Abstract
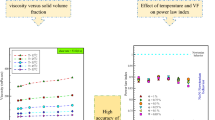
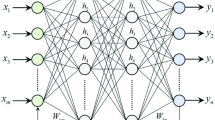
This study was on the optimization of the viscosity of MWCNT-MgO (35–65%)/5W50 nanofluid and comparison of experimental results with the designed artificial neural network (ANN). The experimental examination was performed at solid volume fraction (SVF) s of 0.05, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1% and the temperature of 5–55 °C. A mathematical relationship was proposed to predict its viscosity using the RSM method in Design-Expert software. The viscosity of this nanofluid was also optimized concerning temperature, SVF, and shear rate (SR). A point with a specification of T = 54.45 (°C), SVF = 0.06%, and SR = 11,899.24 (1/s) had an optimum viscosity of 39.0754 mPa s. Specification parameters of the ANN model were reported in this study as well. The results of the proposed mathematical correlation could not accurately predict, as well as the ANN and the predictions provided by ANN were more accurate.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Choi, S.U.: Thermal conductivity of nanoparticle-fluid mixture. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 13(4), 474–480 (1999)
Salari, M.; Malekshah, E.H.; Esfe, M.H.: Three dimensional simulation of natural convection and entropy generation in an air and MWCNT/water nanofluid filled cuboid as two immiscible fluids with emphasis on the nanofluid height ratio's effects. J. Mol. Liq. 227, 223–233 (2017)
Esfe, M.H.; Saedodin, S.; Biglari, M.; Rostamian, H.: Experimental investigation of thermal conductivity of CNTs-Al2O3/water: a statistical approach. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 69, 29–33 (2015)
Esfe, M.H.; Yan, W.M.; Akbari, M.; Karimipour, A.; Hassani, M.: Experimental study on thermal conductivity of DWCNT-ZnO/water-EG nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat and Mass Transfer 68, 248–251 (2015)
Esfe, M.H.; Hajmohammad, H.; Moradi, R.; Arani, A.A.A.: Multi-objective optimization of cost and thermal performance of double walled carbon nanotubes/water nanofluids by NSGA-II using response surface method. Appl. Therm. Eng. 112, 1648–1657 (2017)
Esfe, M.H.; Arani, A.A.A.; Badi, R.S.; Rejvani, M.: ANN modeling, cost performance and sensitivity analyzing of thermal conductivity of DWCNT–SiO 2/EG hybrid nanofluid for higher heat transfer. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 131(3), 2381–2393 (2018)
Esfe, M.H.; Esfandeh, S.; Afrand, M.; Rejvani, M.; Rostamian, S.H.: Experimental evaluation, new correlation proposing and ANN modeling of thermal properties of EG based hybrid nanofluid containing ZnO-DWCNT nanoparticles for internal combustion engines applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 133, 452–463 (2018)
Esfe, M.H.; Rostamian, H.; Shabani-Samghabadi, A.; Arani, A.A.A.: Application of three-level general factorial design approach for thermal conductivity of MgO/water nanofluids. Appl. Therm. Engi. 127, 1194–1199 (2017)
Esfe, M.H.; Hajmohammad, M.H.; Razi, P.; Ahangar, M.R.H.; Arani, A.A.A.: The optimization of viscosity and thermal conductivity in hybrid nanofluids prepared with magnetic nanocomposite of nanodiamond cobalt-oxide (ND-Co3O4) using NSGA-II and RSM. Int. Commun. Heat and Mass Transfer 79, 128–134 (2016)
Fereidoon, A.; Saedodin, S.; Hemmat Esfe, M.; Noroozi, M.J.: Evaluation of mixed convection in inclined square lid-driven cavity filled with Al2O3/water nano-fluid. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 7(1), 55–65 (2013)
Illbeigi, M.; Solaimany Nazar, A.: Numerical simulation of laminar convective heat transfer and pressure drop of water based-Al2O3 nanofluid as a non newtonian fluid by computational fluid dynamic (CFD). Transp. Phenom. Nano Micro Scales 5(2), 130–138 (2017)
Esfe, M.H.; Arani, A.A.A.; Niroumand, A.H.; Yan, W.M.; Karimipour, A.: Mixed convection heat transfer from surface-mounted block heat sources in a horizontal channel with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 89, 783–791 (2015)
Eshaghi, A.; Mojab, M.: Hydrophilicity of silica nano-porous thin films: calc fects of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on rheological behavior of engine ination Temperature Effects. J. Nanostruct. 7(2), 127–133 (2017)
Koca, H.D.; Doganay, S.; Turgut, A.; Tavman, I.H.; Saidur, R.; Mahbubul, I.M.: Effect of particle size on the viscosity of nanofluids: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 82, 1664–1674 (2018)
Tseng, W.J.; Lin, K.C.: Rheology and colloidal structure of aqueous TiO2 nanoparticle suspensions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 355(1–2), 186–192 (2003)
