kamen BA, Anderson R (1990) Cholesterol controls the clustering of the glycophospholipid-anchored membrane receptor for 5-methyltetrahydrofolate. J Cell Biol 111(6):2931–2938
Shuaib A, Wang CX, Yang T, Noor R (2002) Effects of nonpeptide V1 vasopressin receptor antagonist SR-49059 on infarction volume and recovery of function in a focal embolic stroke model. Stroke 33(12):3033–3037
Sinensky M, Beck L, Leonard S, Evans R (1990) Differential inhibitory effects of lovastatin on protein isoprenylation and sterol synthesis. J Biol Chem 265(32):19937–19941
Stamatovic SM, Johnson AM, Sladojevic N, Keep RF, Andjelkovic AV (2017) Endocytosis of tight junction proteins and the regulation of degradation and recycling. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1397(1):54–65
Tabouillot T, Muddana HS, Butler PJ (2011) Endothelial cell membrane sensitivity to shear stress is lipid domain dependent. Cell Mol Bioeng 4(2):169–181
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31(2):455–461
Watson PMD, Paterson JC, Thom G, Ginman U, Lundquist S, Webster CI (2013) Modelling the endothelial blood-CNS barriers: a method for the production of robust in vitro models of the rat blood-brain barrier and blood-spinal cord barrier. BMC Neurosci 14(1):59
Wiederstein M, Sippl MJ (2007) ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 35(suppl 2):W407–W410
Yang J, Yan R, Roy A, Xu D, Poisson J, Zhang Y (2015) The I-TASSER suite: protein structure and function prediction. Nat Methods 12(1):7
Zhang Y (2008) I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinformatics 9(1):40
Acknowledgements
This research was a part of a Ph.D. thesis and supported by Basic Electrophysiology Research Center, Neuroscience Institute, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Each author acknowledges he/she has participated in the analysis, drafting, and final approval of the manuscript in a substantive way and is prepared to take public responsibility for the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gholami, L., Jokar, S., Fatahi, Y. et al. Targeting Caveolin-1 and Claudin-5 with AY9944, Improve Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability; Computational Simulation and Experimental Study. Cell Mol Neurobiol 42, 1125–1139 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-01004-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-01004-z