Hemmati-Sarapardeh, A.; Varamesh, A.; Husein, M.M.; Karan, K.: On the evaluation of the viscosity of nanofluid systems: modeling and data assessment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 81, 313–329 (2018)
Murshed, S.S.; Estellé, P.: A state of the art review on viscosity of nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 76, 1134–1152 (2017)
Jeong, J.; Li, C.; Kwon, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.H.; Yun, R.: Particle shape effect on the viscosity and thermal conductivity of ZnO nanofluids. Int. J. Refrig. 36(8), 2233–2241 (2013)
Sepyani, K.; Afrand, M.; Esfe, M.H.: An experimental evaluation of the effect of ZnO nanoparticles on the rheological behavior of engine oil. J. Mol. Liq. 236, 198–204 (2017)
Pramuanjaroenkij, A.; Tongkratoke, A.; Kakaç, S.J.J.O.E.P.: Numerical study of mixing thermal conductivity models for nanofluid heat transfer enhancement. J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys. 91(1), 104–114 (2018)
Ehteram, H.; Abbasian Arani, A.; Sheikhzadeh, G.; Aghaei, A.; Malihi, A.: The effect of various conductivity and viscosity models considering Brownian motion on nanofluids mixed convection flow and heat transfer. Transp. Phenom. Nano Micro Scales 4(1), 19–28 (2016)
Esfe, M.H.; Motahari, K.; Sanatizadeh, E.; Afrand, M.; Rostamian, H.; Ahangar, M.R.H.: Estimation of thermal conductivity of CNTs-water in low temperature by artificial neural network and correlation. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 76, 376–381 (2016)
Zeeshan, A.; Shehzad, N.; Ellahi, R.; Alamri, S.Z.: Convective poiseuille flow of Al2O3-EG nanofluid in a porous wavy channel with thermal radiation. Neural Comput. Appl. 30(11), 3371–3382 (2018)
Raei, B.; Shahraki, F.; Jamialahmadi, M.; Peyghambarzadeh, S.M.: Experimental investigation on the heat transfer performance and pressure drop characteristics of γ-Al2O3/water nanofluid in a double tube counter flow heat exchanger. Transp. Phenom. Nano Micro Scales 5(1), 64–75 (2016)
Mohebbi, R.; Rashidi, M.M.; Izadi, M.; Sidik, N.A.C.; Xian, H.W.: Forced convection of nanofluids in an extended surfaces channel using lattice Boltzmann method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 117, 1291–1303 (2018)
Shi, L.; He, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.: Thermophysical properties of Fe3O4@ CNT nanofluid and controllable heat transfer performance under magnetic field. Energy Convers. Manag. 177, 249–257 (2018)
Shi, L.; Hu, Y.; He, Y.: Magneto-responsive thermal switch for remote-controlled locomotion and heat transfer based on magnetic nanofluid. Nano Energy 71, 104582 (2020)
Choi, S.U.; Eastman, J.A.: Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles (No. ANL/MSD/CP-84938; CONF-951135-29). Argonne National Lab., IL, United States (1995)
Esfe, M.H.; Arani, A.A.A.; Rezaie, M.; Yan, W.M.; Karimipour, A.: Experimental determination of thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of Ag–MgO/water hybrid nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 66, 189–195 (2015)
Esfe, M.H.; Esfandeh, S.; Arani, A.A.A.: Proposing a modified engine oil to reduce cold engine start damages and increase safety in high temperature operating conditions. Powder Technol. 355, 251–263 (2019)
Esfe, M.H.; Arani, A.A.A.; Esfandeh, S.; Afrand, M.: Proposing new hybrid nano-engine oil for lubrication of internal combustion engines: Preventing cold start engine damages and saving energy. Energy 170, 228–238 (2019)
Esfe, M.H.; Arani, A.A.A.; Esfandeh, S.: Improving engine oil lubrication in light-duty vehicles by using of dispersing MWCNT and ZnO nanoparticles in 5W50 as viscosity index improvers (VII). Appl. Therm. Eng. 143, 493–506 (2018)
Esfe, M.H.; Hosseinizadeh, E.; Esfandeh, S.: Flooding numerical simulation of heterogeneous oil reservoir using different nanoscale colloidal solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 302, 111972 (2020)
Esfe, M.H.; Esfandeh, S.: 3D numerical simulation of the enhanced oil recovery process using nanoscale colloidal solution flooding. J. Mol. Liq. 301, 112094 (2020)
Esfe, M.H.; Esfandeh, S.; Hosseinizadeh, E.: Nanofluid flooding for enhanced oil recovery in a heterogeneous two-dimensional anticline geometry. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 118, 104810 (2020)
Sheikholeslami, M.; Gerdroodbary, M.B.; Moradi, R.; Shafee, A.; Li, Z.: Application of neural network for estimation of heat transfer treatment of Al2O3–H2O nanofluid through a channel. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 344, 1–12 (2019)
Namburu, P.K.; Kulkarni, D.P.; Dandekar, A.; Das, D.K.: Experimental investigation of viscosity and specific heat of silicon dioxide nanofluids. Micro Nano Lett. 2(3), 67–71 (2007)
Safaei, M.R.; Hajizadeh, A.; Afrand, M.; Qi, C.; Yarmand, H.; Zulkifli, N.W.B.M.: Evaluating the effect of temperature and concentration on the thermal conductivity of ZnO-TiO2/EG hybrid nanofluid using artificial neural network and curve fitting on experimental data. Phys. A 519, 209–216 (2019)
Karimipour, A.; Ghasemi, S.; Darvanjooghi, M.H.K.; Abdollahi, A.: A new correlation for estimating the thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of CuO/liquid paraffin nanofluid using neural network method. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 92, 90–99 (2018)
Hosseinian Naeini, A.; Baghbani Arani, J.; Narooei, A.; Aghayari, R.; Maddah, H.: Nanofluid thermal conductivity prediction model based on artificial neural network. Transp. Phenom. Nano Micro Scales 4(2), 41–46 (2016)
Esfe, M.H.; Kamyab, M.H.: Viscosity analysis of enriched SAE50 by nanoparticles as lubricant of heavy-duty engines. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 140(1), 79–93 (2020)
Al-Waeli, A.H.; Sopian, K.; Kazem, H.A.; Yousif, J.H.; Chaichan, M.T.; Ibrahim, A.; Ruslan, M.H.: Comparison of prediction methods of PV/T nanofluid and nano-PCM system using a measured dataset and artificial neural network. Sol. Energy 162, 378–396 (2018)
Esfe, M.H.; Tilebon, S.M.S.: Statistical and artificial based optimization on thermo-physical properties of an oil based hybrid nanofluid using NSGA-II and RSM. Phys. A 537, 122126 (2020)
Arani, A.A.A.; Alirezaie, A.; Kamyab, M.H.; Motallebi, S.M.: Statistical analysis of enriched water heat transfer with various sizes of MgO nanoparticles using artificial neural networks modeling. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 554(1–9), 123950 (2020)
Bahiraei, M.; Hosseinalipour, S.M.; Zabihi, K.; Taheran, E.: Using neural network for determination of viscosity in water-TiO2 nanofluid. Adv. Mech. Eng. 4, 742680 (2012)
Esfe, M.H.; Hajmohammad, M.H.: Thermal conductivity and viscosity optimization of nanodiamond-Co3O4/EG (40: 60) aqueous nanofluid using NSGA-II coupled with RSM. J. Mol. Liq. 238, 545–552 (2017)
Meybodi, M.K.; Naseri, S.; Shokrollahi, A.; Daryasafar, A.: Prediction of viscosity of water-based Al2O3, TiO2, SiO2, and CuO nanofluids using a reliable approach. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 149, 60–69 (2015)
Vakili, M.; Khosrojerdi, S.; Aghajannezhad, P.; Yahyaei, M.: A hybrid artificial neural network-genetic algorithm modeling approach for viscosity estimation of graphene nanoplatelets nanofluid using experimental data. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 82, 40–48 (2017)
Mehrabi, M.; Sharifpur, M.; Meyer, J.P.: Viscosity of nanofluids based on an artificial intelligence model. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 43, 16–21 (2013)
Esfe, M.H.; Wongwises, S.; Naderi, A.; Asadi, A.; Safaei, M.R.; Rostamian, H.; Karimipour, A.: Thermal conductivity of Cu/TiO2–water/EG hybrid nanofluid: experimental data and modeling using artificial neural network and correlation. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 66, 100–104 (2015)
Cisne, R.L.; Vasconcelos, T.F.; Parteli, E.J.; Andrade, J.S.: Particle transport in flow through a ratchet-like channel. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 10(3), 543–550 (2011)
Vasconcelos, T.F.; Morais, A.F.; Cisne Jr., R.L.; Parteli, E.J.; Andrade Jr., J.S.: Particle separation in a ramified structure. Chem. Eng. Sci. 65(4), 1400–1406 (2010)
Esfe, M.H.: On the evaluation of the dynamic viscosity of non-Newtonian oil based nanofluids. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 135(1), 97–109 (2019)
Zhao, N.; Li, Z.: Experiment and artificial neural network prediction of thermal conductivity and viscosity for alumina-water nanofluids. Materials 10(5), 552 (2017)
Esfe, M.H.; Saedodin, S.; Malekshah, E.H.; Babaie, A.; Rostamian, H.: Mixed convection inside lid-driven cavities filled with nanofluids. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 135(1), 813–859 (2019)
Esfe, M.H.; Saedodin, S.; Sina, N.; Afrand, M.; Rostami, S.: Designing an artificial neural network to predict thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of ferromagnetic nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 68, 50–57 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemmat Esfe, M., Kamyab, M.H. Optimization of Viscosity in MWCNT-MgO (35–65%)/5W50 Nanofluid and Comparison of Experimental Results with the Designed ANN. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 827–840 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05001-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05001-8